What is the process of transcription and translation?
Transcription uses a strand of DNA as a template to build a molecule called RNA. The RNA molecule is the link between DNA and the production of proteins. During translation, the RNA molecule created in the transcription process delivers information from the DNA to the protein-building machines. DNA → RNA → Protein.
What is the pathway of transcription from DNA to mRNA?
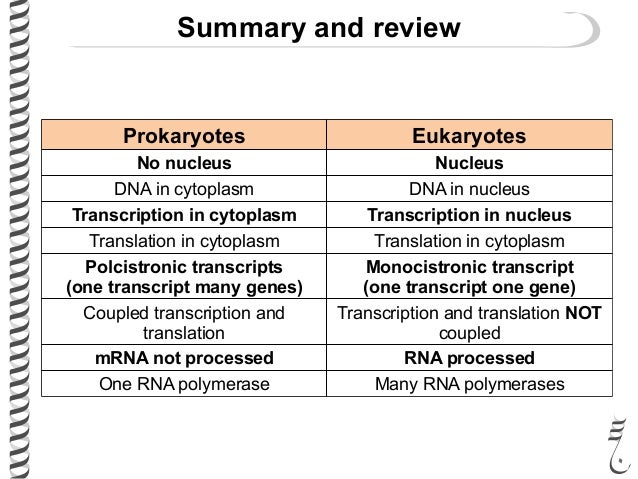
In bacteria, transcription from DNA to mRNA is a direct pathway. However in eukaryotes once mRNA is synthesized by RNA Polymerase II, the mRNA goes through further modification (Fig. 11). The product following transcription is known as a primary transcript (or pre-mRNA).
What happens after transcription is completed in prokaryotic cells?
In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, once a specific sequence of nucleotides has been transcribed then transcription is completed. This specific sequence of nucleotides is called the ‘terminator sequence’. Once the terminator sequence is transcribed, RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA template strand and releases the RNA molecule.
How is DNA used as a template for transcription?
Transcription Transcription is the process of producing a strand of RNA from a strand of DNA. Similar to the way DNA is used as a template in DNA replication, it is again used as a template during transcription. The information that is stored in DNA molecules is rewritten or ‘transcribed’ into a new RNA molecule.
Which process takes place in the nucleus transcription?
Transcription takes place in the nucleus of the eukaryotic cells. It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA molecule. RNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. Translation reads the genetic code in mRNA and makes a protein.
Can translation occurs in the nucleus?
IS THE TRANSLATION MACHINERY PRESENT IN THE NUCLEUS? For nuclear translation to occur, essential components such as ribosomes, tRNAs, and translation factors must be present in the nucleus, in addition to the mRNA.
What is the process in which translation and transcription occurs?
The process by which DNA is copied to RNA is called transcription, and that by which RNA is used to produce proteins is called translation.
Does translation occur in the nucleolus?
The genes that encode ribosomal proteins are transcribed outside of the nucleolus by RNA polymerase II, yielding mRNAs that are translated on cytoplasmic ribosomes. The ribosomal proteins are then transported from the cytoplasm to the nucleolus, where they are assembled with rRNAs to form preribosomal particles.
Where does the transcription take place?
The process of Transcription takes place in the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and in nucleus in eukaryotes. It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA (mRNA) molecule. During transcription, a strand of mRNA is made that is complementary to a strand of DNA .
Where does the process of translation takes place?
ribosomesTranslation takes place on ribosomes in the cell cytoplasm, where mRNA is read and translated into the string of amino acid chains that make up the synthesized protein.
What is difference between transcription and translation?
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a protein.
What is the process of translation?
In biology, the process by which a cell makes proteins using the genetic information carried in messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA is made by copying DNA, and the information it carries tells the cell how to link amino acids together to form proteins.
Which process is part of translation but not transcription?
Which process is part of translation but not transcription? A DNA template is used to create an mRNA strand. A tRNA template is used to create a DNA strand.
What occurs in the nucleus?
The nucleus controls and regulates the activities of the cell (e.g., growth and metabolism) and carries the genes, structures that contain the hereditary information. Nucleoli are small bodies often seen within the nucleus. The gel-like matrix in which the nuclear components are suspended is the nucleoplasm.
What happens in the nucleolus?
The nucleolus makes ribosomal subunits from proteins and ribosomal RNA, also known as rRNA. It then sends the subunits out to the rest of the cell where they combine into complete ribosomes. Ribosomes make proteins; therefore, the nucleolus plays a vital role in making proteins in the cell.
