Why are halogens the most reactive nonmetal group?
The most reactive nonmetal is fluorine. Fluorine is a halogen, which is Group 17 on the periodic table, and the halogens are the most reactive nonmetals. This is because they all have one empty space in their valence electron shells. Complete info about it can be read here.
What is the Order of reactivity of halogens?
In the table below, the following formula names are used:
- KCl - potassium chloride solution
- KBr - potassium bromide solution
- KI - Potassium iodide solution
What are the reactions of halogens?
Reactions with metals. The halogens react with metals to produce salts (the word 'halogen' means 'salt former'). For example, chlorine reacts with sodium: Sodium + chlorine → sodium chloride.
Why does reactivity of halogens decrease?
Therefore, the halogen reactivity decreases down the group due to the fact the atomic radius increases and shielding increases down the group as the molecules get bigger as they contain more electron shells, so the attraction between the incoming electron theyre trying to GAIN and the positive nucleus in weaker, so they are unable to attract the electron as easily as higher up halogens which attract the incoming electron with a lot stronger force.
Which is the most reactivity element in halogen?
FluorineFluorine is the most reactive of the halogens and, in fact, of all elements, and it has certain other properties that set it apart from the other halogens. Chlorine is the best known of the halogen elements.
Why is group 17 most reactive?
Fluorine is a most reactive element in group 17 because of its small size and high electronegativity by which it accepts electrons easily and forms a bond with another element.
Why is group 7 the most reactive?
This is because group 7 elements react by gaining an electron. As you move down the group, the amount of electron shielding increases, meaning that the electron is less attracted to the nucleus. For this reason, fluorine is the most reactive halogen and astatine is the least reactive of the halogens.
What is the most reactive element group?
alkali metalsThe most reactive elementary group is alkali metals (situated far apart from intermediate metals and noble gases). Cesium is second from the bottom of this group, has 6 shells of electrons, and it matches the features of a reactive atom, making it the most reactive element.
Why is fluorine most reactive halogen?
(2) It requires only one electron to complete the octet.
(3) The atomic size of flourine is the smallest among the halogens. Hence, the nuclear attraction on the outermost electrons is maximum. Hence, fluorine is the most reactive among the halogens.
Why is chlorine The most reactive halogen?
Halogens are notorious electron-hogs; powerfully attracting electrons from atoms of other elements, particularly from the alkali metals. This makes the halogens highly reactive. Chlorine, being one of the smaller halogens, will react strongly with most elements.
Is fluorine the most reactive element?
Among the halogens, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine, fluorine is the most reactive one. It forms compounds with all other elements except the noble gases helium (He), neon (Ne) and argon (Ar), whereas stable compounds with krypton (Kr) and xenon (Xe) are formed.
Which halogen is the least reactive?
IodineThe smallest halogen, fluorine, is the most electronegative element in the periodic table. The halogens get less reactive – fluorine, top of the group, is the most reactive element known. Iodine is the least reactive halogen (besides astatine which is often ignored because it is extremely rare).
What is the reactivity order of halogens?
Q. Order of reactivity towards halogenation is F2>Cl2>Br2>I2.
Is group 17 highly reactive?
The halogens are a group of elements found in group 17 of the periodic table. Their name means salt-producer, and they are the most reactive non-metal elements.
Why is group 1 the most reactive?
Group 1 of the periodic table includes hydrogen and the alkali metals. Because they have just one valence electron, group 1 elements are very reactive.
Why are halogens so reactive?
Halogens are highly reactive because they readily gain an electron to fill their outermost shell. Alkali metals are highly reactive because they readily lose the single electron in their outermost shell.
Why does halogen reactivity decrease down the group?
From the trend of reactivity of halogens, it is pretty much clear that the reactivity decreases down the group because, with The increase in atomic mass, the electronegativity is reduced, so does the electron affinity.
Is At-85 radioactive?
As to the general trend, At (Astatine) is the least reactive halogen but it is not widely accepted because At-85 is a highly radioactive halogen With a half life of only 8.1 hours.
Which group of elements are less reactive?
The non-metal elements in Group 7 - known as the halogens - get less reactive as you go down the group. This is the opposite trend to that seen in the alkali metals in Group 1 of the periodic table.
What are the elements in Group 7?
The Group 7 elements are known as the halogens. They are reactive non-metals and are always found in compounds with other elements. Chlorine, bromine and iodine are all halogens. Part of. Chemistry (Single Science)
What are the two substances that react with iron wool?
You can see the trend in reactivity if you react the halogens with iron wool. Halogen. Reaction with iron wool. Fluorine. Reacts with almost anything instantly. Very few scientists handle fluorine because it is so dangerous. Chlorine. Reacts with heated iron wool very quickly. Bromine.
What are Halogens?
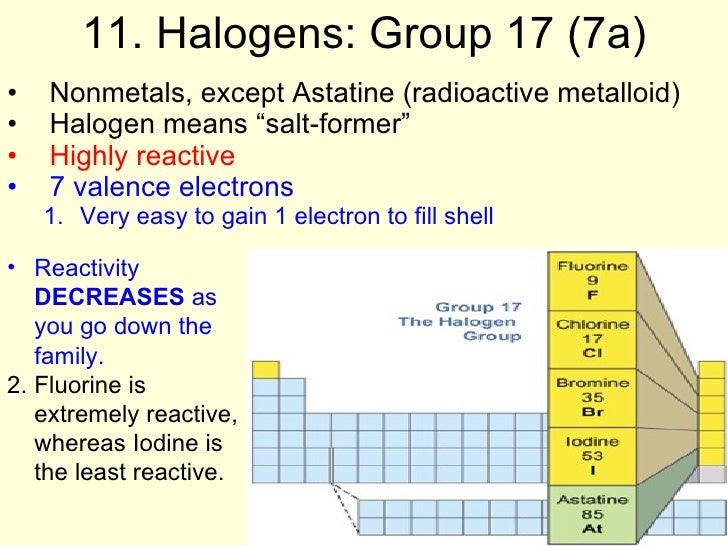
Halogens is the collective name given to a group of non-metallic elements. The name "halogens" owes its origin to the Greek language. "Halogens" means "salt formers". Halogens can be defined as elements that form salts when they react with metals. There are six halogens- fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and tennessine.
Where Are Halogens on the Periodic Table?
The periodic table is a useful tool for chemists. It is arranged in seven rows called periods and eighteen columns called groups. It places elements with similar chemical properties in groups. The halogens are located in group 17 on the periodic table.
Halogen Properties
There is an evident gradation in halogens' properties, both physical and chemical. The halogen properties can be depicted in the following way.
Why Are Halogens So Reactive?
To the question, " are halogens reactive", the answer is yes and the reason lies in their electron configuration. Atoms of all the halogens have seven valence electrons. The halogen atoms are very close to a stable electron configuration. This explains why halogens are reactive.