See more
Is the biceps femoris an antagonist to the rectus femoris?
Answer and Explanation: There are multiple antagonists to the biceps femoris. The most correct answer would be the rectus femoris because it also has actions at the hip and...
What is the biceps antagonist?
During a biceps curl, the opposing muscle group—the antagonist—is the triceps.
Which muscles are antagonists?
Examples of Antagonistic MusclesBiceps and triceps.Gluteus maximum and hip flexors.Hamstrings and quadriceps.Pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi.Gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior.Abductor and adductor.
Which muscle is a synergist to the biceps femoris?
Synergist: Prime Movers: Gluteus maximus, Adductor magnus (posterior part).
Are hamstrings antagonist?
In this scenario, our hamstring is the agonist muscle (in that it's contracted, and applying the necessary force to move the knee) and the quadriceps are the antagonist muscle (these are relaxed, and offer a counterbalance for the force that the agonist muscle is applying).
Are biceps brachii and triceps brachii antagonists?
On the posterior side of the arm is the triceps brachii muscle. It the antagonist to the biceps brachii.
What are examples of antagonists?
Antagonist ExamplesDarth Vadar is the main antagonist of Luke Skywalker in Star Wars.Mr. ... The wolf is the antagonist in "The Three Little Pigs."MacDuff is an antagonist of Macbeth in Macbeth.In Dr. ... In the movie Aladdin, Jafar is the antagonist.More items...
Are quadriceps agonist or antagonist?
Antagonistic muscle pairs in action The hamstrings are the agonist and the quadriceps are the antagonist. In the contact and recovery phase, the quadriceps contract to extend the knee while the hamstrings lengthen to allow the movement.
What are the antagonistic muscles give one example?
Antagonistic muscles are those muscles which produce movements in an antagonistic pair of muscles by opposing the movement of the agonistic muscle . i.e. when one contacts the other relaxes and vice versa. Example- biceps and triceps, quadriceps and hamstrings.
What are agonist and antagonist muscles?
The muscle that is contracting is called the agonist and the muscle that is relaxing or lengthening is called the antagonist. One way to remember which muscle is the agonist – it's the one that's in 'agony' when you are doing the movement as it is the one that is doing all the work.
What is the antagonist of the rectus femoris?
The hamstrings are the antagonist muscles to the rectus femoris. That means they produce the opposite action.
What are synergist and antagonist muscles?
Following contraction, the antagonist muscle paired to the agonist muscle returns the limb to the previous position. Synergist muscles act around a movable joint to produce motion similar to or in concert with agonist muscles, allowing for a range of possible movements.
Where is the biceps femoris located?
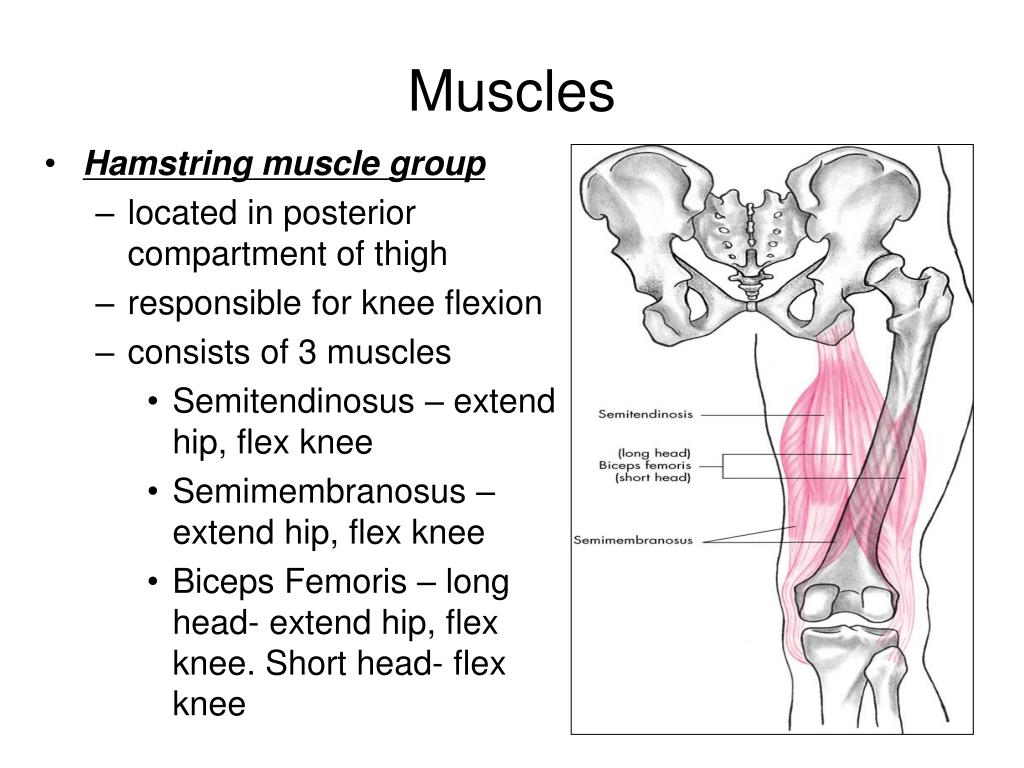
Biceps femoris is a muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh, and lies in the posterolateral aspect. It arises proximally by two 'heads', termed the 'long head' (superficial) and the 'short head' (deep). It is part of the hamstrings. [1] [2] [1] Anatomy[edit| edit source] Origin[edit| edit source]
How many heads does the biceps femoris have?