Does replication occur in the nucleus?
DNA replication occurs in the nucleus in eukaryotic cells and in the nucleoid region of prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are cells that have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles, such as plant cells and animal cells. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in the nucleus, and thus this is where DNA replication occurs.
How does translation start?
Translation begins when an mRNA connects to the small subunit of a ribosome. Ribosomes are made up of proteins and another type of RNA, ribosomal RNA (or rRNA). Initiation of translation begins when rRNA binds to a specific sequence of the mRNA, known as the ribosome binding site. This connection is based on complementary base pairing of adjacent R-nucleotides of rRNA and and mRNA, which is guided into place by special proteins known as initiation factors. One of the initiation factors also serves as a docking station for the first tRNA to connect to the start codon of mRNA, which is AUG for the synthesis of all proteins. tRNAs have a complementary triplet code that connects to the codon of the mRNA, known as an anticodon. The anticodon of the initial tRNA is UAC. Attached to the initial tRNA is the amino acid, Methionine (Met). Once the anticodon (UAC) of the initial methionine-containing tRNA is successfully paired to the complementary start codon of the mRNA (AUG), the large subunit of the ribosome attaches to the mRNA. The initial tRNA (with the anticodon, UAC) acts like a key, locking the small and large subunits together with the mRNA sandwiched between. Once both subunits are attached, the initiation factors are removed. After the initial tRNA signals the attachment of the large subunit of the ribosome, all subsequent tRNAs enter the large subunit through its A site. The next tRNA enters the A site due to complementary base pairing of the codon of the mRNA and the anticodon of the tRNA. Once the codon-anticodon pairing is successful, the new tRNA in the A site is positioned such that the amino acid it is carrying is adjacent to the amino acid already present in the P site. This proximity encourages a peptide bond to form between the two adjacent amino acids.
Where does translation occur in prokaryotes?
Translation occurs at ribosomes in all cells. Since prokaryotic DNA is not bound by a nucleus, translation in prokaryotes occurs before transcription is complete. Transcription and translation occur simultaneously. This has the advantage of being much faster than in eukaryotes.
How does DNA bond with RNA polymerase?
As the DNA is thread through the RNA Polymerase, hydrogen bonds are split between the the DNA molecule, by a zipper. Once DNA is inserted in to RNA Polymerase, ribonucleotides (R-nucleotides) enter an entrance portal into the RNA Polymerase and match up with the D-nucleotides based on complementary base pairing .
What is the role of tRNAs in translation?
During translation, tRNAs read the messages from the mRNA and link a specific amino acid sequence generating proteins. Where bacterial transcription is initiated by a sigma protein, RNA Polymerases in eukaryotes require a group of proteins known as basal transcription factors.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in eukaryotic transcription?
In eukaryotes, there are three different RNA Polymerases (I, II, and III). RNA Polymerase I is primarily responsible for the synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA), the molecule that makes up ribosomes. Most eukaryotic RNA Polymerase are RNA Polymerase II. RNA Polymerase II is responsible for synthesizing mRNA, making it the only RNA Polymerase capable of transcribing protein-coding genes. RNA Polymerase III is responsible for synthesizing transfer RNA (tRNA). During translation, tRNAs read the messages from the mRNA and link a specific amino acid sequence generating proteins.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology. The central dogma of molecular biology suggests that DNA serves as a template for the direct synthesis of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, in a process known as transcription. Secondly, mRNA is “read” at a ribosome by transfer RNAs (tRNAs) , which work together to assemble a specific chain of amino acids, ...
Where does RNA splicing begin?
RNA splicing begins when a primary snRNP binds to a guanine R-nucleotide (G) adjacent to an uracil R-nucleotide (U) at the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA. This marks the exon-intron boundary. Another secondary snRNP reads from 5’à3’ down the mRNA and when it comes in contact with an adenine (A), and it attaches at that point.
Where does transcription take place?
Transcription takes place in a protein, and translation takes place in the nucleus. Transcription takes place in the cytoplasm, and translation takes place in the nucleus. Transcription takes place in the nucleus, and translation takes place in ribosomes.
What are the two main processes of central dogma?
Explanation: The regulation of gene is regulated and controlled by two main processes of central dogma called transcription and translation . Transcription is the process of formation of messenger RNA or mRNA from a single strand of DNA whereas translation is the formation of protein from mRNA. This process takes place in different sites in ...