What are the different types of Rhizopus?
The genus Rhizopus contains several species. The most common ones are Rhizopus arrhizus, Rhizopus azygosporus, Rhizopus microsporus, Rhizopus schipperae, and Rhizopus stolonifer.
What is Rhizopus oryzae?
Rhizopus oryzae is a species of filamentous fungi within the group Mucormycetes, a body of organisms largely found in decaying organic matter and responsible for causing infections in immunocompromised individuals [1].
What is the natural habitat of Rhizopus?
Description and Natural Habitats. Rhizopus is a cosmopolitan filamentous fungus found in soil, decaying fruit and vegetables, animal feces, and old bread. While Rhizopus spp. are common contaminants, they are also occasional causes of serious (and often fatal) infections in humans. Some species are plant pathogens [ 531, 1295, 2144, 2202 ].
What is the scientific name of this organism called Rhizopus?
Rhizopus Click on organism name to get more information. Rhizopus americanus Rhizopus artocarpi Rhizopus azygosporus Rhizopus caespitosus
What is Rhizopus classified?
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. They are multicellular.
What group of fungi does Rhizopus belong to?
Rhizopus is probably the best-known genus in the class of Zygomycetes fungi, which normally live on dead and decaying plant material. These fungi exhibit a complex metabolism and produce a variety of enzymes that enable them to utilize a wide range of nutrients.
Is Rhizopus a ascomycota?
Members of the subdivision Ascomycota include molds that have septate hyphae and some yeasts....Classification of Fungi.GroupZygomycotaCommon NameBread moldsHyphal Organizationcoenocytic hyphaeReproduction CharacteristicsAsexual: sporangiospores Sexual: zygosporesExampleRhizopus stolonifer5 more columns
Is Rhizopus a Phycomycetes?
Mucormycosis is an invasive fungal infection caused by various members of the class Phycomycetes, especially Mucoraceae, subdivided into the genera Absidia, Rhizopus, and Mucor.
Is Rhizopus a bacteria?
Rhizopus microsporus is a fungal plant pathogen infecting maize, sunflower, and rice.
What are ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes?
(i) Ascomycetes are saprophytic, decomposers, parasitic or coprophilous. (i) Basidiomycetes are parasites. (ii) They produce ascospores and conidia. (ii) They produce basidiospores. (iii) Ascospores are produced endogenously in asci.
Is Rhizopus a Mucor?
Several different types of fungi can cause mucormycosis. These fungi are called mucormycetes and belong to the scientific order Mucorales. The most common types that cause mucormycosis are Rhizopus species and Mucor species.
What are the classification of fungi?
Fungi are usually classified in four divisions: the Chytridiomycota (chytrids), Zygomycota (bread molds), Ascomycota (yeasts and sac fungi), and the Basidiomycota (club fungi). Placement into a division is based on the way in which the fungus reproduces sexually.
1. What is Rhizopus?
Rhizopus is a genus of saprophytic fungus that live on plants and specialised parasitic fungi that live on mammals. They're in everything from matu...
2. What is taxonomy and phylogeny rhizopus?
Taxonomy and phylogeny rhizopus are kinds of the same. The phylum Zygomycota includes the genus Rhizopus, which has the same common name as the phy...
3. What is the structure of rhizopus?
Rhizopus, like most fungus, is made up of filaments (hyphae) that branch into a feeding structure called a mycelium. The filaments of all bread mou...
4. How does Rhizopus interact?
Bread moulds, such as rhizopus, are significant heterotrophs that consume a lot of organic material and provide nutrients that autotrophs can absor...
5. Where does Rhizopus stolonifer prefers to live in a variety of environments?
Rhizopus stolonifer is saprophytic, meaning that it feeds on dead organic debris. It is also termed parasitic since it consumes all nutrients from...
What is a rhizopus?
Pilophora Wallr. (1833) Rhizopus is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances , including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. They are multicellular.
What is the name of the rhizoid that produces colonies that are genetically different from either parent?
