What amino acid is technically not an amino acid?
Cystine is not technically an amino acid. It is a dimer of cysteine amino acids. In this dibasic form, cystine is unable to be reabsorbed and thus may precipitate in the urine as cystine stones. Ornithine is also technically not an amino acid. However, it is an important molecule for biochemical pathways in the body including the urea cycle.
How do the twenty amino acids differ from one another?
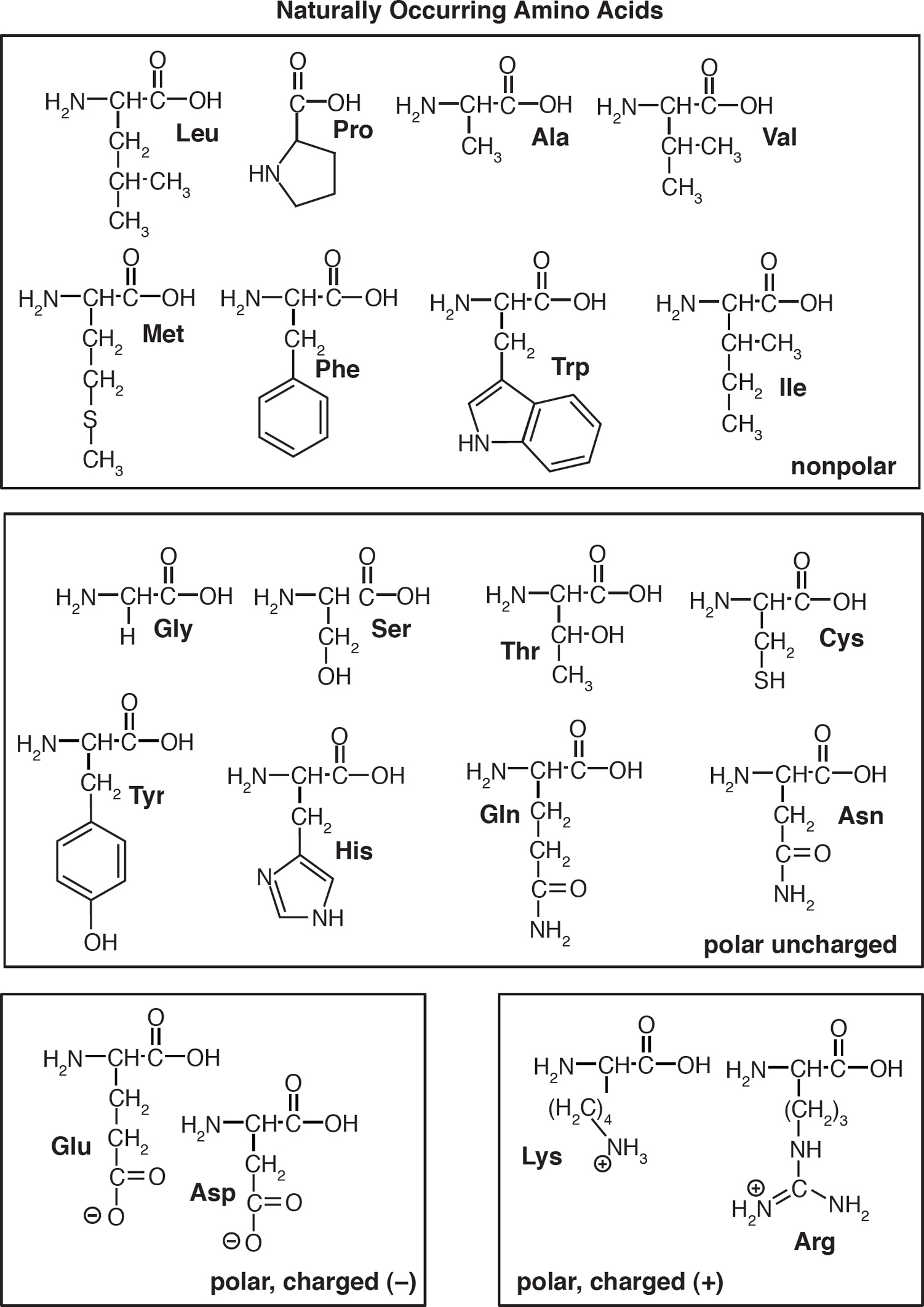
The side groups are what make each amino acid different from the others. Of the 20 side groups used to make proteins, there are two main groups: polar and non-polar. The polar and nonpolar chemical traits allow amino acids to point towards water (hydrophilic) or away from water (hydrophobic). Why are there so many different kinds of proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids?
