Where do podocytes cling to the capillary walls of the nephron?
*The podocytes cling to the capillary walls of the glomerulus within the glomerular capsule. Parts of the nephron are lined with epithelial cells containing large numbers of mitochondria to assist in diffusion. *Diffusion is a passive process and does not require energy.
What are podocytes in the kidney?
Podocytes are found lining the Bowman's capsules in the nephrons of the kidney. The foot processes known as pedicels that extend from the podocytes wrap themselves around the capillaries of the glomerulus to form the filtration slits.
Where are the nephrons of the kidney located?
Where are the nephrons located? The nephrons are located in the cortex and medulla of the kidney. The cortex contains the renal corpuscle, distal convoluted tubule and proximal convoluted tubule. Whereas, the medulla contains the loop of Henle and collecting ducts.
What are the two parts of a nephron?
A nephron consists of a filter called glomerulus and a tubule. The glomerulus filters the fluid and waste products holding back the blood cells and large molecules, especially proteins. What are the two main parts of a nephron structure? The two main parts of a nephron structure include:
Which part of the nephron contains podocytes group of answer choices?
Which part of the nephron contains podocytes? *The podocytes cling to the capillary walls of the glomerulus within the glomerular capsule. Parts of the nephron are lined with epithelial cells containing large numbers of mitochondria to assist in diffusion.
What is located within the glomerular capsule?
*The glomerulus, a knot of capillaries, is located inside the glomerular capsule. Section: 11.02. A nephron is a two-way system with glomerular filtrate traveling back and forth within the nephron.
What are the parts of nephron?
Each nephron is composed of a renal corpuscle (glomerulus within Bowman's capsule), a proximal tubule (convoluted and straight components), an intermediate tubule (loop of Henle), a distal convoluted tubule, a connecting tubule, and cortical, outer medullary, and inner medullary collecting ducts.
Which of the labeled structures in the diagram contains podocytes?
Which of the labeled structures in the diagram contains podocytes? glomerular filtration. Which of the following structures found in the kidney is the site where filtration of the blood occurs?
Which layer of the Bowman's capsule has podocytes?
inner visceral layerThe Bowman's capsule surrounds the glomerulus (Fig. 7.4). It consists of two layers of epithelial cells—the outer parietal and the inner visceral layer. The epithelial cells that form the visceral layer of Bowman's capsule are provided with foot-like processes known as podocytes (Fig.
What are podocytes?
Podocytes are highly specialized cells of the kidney glomerulus that wrap around capillaries and that neighbor cells of the Bowman's capsule.
What are the 3 parts of nephron and their functions?
The glomerulus is the site in the nephron where fluid and solutes are filtered out of the blood to form a glomerular filtrate. The proximal and distal tubules, the loop of Henle, and the collecting ducts are sites for the reabsorption of water and ions.
Which part of the nephron can be found in the medulla of the kidney?
The nephron is made up of the renal corpuscle and renal tubule. Cortical nephrons are found in the renal cortex, while juxtamedullary nephrons are found in the renal cortex close to the renal medulla.
What are the foot processes on podocytes?
The podocytes have long foot processes called pedicels, for which the cells are named (podo- + -cyte). The pedicels wrap around the capillaries and leave slits between them. Blood is filtered through these slits, each known as a filtration slit, slit diaphragm, or slit pore.
Does the renal corpuscle include podocytes?
The renal corpuscle filtration barrier is composed of: the fenestrated endothelium of glomerular capillaries, the fused basal lamina of endothelial cells and podocytes, and the filtration slits of the podocytes.
How many podocytes are in a kidney?
Podocyte number per glomerulus increased from 326 ± 154 per glomerulus at the pre-capillary loop stage to 584 ± 131 per glomerulus at the capillary loop stage of glomerular development to reach a value of 589 ± 166 per glomerulus in mature glomeruli.
What are the place and function of podocytes?
Podocytes play an important role in glomerular function. Together with endothelial cells of the glomerular capillary loop and the glomerular basement membrane they form a filtration barrier. Podocytes cooperate with mesangial cells to support the structure and function of the glomerulus.
What is the main function of a nephron?
A nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. It regulates the concentration of water and minerals such as sodium by filtering the...
How does a nephron filter blood?
A nephron consists of a filter called glomerulus and a tubule. The glomerulus filters the fluid and waste products holding back the blood cells and...
What are the two main parts of a nephron structure?
The two main parts of a nephron structure include: Renal tubule Renal corpuscle
Where are the nephrons located?
The nephrons are located in the cortex and medulla of the kidney. The cortex contains the renal corpuscle, distal convoluted tubule and proximal co...
What is the cup-shaped structure surrounding the renal corpuscle called?
The cup-shaped structure surrounding the renal corpuscle is known as the Bowman’s capsule or glomerulus that helps in blood filtration.
How do kidneys interact with other organ systems?
*The kidneys play a major role in homeostasis in the body and interact with every other organ system. The reabsorption of water in the kidneys always precedes the reabsorption of salt.
Where is water reabsorbed?
It is reabsorbed at the proximal convoluted tubule. *Nutrients such as glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed at the proximal convoluted tubule. Section: 11.03. Approximately 99% of the water that is filtered in the glomerulus is reabsorbed.
Which parts of the nephron are in order of how filtration would occur?
Place the parts of the nephron in order of how filtration would occur. 1. ascending limb of loop; 2. descending limb of loop; 3. proximal convoluted tubule; 4. glomerulus; 5. collecting duct; 6. distal convoluted tubule
Does glucose go into the glomerular filtrate?
No glucose is filtered into the glomerular filtrate. The kidneys produce glucose in diabetes. The carriers for glucose reabsorption reach their maximum rate of transport. The ascending limb of the loop of Henle secretes glucose into the urine.