Sporangiophores arise among distinctive, root-like rhizoids. In sexual reproduction, a dark zygospore is produced at the point where two compatible mycelia fuse. Upon germination, a zygospore produces colonies that are genetically different from either parent.
How do rhizopus reproduce?
They reproduce by forming asexual and sexual spores. In asexual reproduction, sporangiospores are produced inside a spherical structure, the sporangium. Sporangia are supported by a large apophysate columella atop a long stalk, ...
Is rhizopus a fungus?
Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic agents of human zy gomycosis (fungal infection) and can be fatal. Rhizopus infections may also be a complication of diabetic ketoacidosis. This widespread genus includes at least eight species. Rhizopus 400x magnification.
What are the different types of rhizopus?
The most common ones are Rhizopus arrhizus, Rhizopus azygosporus, Rhizopus microsporus, Rhizopus schipperae, and Rhizopus stolonifer. Some morphological features, such as the length of rhizoids and sporangiophores, the diameter of sporangia, the shape of columellae, and the size, ...
How long does it take for a rhizopus to grow?
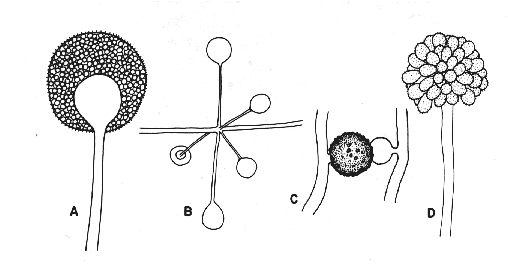
Macroscopic Features. Colonies of Rhizopus grow very rapidly, fill the Petri dish, and mature in 4 days. The texture is typically cotton-candy like. From the front, the color of the colony is white initially and turns grey to yellowish brown in time. The reverse is white to pale.
What is the best treatment for rhizopus infection?
Early diagnosis is crucial and surgical debridement or surgical resection, as well as antifungal therapy, are usually required. Amphotericin B is the most commonly used antifungal agent [ 408, 502, 696, 723, 1233 ]. Noteworthy, the addition of hyperbaric oxygen to amphotericin B did not have any improving effect on survival of experimental animals compared to amphotericin B alone or placebo air treatments [ 192 ]. Liposomal amphotericin B [ 696, 1004, 1470] and other lipid-based amphotericin B formulations such as amphotericin B colloidal dispersion [ 1588] have also been used in some cases with zygomycosis.
What are the most common predisposing factors for zygomycosis?
Zygomycosis includes mucocutaneous, rhinocerebral, genitourinary, gastrointestinal, pulmonary, and disseminated infections [ 104, 408, 502, 696, 963, 1318, 2042, 2220 ]. Diabetic ketoacidosis and immunosuppression due to various reasons, such as organ transplantation are the most frequent predisposing factors [ 408, 696, 910, 1731 ]. Desferoxamine treatment, renal failure, extensive burns, trauma, and intravenous drug use may also predispose to development of zygomycosis [ 1918 ]. While heatstroke has been described as a risk factor for disseminated zygomycosis [ 104 ], contaminated adhesive tapes and wooden tongue depressors have been reported to lead to nosocomial outbreaks of zygomycosis [ 812 ]. Vascular invasion that causes necrosis of the infected tissue, and perineural invasion are the most frustrating features of these infections [ 763 ]. Zygomycosis is frequently fatal.
What is the most commonly used antifungal agent?
Amphotericin B is the most commonly used antifungal agent [ 408, 502, 696, 723, 1233 ]. Noteworthy, the addition of hyperbaric oxygen to amphotericin B did not have any improving effect on survival of experimental animals compared to amphotericin B alone or placebo air treatments [ 192 ].
Is apophysis hemispherical or ovoid?
Apophysis is absent or rarely apparent and columellae are hemispherical. Sporangiospores (4-11 µm in diameter) are unicellular, round to ovoid in shape, hyaline to brown in color, and smooth or striated in texture [ 1295, 2144 ].
