- It is used in infant formula milks as sugar
- It is used in pharmaceutical industries as an ingredient
- It is used in the beverage industry to sweeten stout bear
What foods contain disaccharides?
There are three types of disaccharides:
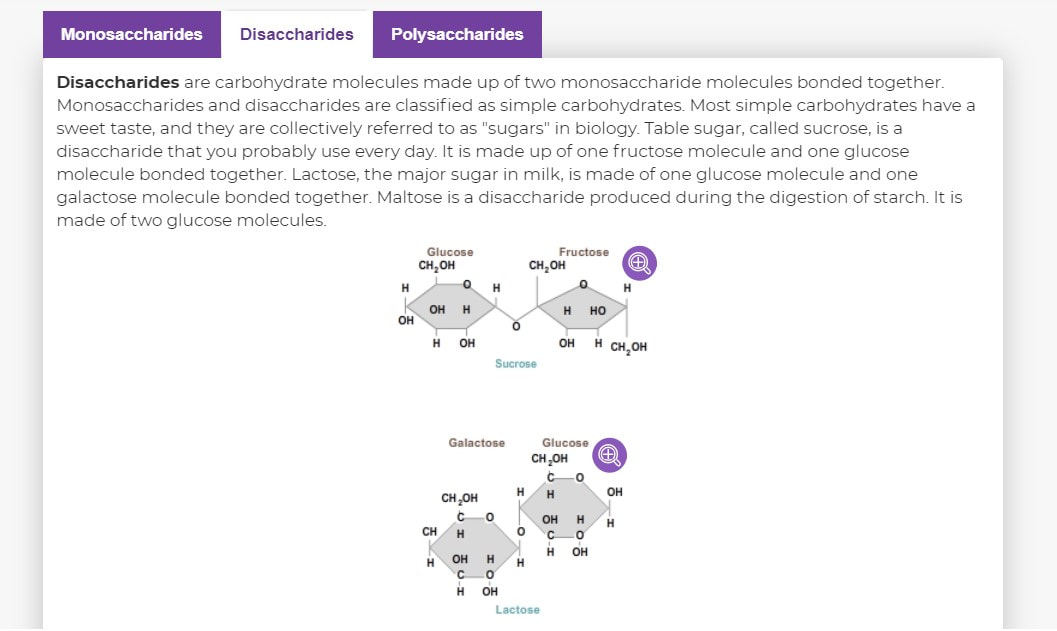
- Sucrose (ordinary table sugar) is made up of two sugars: glucose and fructose.
- Lactose (glucose Plus galactose) is the main sugar in milk.
- maltose (glucose + glucose) is a byproduct of starch digestion.
What are disaccharides used for?
Disaccharides are used as energy carriers and to efficiently transport monosaccharides. Specific examples of uses include: In the human body and in other animals, sucrose is digested and broken into its component simple sugars for quick energy. What are the properties of disaccharides? Disaccharides have the following physical properties.
What are the main functions of monosaccharides?
Nutrient Utilization in Humans: Metabolism Pathways
- Nutrients of Human Metabolism. ...
- Historical Overview of Energy Metabolism. ...
- Energy Conservation: Mechanisms of ATP Synthesis. ...
- Oxidative Phosphorylation: The Main Mechanism of ATP Synthesis in Most Human Cells. ...
- Oxidation of Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Converge on the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle. ...
What are the examples of disaccharides?
What are 5 examples of disaccharides?
- Sucrose. Sucrose, commonly known as table sugar in its refined form, is a disaccharide found in many plants.
- Maltose. Maltose, also known as malt sugar, is formed from two glucose molecules.
- Lactose.
- Trehalose.
- Lactulose.
- Cellobiose.
- Chitobiose.
Why is disaccharide so important?
In your body, a disaccharide function is to provide your body with a quick source of energy. Because they're only made up of two sugar molecules, they're easily broken down by enzymes in your digestive system into their respective monosaccharides and then absorbed into your bloodstream.
What are the three important disaccharides?
Disaccharides. Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide units, linked together with glycosidic bonds in the α or β orientation. The most important of them are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
What are the biologically important disaccharides?
