Electrical engineers say that, in an electrical circuit, electricity flows one direction: out of the positive terminal of a battery and back into the negative terminal. Electronic technicians say that electricity flows the other direction: out of the negative terminal of a battery and back into the positive terminal.
What is a path through which electricity can flow is?
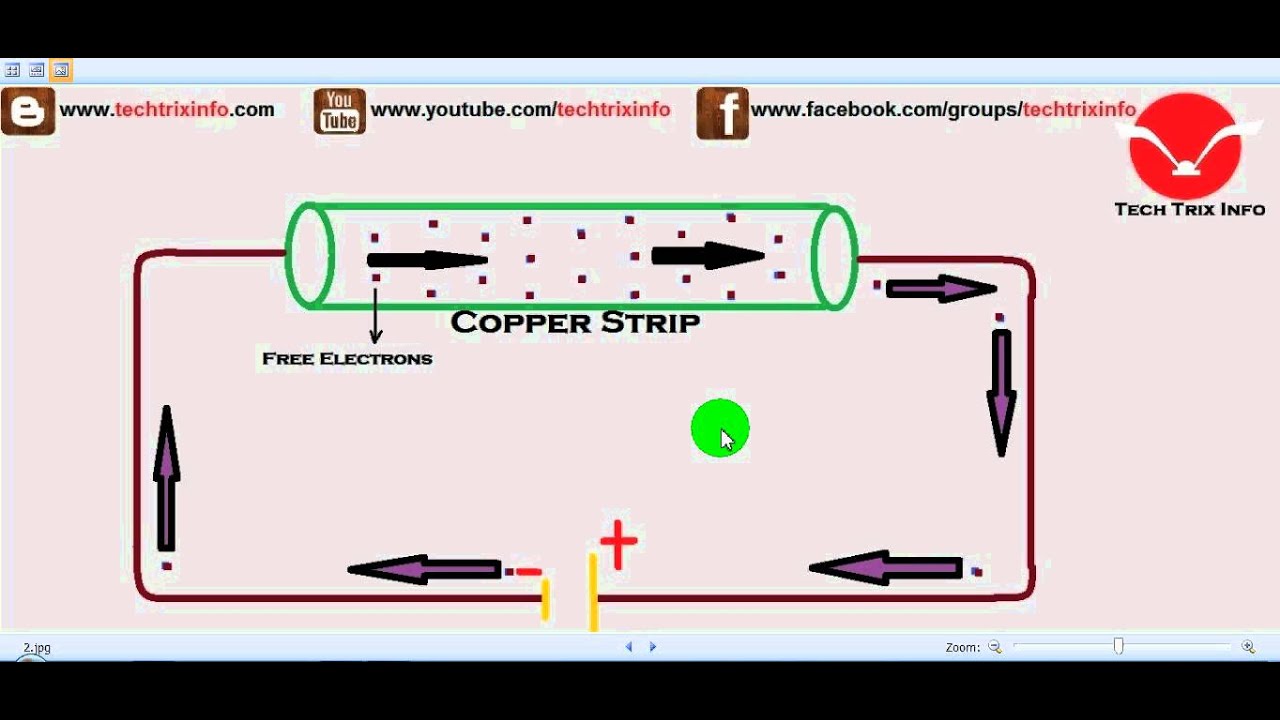
circuit A path through which electric charges flow. A continuous, unbroken path through which electrons can flow is a closed circuit. Charges, or current, can flow only through a closed circuit. A break or opening in a circuit creates an open circuit.
What can hinder the flow of electricity?
“Corrosion, if that’s the problem, can cause voltage and current flow degradation, which a sensor could interpret as a system fault.” Which brings us to the fundamentals of electrical maintenance: keeping corrosion out of the system and making proper repairs the first time.
What are the different ways to produce electricity?
- Tackle difficult tasks when you're in a good mood In a 2016 study, researchers found that people were less likely to try to accomplish difficult things when they were ...