Clinical relevance[edit| edit source] We know that biceps femoris muscle usually has 2 heads, namely short head and long head of biceps femoris. These two heads insert on the head of fibula, where at the site of insertion they divide into two portions by fibular collateral ligaments.
Does foam rolling help quadriceps?
The present study offers findings that foam rolling to quadricepsalone is effective in decreasing the activation of biceps femoris muscle. Foam rolling on patients muscle can lead to alteration in range of motion, performance and muscular co-activation around the particular joint.
What muscle is the biceps femoris?
Long head of muscle highlighted in red, short head (yellow) labeled in the lower part of the image. The biceps femoris ( / ˈbaɪsɛps ˈfɛmərɪs /) is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back.
Where is the biceps femoris located?
FMA. 22356. Anatomical terms of muscle. The biceps femoris ( / ˈbaɪsɛps ˈfɛmərɪs /) is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it has two parts, one of which (the long head) forms part of the hamstrings muscle group.
Why is the long head of the biceps femoris a weaker knee flex
The long head of the biceps femoris is a weaker knee flexor when the hip is extended (because of active insufficiency ). For the same reason the long head is a weaker hip extender when the knee is flexed.
Which nerve innervates the biceps femoris?
It is a composite muscle as the short head of the biceps femoris develops in the flexor compartment of the thigh and is thus innervated by common fibular branch of the sciatic nerve (L5, S1), while the long head is innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve (L5, S1).
What nerve descends along the medial border of the lateral hamstring?
The tendon of insertion of this muscle forms the lateral hamstring; the common fibular (peroneal) nerve descends along its medial border.
Where does the aponeurosis tendon slip?
There is a second small insertional attachment by a small tendon slip into the lateral condyle of the tibia.
Which muscle is an antagonist?
We could also say that the antagonist is the main muscle that does the opposite of the action that it is resisting. For example, we could say that gluteus maximus is an antagonist of the primary hip flexor, iliopsoas because gluteus maximus is a hip extensor.
What muscles work together to create a movement?
We describe muscles that work together to create a movement as synergists. For example, iliacus, psoas major, and rectus femoris all can act to flex the hip joint. There are some sections within other muscles that can also assist with flexion of the hip joint, for example, the anterior fibers of gluteus minimus and gluteus medius can assist with flexion of the hip joint, depending on the position of the hip when it’s being flexed. All of these muscles together could be referred to as synergists for flexion of the hip joint.
What is the agonist in the body?
Muscle agonists. We describe the main muscle that does an action as the agonist. It is sometimes also called the “prime mover”. Many actions in the body do have one muscle that is responsible for more of the work in that action than any other muscle. For example, the agonist, or prime mover, for hip flexion would be the iliopsoas.
Is Triceps Brachii a synergist?
Triceps brachii is the antagonist and brachialis is a synergist with biceps brachii. As we begin to study muscles and their actions, it’s important that we don’t forget that our body functions as a whole organism. Although we learn the actions of individual muscles, in real movement, no muscle works alone. While we often have one main muscle ...