There are several forms of disaccharides but the most common ones are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Why are monosaccharides and disaccharides important?
Simple Carbohydrates: One or two sugars (monosaccharides or disaccharides) combined in a simple chemical structure. These easily are utilized for energy, causing a rapid rise in blood sugar and insulin secretion from the pancreas.
What is the biological importance of monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides?
The ribose and deoxyribose monosaccharides are vital elements of RNA and DNA, which are the building blocks of life. While monosaccharides cannot be broken down into smaller sugars, disaccharides and polysaccharides are broken down into monosaccharides in processes like digestion.
What do you understand by disaccharide?
disaccharide, also called double sugar, any substance that is composed of two molecules of simple sugars (monosaccharides) linked to each other.
How are disaccharides used in the body?
When we consume disaccharides our bodies break them down into single sugars. These sugars are glucose, fructose and galactose, and they are used as energy for our body. Lactose, for example, can be found in breast milk and is used as an energy source by infants.
Are disaccharides good for you?
Simple sugars are carbs with one (monosaccharide) or two (disaccharide) sugar molecules. Many healthy foods like fruit and vegetables naturally contain sugar and shouldn't be avoided as they benefit your health. However, excess added sugar is linked to obesity and increased heart disease and cancer risk.
What are disaccharides provide any two examples with their structure and function?
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar ) is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides (simple sugars) are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Why are monosaccharides important to humans?
Carbohydrates broken down to mainly glucose are the preferred source of energy for our body, as cells in our brain, muscle and all other tissues directly use monosaccharides for their energy needs.
Why is monosaccharides important in nutrition?
The most nutritionally important and abundant monosaccharide is glucose, which is used as the major cell fuel in the human body and can be found unbound in body tissues and fluids. Glucose is the building block of several polysaccharides. Galactose and fructose are also used as cell fuel.
What is the main difference between monosaccharides and disaccharides?
Monosaccharides are simple molecules of carbohydrates that cannot be broken into other carbohydrates. Glucose and fructose are examples of monosaccharides. Disaccharides are carbohydrates made of two monosaccharides and with the loss of one molecule of water dehydration.
What are the functions of disaccharides?
Functions of Disaccharides. Disaccharides are carbohydrates found in many foods and are often added as sweeteners. Sucrose, for example, is table sugar, and it is the most common disaccharide that humans eat. It is also found in other foods like beetroot.
What is the process of forming a disaccharide from two monosaccharides?
For this reason, the process of forming a disaccharide from two monosaccharides is called a dehydration reaction or condensation reaction. When disaccharides are broken down into their monosaccharide components via enzymes, a water molecule is added. This process is called hydrolysis. It should not be confused with the process of dissolution, ...
What is the most common polysaccharide used for storage in plants?
Starch is the most common polysaccharide used for storage in plants, and it is broken down into maltose. Plants also use disaccharides to transport monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, and galactose between cells. Packaging monosaccharides into disaccharides makes the molecules less likely to break down during transport.
What is the chemical formula for disaccharides?
Three common disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose. They have 12 carbon atoms, and their chemical formula is C 12 H 22 O 11. Other, less common disaccharides include lactulose, trehalose, and cellobiose.
What is the energy storage source of sugar cane?
Since it is an energy storage source, many plants such as sugar cane are high in sucrose. Trehalose is used for transport in some algae and fungi. Plants also store energy in polysaccharides, which are many monosaccharides put together. Starch is the most common polysaccharide used for storage in plants, and it is broken down into maltose.
When disaccharides are formed from monosaccharides, an OH (hydroxyl) group is removed
When disaccharides are formed from monosaccharides, an -OH (hydroxyl) group is removed from one molecule and an H (hydrogen) is removed from the other. Glycosidic bonds are formed to join the molecules; these are covalent bonds between a carbohydrate molecule and another group (which does not necessarily need to be another carbohydrate). The H and -OH that were removed from the two monosaccharides join together to form a water molecule, H 2 O. For this reason, the process of forming a disaccharide from two monosaccharides is called a dehydration reaction or condensation reaction.