- Give your brain the right amount of autonomy When faced with a choice, our brains often want to default to the easiest option. ...
- Practice a growth mindset
What does a circuit need to make electricity flow?
What are the steps in making a series circuit?
- Examine and identify each component.
- Practice attaching the leads to each other.
- With the switch in the open (off) position, place components on the template and attach the wires.
- Observe that the circuit looks like a circle.
- Close the switch and listen for the sound of the motor.
How does electricity flow in a circuit?
In a complete circuit, the electrons flow from the negative terminal (connection) on the power source, through the connecting wires and components, such as bulbs, and back to the positive terminal.
Does current flow positive to negative?
The flow of electrons is termed electron current. Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive. Conventional current or simply current, behaves as if positive charge carriers cause current flow. Conventional current flows from the positive terminal to the negative.
Does current go from north to south?
In the top coil, the direction of the current flow is in the same direction as the magnetic field outside the coil but opposite to the direction of the magnetic filed within the coil i.e. it's going from the north pole to the south pole.
What flows from positive to negative?
Electric current flows from the positive terminal of a battery to the negative terminal.
What is the direction of electric current flow?
The direction of electric current flow is a little difficult to understand to those who have been taught that current flows from positive to negative. There are two theories behind this phenomenon. One is the theory of conventional current and the other is the theory of actual current flow. When Benjamin Franklin was studying charges, the structure of an atom and atomic particles were unknown. Hence he assumed the point of charge accumulation as positive and the point which is deficient of charges as negative. Therefore, the charge is said to flow from positive to negative. This is called conventional current.
Which direction do electrons move in a conductor?
Also, many experiments have revealed that it is free electrons in a conductor that flows. Negatively charged electrons move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. This is the direction of the actual current flow.
What is the unit of current?
The unit of current is ampere or A. one ampere is equal to the one coulomb per second whereas one coulomb is equal to 6.25 x 10 18 electrons. By saying that one ampere of current is flowing through a circuit, it is meant that 6.25 x 10 18 electrons are crossing a point in the circuit per second. Also read:
What is electric current?
Electric current is normally referred to as the flow of charges through a conductor. It can be defined as the amount of charge that flows past a cross-section area in a conductor. In other words, the term “current” can be defined as the rate of flow of charges through a conductor. Read more about Electic Current.
Can a positive ion be attracted by a negative ion?
One can either consider the flow of current from positive to negative or vice versa during circuit analysis. In fact, positively charged ions can be attracted by negatively charged electrons.
Does a negative charge make a difference in a circuit?
Mathematically, negative charge flowing in one direction is equivalent to positive charges flowing in the opposite direction. Hence it does not make a difference. One can either consider the flow of current from positive to negative or vice versa during circuit analysis. In fact, positively charged ions can be attracted by negatively charged electrons.
Is electric current a flow of electrons?
This is called conventional current. But in reality, an electric current is nothing but the flow of electrons. Electrons are negatively charged particles and are attracted towards the positive charge. Also, many experiments have revealed that it is free electrons in a conductor that flows. Negatively charged electrons move from ...
What is the direction of current in a wire?
Nevertheless, the direction of “current” flow in a wire is the direction that positive charges would flow. (This convention was established well before they knew what actually happened inside the wire.)
What happens when you connect a battery to a circuit?
Similarly when you connect a battery to a circuit one of its terminal (negative) is at higher potential and the other (positive) is at lower potential so Current (electrons) flow from a point of higher potential (which is negative terminal) to a point of lower potential (which is positive terminal). Sponsored by FinanceBuzz.
Why does electricity go from negative to positive?
Now, because electricity turned out to be the flow of electrons, and electrons are negatively charges. So the “electron flow” (this is supposed to make it different than “current”) goes from negative to positive.
What happens when electricity zooms through AC cables?
