Which strand only produces single-stranded DNA molecules?
D) The lagging strand only produces single-stranded DNA molecules.
Which three proteins are involved in transporting amino acids to the ribosomes?
B) mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are all involved in transporting amino acids to the ribosomes.
Which strands are synthesized continuously?
A) The leading and lagging strands are both synthesized continuously.
Which direction does DNA synthesis occur?
A) They allow DNA synthesis to occur in the 3' to 5' direction .
Does translation involve ribosomes?
A) Bacterial translation does not involve ribosomes.
What enzyme breaks hydrogen bonds?
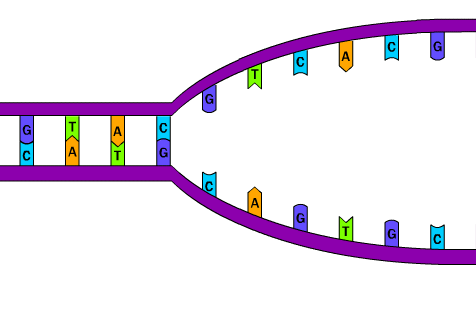
The enzymes that break the hydrogen bonds present between the DNA base pairs are known as DNA helicases. These enzymes are vital enzymes as they are responsible for unwinding of double-stranded DNA, which is required for DNA replication.
How do DNA helicases break hydrogen bonds?
DNA helicases break hydrogen bonds and separate the DNA by using energy through breakdown of ATP molecules. In given diagram, DNA helicase is represented by blue figure (2).
What are the enzymes that attach the free nucleotides to the template or parent DNA strand?
The enzymes that attach the free nucleotides to the template or parent DNA strand, during DNA replication are called DNA-dependent DNA polymerases or simply DNA polymerases . These enzymes are also vital enzymes as each cell replicates it genetic material prior to cell division.
How many identical DNA strands are there in DNA polymerase?
DNA polymerase forms two identical, daughter DNA strands from an original, parent DNA molecule. In given diagram, DNA polymerases are represented by yellow figures (6 and 8).
Which strand of DNA is linked together?
They link the leading strand DNA polymerase and the lagging strand DNA polymerase together.
What are the three types of RNA produced by transcription?
mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA are all produced by transcription.
Which direction does synthesis move?
The synthesis is moving in the opposite direction from the replication fork.
Why do organisms copy their DNA?
An organism must copy its DNA to pass genetic information to its offspring