Where is glucose found in the body?
Glucose – A monosaccharide used for energy; it is found in the blood of animals and created during photosynthesis by plants. Monosaccharide – Simple carbohydrates; two of them join to form a disaccharide. Starch – Long chains of glucose produced by plants for energy storage; it is common in human diets.
Why are disaccharides important?
Important in their own right, disaccharides take great importance as the shortest components of the family of oligo- and polysaccharides and complex carbohydrates. As such a particular attention is given to their conformational properties because their molecular shapes are considered to be important determinants of their properties and those of their larger parents. The disaccharides result from the condensation of a reducing hydroxyl group (C-1 OH in aldose, C-2 OH in ketose) with another hydroxyl group. This linkage may be 1 → n, where n is 1–6, except 5. If two reducing groups are involved, the disaccharide is nonreducing as in sucrose and trehaloses.
What is the repeating disaccharide of CS?
The repeating disaccharide of CS has one glucuronic acid and one N-acetyl galactosamine. Usually sulfation occurs in 4- and/or 6-positions in the repeating disaccharide of CS. It has been demonstrated that in many cancers both the sulfation degree and the sulfation position change in CS. Sometime the quantity of CS in cancer patient plasmas is also different from that of healthy control.
What is the repeating disaccharide unit of chondroitin sulfate?
The C-4 and C-6 of the N-acetylgalactosamine residues are variably sulfated, and less frequently the C-2 of glucuronic acid. Vitreous is known to contain two chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, type IX collagen (see section on collagens) and versican. Versican is a large proteoglycan with a central domain that carries multiple chondroitin sulfate chains. At its N-terminus it has a hyaluronan-binding domain that presumably binds vitreous hyaluronan and this binding is stabilized by a link protein. However, as the hyaluronan is in a 150:1 molar excess to the versican and link protein, the structural role of versican in vitreous remains uncertain. Nonetheless, it is of note that the hereditary vitreoretinopathy Wagner syndrome is caused by splice site mutations in versican.
What is a disaccharide?
Disaccharide s are a specialized type of glycoside in which the anomeric hydroxyl group of one sugar has combined with the... Sucrose, which is formed following photosynthesis in green plants, consists of one molecule of glucose and one of fructose bonded via an α-,β-linkage.
Which disaccharide is found in single-celled organisms and in many insects?
Another important disaccharide, trehalose, which is found in single-celled organisms and in many insects, also consists of two molecules of glucose and an α-linkage, but the linkage is distinct from the one found in maltose.
What is double sugar?
Disaccharide, also called double sugar, any substance that is composed of two molecules of simple sugars ( monosaccharides) linked to each other. Disaccharides are crystalline water-soluble compounds. The monosaccharides within them are linked by a glycosidic bond (or glycosidic linkage), ...
What is the linkage between glucose and maltose?
Maltose, a product of the breakdown of starches during digestion, consists of two molecules of glucose connected via an α-linkage.
Which disaccharide has two -D-glucose units?
Maltose. Maltose is also one of the disaccharides which have two α -D-glucose units which are connected by the first carbon of the glucose and also linked to the fourth carbon of another glucose unit. In the solution, a free aldehyde can be produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution and it is a reducing sugar as it shows ...
What are the two monosaccharides that are formed by hydrolysis?
Disaccharides are those carbohydrates that on hydrolysis with acids or enzymes give two molecules of monosaccharides which can either be the same or different. The oxide linkage is formed after the loss of the water molecule and then the two monosaccharides are formed by that linkage.
What is the structure of sucrose?
Structure of Disaccharides (Sucrose) The most common disaccharide is sucrose which gives D - (+)- glucose and D- (-)- fructose on hydrolysis. Both the monosaccharides i.e. glucose and fructose are connected through the glycosidic linkage between alpha glucose and second carbon beta fructose.
What is the name of the sugar that is produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution?
In the solution, a free aldehyde can be produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution and it is a reducing sugar as it shows reducing properties. 3. Lactose. Commonly it is called milk sugar as this disaccharide is found in milk.