Description
Anatomy
- Origin
1. Long head: ischial tuberosity 2. Short head: linea aspera and lateral supracondylar line of the femur - Insertion
Lateral aspect of fibular head
Function
- Actions
1. Long head: flexes the knee, extends hip, laterally rotates lower leg when knee slightly flexed, assists in lateral rotation of the thigh when hip extended 2. Short head: flexes the knee, laterally rotates lower leg when knee slightly flexed This video is a good summary of the functions of the … - Functional contributions
1. Through a reversed origin insertion action, the long head gives posterior stability to the pelvis 2. Both heads provide rotary stability by preventing forward dislocation of the tibia on the femur during flexion 3. Its contributions to the arcuate ligament complex at the posterolateral corner o…
Clinical Relevance
- We know that biceps femoris muscle usually has 2 heads, namely short head and long head of biceps femoris. These two heads insert on the head of fibula, where at the site of insertion they divide into two portions by fibular collateral ligaments. Any sort of subluxation or dislocation of biceps femoris tendon or abnormal insertion of the tendon, and any or no trauma, meniscal insta…
Techniques
- Palpation
1. Position the client in prone lying with the knee in slight flexion 2. Starting distally locate the lateral proximal border of the popliteal fossa to locate the insertion of the tendon 3. Palpate the hamstrings laterally to locate the biceps femoris 4. Move palm toward the ischial tuberosity (pro… - Length Tension Testing / Stretching
1. With one hand, palpate the patient's ASIS and iliac crest with your thumb and index finger 2. With the other hand, support the patient's leg just above the ankle 3. Raise the patient's leg into hip flexion keeping the knee extended, and add internal rotation of the tibiato bias the biceps femori…
Trigger Point Referral Pattern
- Painreferred from TrPs in the lower half of the biceps femoris (long or short head) focuses on the back of the knee and may extend up the posterolateral area of the thigh as far as the crease of th...
Treatment
- Stretching
1. Position of patient is side lying and support is provided to lower leg with hip and knee flexed 2. Hold the upper leg and bring into abduction 3. During abduction, try to support the leg against your body, so that the patient can extend the knee whilst pressing the hip into flexion 4. With one han… - Quadriceps foam rolling
The present study offers findings that foam rolling to quadriceps alone is effective in decreasing the activation of biceps femoris muscle. Foam rolling on patients muscle can lead to alteration in range of motion, performance and muscular co-activation around the particular joint. According …
Overview
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it has two parts, one of which (the long head) forms part of the hamstrings muscle group.
Further reading
• Kumakura, Hiroo (July 1989). "Functional analysis of the biceps femoris muscle during locomotor behavior in some primates". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 79 (3): 379–391. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330790314. PMID 2504047.
• Marshall, John L.; Girgis, Fakhry G.; Zelko, Russel R. (1972). "The Biceps Femoris Tendon and Its Functional Significance". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 54 (7): 1444–1450. doi:10.2106/00004623-197254070-00006. PMID 4653628. Archived from the …
• Kumakura, Hiroo (July 1989). "Functional analysis of the biceps femoris muscle during locomotor behavior in some primates". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 79 (3): 379–391. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330790314. PMID 2504047.
• Marshall, John L.; Girgis, Fakhry G.; Zelko, Russel R. (1972). "The Biceps Femoris Tendon and Its Functional Significance". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 54 (7): 1444–1450. doi:10.2106/00004623-197254070-00006. PMID 4653628. Archived from the ori…
Structure
It has two heads of origin:
• the long head arises from the lower and inner impression on the posterior part of the tuberosity of the ischium. This is a common tendon origin with the semitendinosus muscle, and from the lower part of the sacrotuberous ligament.
• the short head, arises from the lateral lip of the linea aspera, between the adductor magnus and vastus lateralis extending up almost as high as the insertion o…
Function
Both heads of the biceps femoris perform knee flexion.
Since the long head originates in the pelvis it is involved in hip extension. The long head of the biceps femoris is a weaker knee flexor when the hip is extended (because of active insufficiency). For the same reason the long head is a weaker hip extender when the knee is flexed.
When the knee is semi-flexed, the biceps femoris in consequence of its oblique direction rotate…
Clinical significance
Avulsion of the biceps femoris tendon is common in sports that require explosive bending of the knee as seen in sprinting.
External links
• UWash - long head
• UWash - short head
• Anatomy photo:14:06-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
• Anatomy photo:14:st-0402 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center