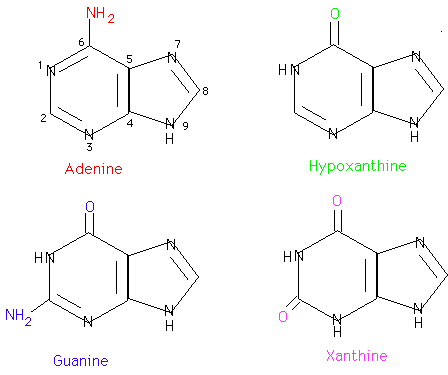
In DNA, four bases have been found. They are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached. The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrog…
Uracil
Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. The others are adenine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine. Uracil is a demethylated for…
What are the 4 nucleotides in DNA?
Each nucleotide contains three components:
- A five carbon sugar
- A phosphate molecule
- A nitrogen-containing base.
Which nucleotides base pair with each other?
The following abbreviations are commonly used to describe the length of a D/R NA molecule :
- bp = base pair—one bp corresponds to approximately 3.4 Å (340 pm) of length along the strand, and to roughly 618 or 643 daltons for DNA and RNA respectively.
- kb (= kbp) = kilo–base-pair = 1,000 bp
- Mb (= Mbp) = mega–base-pair = 1,000,000 bp
- Gb = giga–base-pair = 1,000,000,000 bp.
What are the three parts of a RNA nucleotide?
- Nitrogenous Base. Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases.
- Pentose Sugar. In DNA, the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose.
- Phosphate Group. A single phosphate group is PO 43-.
What three things that make up nucleotides?
Nucleotides each have three parts: phosphate, sugar molecule, and one of four bases. The bases include: A, (adenine), g (guanine), t (thymine), c (cytosine). The phosphate and sugar molecule bonds form the backbone or hand rail of the DNA (staircase), but the genetic key is in the steps (of the stairs): the bases.
What is not found in RNA?
Thymine base is not present in RNA. In RNA, uracil is found in place of thymine.
Which nucleotide is not found in RNA quizlet?
thymine. Which of the following is not found in RNA? Uracil.
Which of the following nucleotides are only found in RNA?
So the correct option is ' Uracil '.
What is not found in RNA quizlet?
The correct answer is Uracil. Uracil is one of the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA. The other three nitrogenous bases in RNA are also found in DNA, but uracil is not found in DNA.
Is ribose found in RNA?
Unlike DNA, RNA is usually single-stranded. Additionally, RNA contains ribose sugars rather than deoxyribose sugars, which makes RNA more unstable and more prone to degradation. RNA is synthesized from DNA by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase during a process called transcription.
Which one of the following is not a type of RNA?
Which of the following is not a type of RNA? a codon.
What are RNA nucleotides?
RNA nucleotides form polymers of alternating ribose and phosphate units linked by a phosphodiester bridge between the #3 and #5 carbons of neighboring ribose molecules. RNA nucleotides differ from DNA nucleotides by a hydroxyl group linked to the #2 carbon of the sugar.
What is found in RNA?
RNA consists of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the thymine, another pyrimidine that is found in DNA. Like thymine, uracil can base-pair with adenine (Figure 2).
What are the nucleotides in RNA?
What are the nucleotides found in RNA? Each nucleotide in RNA contains a ribose sugar, with carbons numbered 1' through 5'. A base is attached to the 1' position, in general, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or uracil (U). Adenine and guanine are purines, cytosine, and uracil are pyrimidines. Similarly, you may ask, what are the nucleotides ...
Where are nucleotides found in RNA?
The easiest way to get nucleotides is through diet. Nucleotides are also synthesised in the body.
What is the base of a pyrimidine?
A base is attached to the 1' position, in general, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or uracil (U). Adenine and guanine are purines, cytosine, and uracil are pyrimidines. Click to see full answer.
What are the three parts of RNA?
Like DNA, RNA polymers are make up of chains of nucleotides *. These nucleotides have three parts: 1) a five carbon ribose sugar, 2) a phosphate molecule and 3) one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine or uracil. Beside above, where are RNA nucleotides found?
Is uracil present in DNA?