Is sucrose dextrorotatory or laevorotatory?
Sucrose being dextrorotatory in nature gives dextrorotatory glucose as well as laevorotatory fructose on hydrolysis. The overall mixture is laevorotatory and this is because the laevorotation of fructose (-92.4) is more than the dextrorotation of glucose (+52.5).
Why are disaccharides smaller than sucrose?
As you might most likely tell by looking at this picture of the monosaccharide glucose to the past picture of the monosaccharide sucrose, disaccharides are smaller than monosaccharides, which is one reason disaccharides can be directly assimilated into the circulation system through the stomach related tract.
What is monosaccharide in biology?
Monosaccharide is carbohydrate or sugars that cannot be further hydrolyzed to produce simpler sugars. Cyclic disaccharides respond with alcohols to shape acetals and ketals. Occasionally, this liquor is really a sugar since they work very comparatively to alcohols. So, when this happens singular monosaccharides interface together to make an acetal.
What is the process of framing a disaccharide from two monosaccharides?
Hence, the way toward framing a disaccharide from two monosaccharides is known as a lack of hydration response or buildup response. At the point when disaccharides are separated into their monosaccharide segments by means of proteins, a water atom is included. This procedure is called hydrolysis.
What is the most basic unit of carbohydrate?
Disaccharides are sugars (carbohydrate molecules) that are formed when 2 simple sugars i.e. monosaccharides unite to form a disaccharide. Monosaccharide is the simplest form or types of carbohydrate.They are therefore known as the most basic unit of carbohydrate. Monosaccharide is carbohydrate or sugars that cannot be further hydrolyzed ...
What is the linkage between glucose and maltose?
It has two monosaccharide glucose particles bound together, the connection is between the primary carbon iota of glucose and the fourth carbon of another glucose atom. This, as you probably are aware, is the one-four glycosidic linkage.
What is the most widely recognized polysaccharide used for capacity in plants?
Starch is the most widely recognized polysaccharide used for capacity in plants, and it is separated into maltose. Plants likewise use monosaccharides to transport disaccharides like glucose, fructose, and galactose between cells.
Why do plants use lactase?
Plants use disaccharides to transport fructose, glucose , and galactose starting with one cell then onto the next.
What are the properties of disaccharides?
Properties. Following are the common properties of disaccharides; Water Solubility. Due to the presence of a large number of hydroxyl groups, disaccharides are easily soluble in water. These hydroxyl groups form hydrogen bonds with the water molecules when dissolved in aqueous solutions. Polarity.
Why do disaccharides not behave as reducing agents?
These disaccharides do not behave as a reducing agent because they do not have a free aldehydic or ketonic functional group. The functional groups of both the monosaccharides are consumed in the process of glycosidic bond formation. Sucrose is an example of a non-reducing disaccharide.
How are disaccharides made?
As mentioned earlier, disaccharides are made when two monosaccharide subunits are combined. The two similar or different monosaccharide molecules are attached via a glycosidic bond to form a disaccharide. As a water molecule is released in this condensation process, it is also known as a dehydration reaction.
Which disaccharide retains its free functional group that can participate in the redox reaction?
In these disaccharides, one of the monosaccharides retains its free functional group that can participate in the redox reaction. The functional group of only one monosaccharide is consumed in the formation of the glycosidic bond. An example of reducing disaccharide is maltose.
Where is sucrose digested?
In the human body, sucrose is digested in the small intestine by an enzyme called invertase or sucrase. This enzyme breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules that are absorbed in the blood and carried to the liver for metabolism.
Where does sucrose come from?
Sucrose is mainly obtained from fruits and nectars. The amount of sucrose in high in the ripening fruits but it decreases as the fruits are ripened. Sucrose is present in large amounts in sugar cane. This is the reason why it is also called cane sugar.
Can disaccharides cross the cell membrane?
Thus, they cannot cross the cell membranes. They must be broken down into monosaccharides to be transported from one cell to another. As we have studied the general structure and properties of disaccharides, let us now jump to the discussion of some common and important disaccharides found in nature.