When electrical energy zooms along through AC cables, the electricity inside the cables vibrates a little bit. Electricity wiggles back and forth, while electrical energy zooms forward at lightspeed. Electricity is the medium, while electrical energy is the waves. Electricity is not a form of energy.
What is the difference between electrical energy and sound waves?
In that case the electrical energy is like sound waves; the waves which rush through the air inside the pipe, while the electricity is like the air itself. Waves versus medium.
What is the rule of complete circuits?
That’s where the famous rule about “complete circuits” comes from: the electricity always fills the entire circle; fills the entire “circuit.”. It forms a closed loop or ring. During the current, no electricity is being gained or lost, and instead electricity just flows around and around repeatedly, in a closed loop.
Why are wires shiny?
Wires are metal, and metals are held together with (surprise!) metallic bonds, in which the nuclei of the metal atoms are surrounded by a “soup” of easily mobile valence electrons. That’s why metals are shiny, and that’s why they conduct electricity. Freely mobile electrons.
How is electrical flow made possible?
The physics are complicated, but in essence, electrical flow in circuit wires is made possible by a utility generator (a turbine powered by wind, water, an atomic reactor, or burning fossil fuels).
What is the force that appears when you flip a light switch?
For most people, electricity is a mysterious force that somehow magically appears when we flip a light switch or plug in an appliance. Yet while the science behind the flow of electricity is very complex, the basics of electrical flow, or current, are easy to understand if you learn some key terms and functions.
What is the definition of current?
Current = Flow of Elecricity. The term current refers to the simple flow of electrons in a circuit or electrical system. You can also liken electrical current to the quantity, or volume, of water flowing through a water pipe. Electrical current is measured in amperage or amps.
What is the measurement of resistance to the flow of electrons through a conductive material?
Ohms are the measurement of resistance to the flow of electrons through a conductive material. The higher the resistance, the lower the flow of electrons. This resistance causes a certain amount of heat to be generated in the circuit. The reason that a hairdryer blows hot air, for example, is because of resistance in the internal wiring, which produces heat. And it is resistance in the tiny wires of an incandescent light bulb that causes it to heat up and glow with light. It is also resistance that can overheat an extension cord if it is used on an appliance that draws too much current.
What are the three types of particles that make up electrical current?
In each atom there are three types of particles: neutrons, protons (which carry a positive electromagnetic charge) and electrons (which carry a negative charge). The important particle here is the electron, since it has the unique characteristic of being able to separate from its atom and move to an adjacent atom. This flow of electrons is what creates electrical current—the jump of negatively-charged electrons from atom to atom.
How do generators work?
This is the principal by which modern generators work: The turbines—whether powered by falling water or steam created by nuclear reactors—rotate huge coils of metal wire inside giant magnets, thereby causing electrical charges to flow .
How many volts does a house have?
The standard circuits in your home carry either about 120 volts (the actual voltage can vary between about 115 to 125 volts) or 240 volts (actual range: about 230 to 250 volts). Most light fixtures and outlets are fed by 120-volt circuits, while dryers, ranges, and other large appliances typically use 240-volt circuits.
Definition of Current
in Which Direction Does Electric Current Flow?
- The direction of electric current flow is a little difficult to understand to those who have been taught that current flows from positive to negative. There are two theories behind this phenomenon. One is the theory of conventional current and the other is the theory of actual current flow. When Benjamin Franklin was studying charges, the structure of an atom and atomi…
Direction of Current Flow in Circuit Analysis
- In terms of circuit analysis, we normally consider the direction of electric current from positive to negative. Mathematically, negative charge flowing in one direction is equivalent to positive charges flowing in the opposite direction. Hence it does not make a difference. One can either consider the flow of current from positive to negative or vi...
Unit of Current
- The unit of current is ampere or A. one ampere is equal to the one coulomb per second whereas one coulomb is equal to 6.25 x 1018 electrons. By saying that one ampere of current is flowing through a circuit, it is meant that 6.25 x 1018 electrons are crossing a point in the circuit per second.