Which characteristics makes nine amino acids?
Generally, amino acids have the following structural properties:
- A carbon (the alpha carbon)
- A hydrogen atom (H)
- A Carboxyl group (-COOH)
- An Amino group (-NH 2)
- A "variable" group or "R" group
What differentiates one amino acid from the other?
What distinguishes the amino acids, then, is what R is. For example, for R=H is glycine, R=CH3 is alanine. The only amino acid that does not look like this is proline, shown below. Proline has the ’N’ present as a secondary amine while all of the other amino acids, the ’N’ is present as primary amine.
How do amino acids bond?
Each amino acid is attached to another amino acid by a covalent bond, known as a peptide bond. When two amino acids are covalently attached by a peptide bond, the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid combine and release a molecule of water.
What are the side groups of amino acids?
The side groups are what make each amino acid different from the others. Of the 20 side groups used to make proteins, there are two main groups: polar and non-polar. These names refer to the way the side groups, sometimes called "R" groups, interact with the environment.
What is the name of the chain of amino acids?
A chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. What distinguishes one amino acid from another? each amino acid has a central carbon (alpha carbon) attached to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen and an R group. The R group has a different structure for each amino acid.
How many amino acids are in a protein?
There are millions upon millions of proteins around the world, and these are all made from the twenty different amino acids. What makes the proteins different from each other are the order in which the amino acids are joined; the primary structure of the protein.
How many amino acids are there in proteins?
In addition to 20 common amino acids, some proteins have uncommon amino acids created by the modification of common amino acid residues, for example, 4-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine, 𝛾-carboxyglutamate, selenocysteine, etc. Related Answer. Ravi Tej.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
Short answer: Essential Amino Acids are ones that cannot be synthesized by the cells of an organism so they have to be obtained through food. There are 9 essential amino acids in humans, but we aren’t the only organism around and others have different essential amino acids. Chemically there are many dozens of amino acids. Genetically there are 22 amino acids — not 20, not 21. The half century old story of 20 amino acids is still fixed in textbooks, but the current story of #21 and #22 is largely unknown… at least Wikipedia gets it right. Chemically, there are many amino acids found in biological systems that are not part of proteins and these aren’t counted. The distinction is based on whether an amino acid is linked to the genetic code and thus incorporated into proteins.
What is the 22nd amino acid?
Theres also Pyrrolysine (Pyr), the 22nd amino acid, but it’s a lot rarer.
What are proteins made of?
Based on the properties of their R groups, in particular, their polarity, or tendency to interact with water at biologica. Proteins are polymers of amino acids, with each amino acid residue joined to its neighbor by a specific type of covalent bond. All 20 of the common amino acids are α-amino acids.
What is the R class of amino acids?
The R classes of amino acids vary. For instance, glycine is a R group which is just a non-chiral hydrogen atom.
Which amino acids are non polar?
Non polar, Aliphatic R Groups: The R groups in this class of amino acids are non polar and hydrophobic. The side chains of alanine, valine, leucine and isoleucine have the tendency to cluster together within proteins, which in turn stabilises protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions.
Which chemical trait allows amino acids to point towards water?
The polar and nonpolar chemical traits allow amino acids to point towards water (hydrophilic) or away from water (hydrophobic).
What are the single units from which larger polypeptides are formed?
Amino Acids: Amino acids are the single units from which larger polypeptides are formed. Amino acids also serve as the precursor molecules for hormones like melatonin.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and vary based on their side chains. This lesson will discuss the side chains of various amino acids and how they are biochemically important.
How are amino acids different from each other?
The various amino acids are different from one another by the presence of unique side chain of variable carbon atoms. This side chain makes all the amino acids different.
What is the structure of an amino acid?
The general structure of amino acid has an amino ( − NH 2) group, carboxylic ( − COOH) group and a hydrogen atom attached to carbon atom along with a side chain. All the amino acids are different from one another by having different side chains.