What are the two molecules that form a disaccharide?
Disaccharides. Disaccharides are sugars ( carbohydrate molecules) that form when two simple sugars i.e. monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide. Learn about Monosaccharides in more detail here. Cyclic monosaccharides react with alcohols to form acetals and ketals. Sometimes this alcohol is actually a carbohydrate since they function very ...
What is the name of the linkage between monosaccharides?
So when this happens individual monosaccharides link together to make an acetal. This linkage is known as glycosidic linkage . This linkage is an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. When two monosaccharides are linked together by glycosidic linkage the resulting product is a disaccharide.
What is the chemical formula of sucrose?
Let us take a look at some chemical properties of sucrose. The molecular formula of sucrose is C12H22O11. If sucrose goes through acid catalysed hydrolysis it will give one mole of D-Glucose and one mole of D-Fructose. The chemical structure of sucrose comprises of α form of glucose and β form of fructose. The glycosidic linkage is α linkage ...
Is maltose a monosaccharide?
Maltose is another disaccharide commonly found. It has two monosaccharide glucose molecules bound together, The link is between the first carbon atom of glucose and the fourth carbon of another glucose molecule. This, as you know, is the one-four glycosidic linkage. Let us look at a few of its properties
Is sucrose a reducing sugar?
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. As you can see from the structure it is combined (linked) at the hemiacetal oxygen and does not have a free hemiacetal hydroxide. Since has no free hemiacetal hydroxide it does not show mutarotation (α to β conversion). Sucrose also does not form osazones for the same reason.
Is maltose a glycosidic linkage?
This, as you know, is the one-four glycosidic linkage. Let us look at a few of its properties. On acid catalysed hydrolysis one mole of maltose gives two moles of D-glucose. Maltose has a free hemiacetal hydroxide, hence it undergoes mutarotation. It exists as both α-Maltose and also β-Maltose.
Is sugar a disaccharide?
Disaccharides. We generally associate sugar with glucose. But did you know the table sugar we use every day is not glucose? It is, in fact, a disaccharide known as sucrose. Let us have a detailed look at disaccharides and their structures and properties.
What is a disaccharide?
A disaccharide is a sugar (a type of carbohydrate) made by linking together two monosaccharides. A dehydration reaction forms a disaccharide. One molecule of water is removed for each linkage formed between the monosaccharide subunits. Both natural and artificial disaccharides are known. Examples of common disaccharides include sucrose, maltose, ...
What are the different types of disaccharides?
Here is a list of some disaccharides, including the monosaccharides they are made from and foods containing them. Sucrose, maltose, and lactose are the most familiar disaccharides, but there are others.
What is glucose and glucose#N#Trehalose?
glucose + glucose#N#Trehalose is also known as tremalose or mycose. It is a natural alpha-linked disaccharide with extremely high water retention properties. In nature, it helps plants and animals reduce long periods without water.
Why is lactose less tolerated?
Lactose, like sucrose, has a sweet flavor. As humans age, lactose becomes less-tolerated. This is because lactose digestion requires the enyzme lactase. People who are lactose intolerant can take a lactase supplement to reduce bloating, cramping, nausea, and diarrhea. 3 .
Can a monosaccharide form a glycosidic bond?
Note multiple disaccharides are possible when monosaccharides bond to each other, since a glycosi dic bond can form between any hydroxyl group on the component sugars. For example, two glucose molecules can join to form maltose, trehalose, or cellobiose. Even though these disaccharides are made from the same component sugars, ...
Is maltose a sugar?
Maltose, unlike some other disaccharides, does not serve a specific purpose in the human body. The sugar alcohol form of maltose is maltitol, which is used in sugar-free foods. Of course, maltose is a sugar, but it is incompletely digested and absorbed by the body (50–60%).
Is sucrose a lipid?
Excess sucrose can be converted from a carbohydrate into a lipid for storage as fat. Sucrose has a sweet flavor. Lactose (milk sugar) is found in human breast milk, where it serves as a chemical energy source for infants. Lactose, like sucrose, has a sweet flavor. As humans age, lactose becomes less-tolerated.