RNA contains cytosine and uracil as pyrimidine [1] bases while DNA has cytosine and thymine. So, URACIL [2] is present in RNA, But not present in DNA. What are the nucleotides of DNA and RNA? DNA is a long polymer with deoxyriboses and phosphate backbone.
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Each nucleotide is a polymer made up of three parts: A five-carbon sugar (2'-deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA) A phosphate molecule. A nitrogenous (nitrogen-containing) base.
How are nucleotides named?
Nucleotides are named based on the number of phosphate residues they contain. For example, a nucleotide that has an adenine base and three phosphate residues would be named adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If the nucleotide has two phosphates, it would be adenosine diphosphate (ADP). If there is a single phosphate, ...
What is the helix of a nucleotide?
The helix of the molecules forms when two complementary bases form hydrogen bonds with each other. Adenine binds with thymine (A-T) in DNA and with uracil in RNA (A-U). Guanine and cytosine complement each other (G-C). To form a nucleotide, a base connects to the first or primary carbon of ribose or deoxyribose.
What is the chemical formula for pyrimidines?
The pyrimidines are cytosine, thymine, and uracil. The chemical formula of adenine is C 5 H 5 N 5. A denine (A) binds to thymine (T) or uracil (U). It's an important base because it's used not only in DNA and RNA, but also for the energy carrier molecule ATP, the cofactor flavin adenine dinucleotide, and the cofactor nicotinamide adenine ...
How do bases form nucleotides?
To form a nucleotide, a base connects to the first or primary carbon of ribose or deoxyribose. The number 5 carbon of the sugar connects to the oxygen of the phosphate group. In DNA or RNA molecules, a phosphate from one nucleotide forms a phosphodiester bond with the number 3 carbon in the next nucleotide sugar.
How many bases does DNA have?
Both DNA and RNA use four bases, but they don't use all the same ones. DNA uses adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine, while RNA uses adenine, guanine, and cytosine but has uracil instead of thymine. The helix of the molecules forms when two complementary bases form hydrogen bonds with each other.
What are the different types of nucleotides?
Although most people learn only the five main types of nucleotides, there are others, including, for example, cyclic nucleotides (e.g., 3'-5'-cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP.) The bases can also be methylated to form different molecules .
What is the function of rRNA?
rRNA reads the messenger RNA, mRNA and acts as an enzyme to form peptide bonds between amino acids, assembling them into a polypeptide chain. Characteristics of a codon: 1-in mRNA, a nucleotide base triplet that CODES for an amino acid or stop signal in translation. 2- codons constitute the genetic code.
Where does mRNA take place?
takes place in the nucleus. part of the DNA that serves as the template for the mRNA formation. (copying) Translation. takes place in the cytoplasm. sequence of mRNA bases determines the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. (transfer) requires several enzymes: mRNA, tRNA, rRna. Gene Expression.
What is the supplier of amino acids?
tRNA (the supplier) -Type of RNA that delivers amino acids to a ribosome during translation. -tRNA acts as the supplier taking bringing the amino acids to assemble proteins. Translation has 3 stages: 1-initiation -mRNA joins with tRNA and ribosome.
How does DNA replication work?
DNA replication and repair, how does it work? 1- a cell replicates its DNA before it divides , cells divide and need an exact copy of DNA. 2-each strand of the double helix serves as a template fro synthesis of a new, complementary strand of DNA (one old strand makes two new strands) 3- DNA enzyme use each strand as a template to assemble new, ...
How many chromosomes are in a human body?
46. Diploid characteristics: body or somatic cells in humans have 23 pairs or 46 total chromosomes. cells having two of each type of chromosome characteristic of the species. Haploid characteristics: Gametes or sex cells sin humans have 23 total chromosomes.
What are the genes that are expressed in eukaryotes?
Gene expression in Eukaryotes: 1- eukaryotic genes may encode "house keeping genes" (genes needed for all necessary cell functions) 2- other eukaryotic genes are specialized and encode only for certain functions. ex. red blood cells make hemoglobin; muscles make myosin.
Do all cells carry the same DNA?
1-all cells in your body carry the same DNA. 2-some genes are transcribed by all cells, but most cells are specialized (differentiated)to use only certain genes. 3-which genes are expressed at a given time depends on the type of cell and conditions.