How does cell respiration affect the pH of blood?
Increases the amount of hydrogen ions in the blood. Decreases the amount of hydroxide ions in the blood. It lowers the pH. *Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide which combines with water to form carbonic acid, thereby lowering the pH of the blood.
Why do some people not drink caffeine right before bedtime?
Why do some people not drink beverages with caffeine right before bedtime? It increases the flow of urine and causes you to go to the bathroom during the night. It decreases the flow of urine and can cause kidney stones. It may affect the ability to sleep but caffeine has very little effect on the urinary system.
Does caffeine affect the urinary system?
It may affect the ability to sleep but caffeine has very little effect on the urinary system. It can cause a headache if consumed late at night. It can lead to diarrhea. It increases the flow of urine and causes you to go to the bathroom during the night. *Caffeine is a diurectic and increases the flow of urine.
What is a loss of the podocytes in the foot called?
A loss of the foot processes of the podocytes (i.e., podocyte effacement) is a hallmark of minimal change disease, which has therefore sometimes been called foot process disease.
What molecules are able to pass through the filtration slits?
Small molecules such as water, glucose, and ionic salts are able to pass through the filtration slits and form an ultrafiltrate in the tubular fluid, which is further processed by the nephron to produce urine . Podocytes are also involved in regulation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
What are the long foot processes called?
The podocytes have long foot processes called pedicels, for which the cells are named ( podo- + -cyte ). The pedicels wrap around the capillaries and leave slits between them. Blood is filtered through these slits, each known as a filtration slit or slit diaphragm or slit pore.
What is the third layer of the Bowman's capsule?
Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. The Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are filtered as the first step in the formation of urine.
What is the name of the cells that live in the visceral layer?
Although various viscera have epithelial layers, the name visceral epithelial cells usually refers specifically to podocytes , which are specialized epithelial cells that reside in the visceral layer of the capsule. The podocytes have long foot processes called pedicels, for which the cells are named ( podo- + -cyte ).
Where are podocytes found in the kidney?
Diagram showing the basic physiologic mechanisms of the kidney. Podocytes are found lining the Bowman's capsules in the nephrons of the kidney. The foot processes known as pedicels that extend from the podocytes wrap themselves around the capillaries of the glomerulus to form the filtration slits.
What is the zipper protein that forms the slit diaphragm?
People have variations in these proteins, and some variations may predispose them to kidney failure later in life. Nephrin is a zipper -like protein that forms the slit diaphragm, with spaces between the teeth of the zipper, big enough to allow sugar and water through, but too small to allow proteins through.
What is the function of the nephron?
The primary function of nephron is removing all waste products including the solid wastes, and other excess water from the blood, converting blood into the urine, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion of numerous substances.
How long is the nephron?
The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 35–55 mm long. At one end, the tube is closed, folded and expanded, into a double-walled, a cuplike structure called the Bowman’s capsule or renal corpuscular capsule, which encloses a cluster of microscopic blood vessels called the glomerulus.
What is the renal corpuscle?
Renal Corpuscle. The renal corpuscle consists of a glomerulus surrounded by a Bowman’s capsule. The glomerulus arises from an afferent arteriole and empties into an efferent arteriole. The smaller diameter of an efferent arteriole helps to maintain high blood pressure in the glomerulus.
What is the third part of the renal tubule called?
The third part of the renal tubule is called the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and this part is also restricted to the renal cortex. The capillaries of the glomerulus are enclosed by a cup-like structure called Bowman’s capsule. This structure extends to form highly coiled tubules called PCT.
What is the basic structure of the kidney?
A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. They are the microscopic structure composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The word nephron is derived from the Greek word – nephros, meaning kidney. There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney.
What is the name of the tubule that is located in the glomerulus?
Renal Tubule. The renal tubule is a long and convoluted structure that emerges from the glomerulus and can be divided into three parts based on function. The first part is called the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) due to its proximity to the glomerulus; it stays in the renal cortex.
What is the function of DCT in blood cells?
Conditional reabsorption of sodium ions and water takes place in DCT. Thus, it maintains the pH and sodium-potassium level in the blood cells.
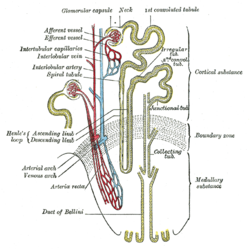
Overview
Function
Podocytes have primary processes called trabeculae, which wrap around the glomerular capillaries. The trabeculae in turn have secondary processes called pedicels. Pedicels interdigitate, thereby giving rise to thin gaps called filtration slits. The slits are covered by slit diaphragms which are composed of a number of cell-surface proteins including nephrin, podocalyxin, and P-cadherin, which restrict the passage of large macromolecules such as serum …
Structure
Podocytes are found lining the Bowman's capsules in the nephrons of the kidney. The foot processes known as pedicels that extend from the podocytes wrap themselves around the capillaries of the glomerulus to form the filtration slits. The pedicels increase the surface area of the cells enabling efficient ultrafiltration.
Podocytes secrete and maintain the basement membrane.
Clinical significance
A loss of the foot processes of the podocytes (i.e., podocyte effacement) is a hallmark of minimal change disease, which has therefore sometimes been called foot process disease.
Disruption of the filtration slits or destruction of the podocytes can lead to massive proteinuria, where large amounts of protein are lost from the blood.
An example of this occurs in the congenital disorder Finnish-type nephrosis, which is characteris…
See also
• List of human cell types derived from the germ layers
External links
• Anatomy photo: Urinary/mammal/vasc1/vasc1 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, renal vasculature (EM, High)
• Histology image: 22401loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - ". Ultrastructure of the Cell: podocytes and glomerular capillaries"