What best defines an intensive property of a substance?
The Difference Between Intensive and Extensive Properties
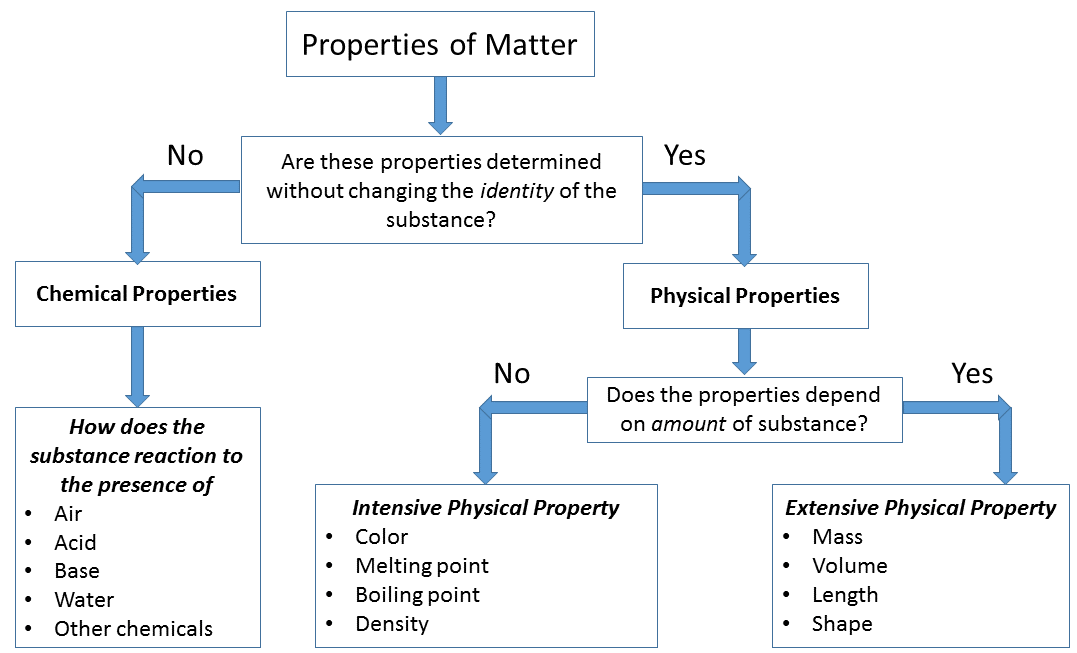
- Intensive Properties. Intensive properties are bulk properties, which means they do not depend on the amount of matter that is present.
- Extensive Properties. Extensive properties do depend on the amount of matter that is present. ...
- Way to Tell Intensive and Extensive Properties Apart. ...
Which is an intensive property of a substance?
The density (d) of a substance is an intensive property that is defined as the ratio of its mass (m) to its volume (V). Considering that mass and volume are both extensive properties, explain why their ratio, density, is intensive.
What is an intensive property of substance?
What Is An Intensive Property? The intensive properties are the properties if the substance does not change even if the amount of the matter changes. This means that the physical properties of the matter do not depend on the size or amount of the matter. Intensive Property Examples: Below are some examples of the intensive property of a matter Density
What is an example of an extensive property?
Examples of extensive properties include:
- amount of substance, n.
- enthalpy, H.
- entropy, S.
- Gibbs energy, G.
- heat capacity, C. p
- Helmholtz energy, A or F.
- internal energy, U.
- mass, m.
What are the 4 extensive properties?
Extensive PropertiesVolume.Mass.Size.Weight.Length.
What are examples of extensive properties?
An extensive property is a physical quantity whose value is proportional to the size of the system it describes, or to the quantity of matter in the system. For example, the mass of a sample is an extensive quantity; it depends on the amount of substance.
Which property is an extensive property of matter?
Examples of extensive properties include mass, volume, and length.
Which of the following has extensive property?
The volume of any matter or substance depends on the mass or amount. Thus, volume is considered as an extensive property. The properties surface tension, viscosity and density do not depend on the mass or amount of the matter. Thus, surface tension, viscosity and density are intensive properties.
Which of the following is not extensive property?
Molarity is the of the following is not an extensive property and molarity is the concentration of the solution and expressed as the number of moles of solute per litre of solution. Molarity = mole of solute/ liter of solution.
Which of the following is an extensive variable?
Extensive variable →H (enthalpy), E (Internal energy) and V (Volume) since variables depend on the amount of substance or volume or size of the system.
Is density a extensive property?
Density is an intensive property because there is a narrow range of densities across the samples. No matter what the initial mass was, densities were essentially the same. Since intensive properties do not depend on the amount of material, the data indicate that density is an intensive property of matter.
Which of the following is a intensive property?
Intensive properties: Properties which are independent of the amount of substance (or substances) present in the system are called intensive properties, e.g. pressure, density, temperature, viscosity, surface tension, refractive index, emf, chemical potential, sp. heat etc, These are intensive properties.
Which property is called intensive property?
The properties of the system whose value is independent of the amount of substance present in the system are called intensive properties, eg, viscosity, surface tension, temperature, pressure etc.
Which of the following is an extensive property quizlet?
An extensive property is a property that changes when the size of the sample changes. Examples are mass, volume, length. If you have salt, and add more to it then the mass would change. An intensive property doesn't change regardless of the mass of the sample.
Is energy an extensive property?
Energy, volume and enthalpy are all extensive properties. Their value depends on the mass of the system.
Which properties of Below is extensive properties?
Intensive PropertiesExtensive PropertiesThese properties are independent of the amount of matter.These properties are dependent on the amount of matter.For example, density, melting point or boiling point, etc.For example, mass, volume, energy, etc.
Answer
C) a physical property that depends on the sample size correct answer.
New questions in Biology
Why do the prevailing winds blow from west to east in the Northern Hemisphere?
What is the density of a substance?
Density : The magnitude of the amount of mass in a given volume. That is to say that the density of a body is the ratio between the mass of a body and the volume it occupies. For example: the density of the sunflower oil is 0.891 g / cm3. Color : Refers to the appearance that a substance has before the human eye.
What are the properties of matter?
Matter can have two types of properties: 1 Extensive properties : Depends on the amount of matter. 2 Intensive properties : (or intrinsic) They do not depend on the amount of matter, ie they remain unchanged.
What is the ratio of concentration to a solution?
Concentration : Given a solution, the concentration is the ratio between the amount of solute (the substance in smaller proportion, usually a solid) and the amount of solvent (substance that dissolves). The greater the amount of solute compared to that of solvent, the solution is said to be more concentrated.
What is the melting point of a substance?
Melting point or melting point : The temperature at which a substance passes from the solid to the liquid state . In general, the melting point is equal to the freezing point (for example, for water, the melting point and the freezing point is 0 degrees). However, with some exceptions such as agar-agar.
Why is the amount of water not specified?
In the example, the amount of water is not specified because the intensive properties do not change with the quantity. If the sample is two liters the temperature will be the same as if the sample is 200 cm3. Boiling temperature : Also called boiling point. It is the maximum temperature at which a substance can reach in liquid state .
What is the refractive index of a diamond?
The refractive index of the vacuum is 1, the refractive index of the air is 1,0002926, the refractive index of the diamond is 2.42. Surface tension : It is a property of liquids. It is the ability of some liquids to prevent increasing their surface.
What is the ability of an object to remain in a state of rest or movement?
Inertia : Inertia is the ability of an object to remain in a state of rest or movement. Every state of rest (immobility) or movement is always relative, since it depends on the point of view of the observer. Length : In the same way that the volume changes with the amount of matter, so does the length.
What are some examples of extensive properties?
Examples of extensive properties include: Volume. Mass. Size. Weight . Length. The ratio between two extensive properties is an intensive property. For example, mass and volume are extensive properties, but their ratio (density) is an intensive property of matter.
How to tell if a substance is intensive or extensive?
One easy way to tell whether a physical property is intensive or extensive is to take two identical samples of a substance and put them together. If this doubles the property (e.g., twice the mass, twice as long), it's an extensive property.
What are the properties of matter?
Key Takeaways: Intensive vs Extensive Properties 1 The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties. 2 Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. Examples include density, state of matter, and temperature. 3 Extensive properties do depend on sample size. Examples include volume, mass, and size.
What is intensive property?
Updated December 04, 2019. Intensive properties and extensive properties are types of physical properties of matter. The terms intensive and extensive were first described by physical chemist and physicist Richard C. Tolman in 1917.
What are the two types of physical properties of matter?
The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties . Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. Examples include density, state of matter, and temperature. Extensive properties do depend on sample size. Examples include volume, mass, and size.