Is Rhizopus spp. zygomycosis pathogenic?
Pathogenicity and Clinical Significance. Rhizopus spp. are among the fungi causing the group of infections referred to as zygomycosis. Although the term mucormycosis has often been used for this syndrome, zygomycosis is now the preferred term for this angio-invasive disease.
What are the hyphae of rhizopus?
The hyphae of rhizopus species are typically non-septate, fast-growers and white in colour. The main identifying feature of the Rhizopus species is the presence of rhizoids at the base. In this context, we will discuss the features, structure and the different reproduction methods in Rhizopus.
What are the two types of hyphae in rhizopus?
Rhizopus consists of two kinds of hyphae, namely vegetative and reproductive hyphae. Vegetative hyphae differentiate into two types, namely s tolon and rhizoids and the reproductive hyphae turn into sporangiophores.
What is the name of the fungus that produces zygospores?
Rhizopus. Rhizopus is a type of fungus that belongs to the class Zygomycetes, as its species produce zygospore in the sexual reproductive phase. They are also called bread, black or pin mould. These can reproduce by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods through fragmentation, sporangiospores and zygospores formation, respectively.
What is the reserve food material of a Rhizopus?
The reserve food material is in the form of glycogen and oil droplets. A cell wall of the thallus is non-cellulose and made of chitin. The hyphae of Rhizopus differentiates into three distinctive parts, namely stolon (intermodal region), rhizoids (nodal region) and sporangiophores.
What is the hyphae of a stolon?
Vegetative Hypha: It typically includes: Stolon: It is the intermodal region called Runner. A stolon is the aerial hyphae that grow horizontally, and it is found attached to the substratum. Stolons are aseptate, branched and non-septate (lacks cross-wall).
Why does the thallus of a rhizopus break?
Sometimes the thallus of the Rhizopus breaks accidentally or due to some other factors into the few fragments, after which each fragment give rise to a new thallus on favourable conditions.
How does a zygospore germinate?
The zygospore lives in a resting phase for some time. On favourable conditions, zygospore forms a germ tube and germinates by forming a new vegetative body.
What is Rhizopus oryzae?
Description and significance. Rhizopus oryzae is a species of filamentous fungi within the group Mucormycetes, a body of organisms largely found in decaying organic matter and responsible for causing infections in immunocompromised individuals [1].
What phylum is R. oryzae in?
The microbe R. oryzae can be classified within the phylum Zygomycota [7]. About 1050 species of different fungi have been recognized as part of this phylum, and can be further subdivided into two categories: Zygomycetes and Trichomycetes [8].
What is the cell wall of R. oryzae?
R. oryzae grows as a result of mycelium accumulation [4]. Such accumulations are composed of tubular filaments known as hyphae. Mycelial cell walls, located in the body of the microbe, are reinforced by polysaccharides such as chitin [4]. Chitin reinforces the hyphae, creates a stronger cell wall, and thus allows for the cell to withstand greater pressures. While chitin provides a source of external, structural support to this microbe’s cells, lipids provide a source of internal, metabolic support as they can act as cellular storage sites [4].
How does R. oryzae reproduce?
The method by which R. oryzae reproduction occurs is dependent upon the available media source. In high nutrient environments, this microbe can reproduce asexually through mitosis, the most common reproductive method used by the species [2].
What gene family is responsible for the increase in chitin and chitosan?
oryzae to degrade organic matter. Additionally, the increase of the CHS and CDA gene families to 23 and 34 genes, respectively, accounts for the increase in chitin and chitosan within the microbe’s cell wall [3].
What is the most common comorbidity of R. oryzae?
One of the most common comorbidities of this infection is diabetes, which continues to affect the health and well-being of millions both nationally and globally [1]. In addition to mucormycosis, R. oryzae causes approximately 90% of the infectious complications of cancer patients, in particular those with hematological malignancies [2].
Can R. oryzae cause postharvest disease?
Current Research. R. oryzae can cause postharvest disease in certain fruits such as apples and bananas [18]. This disease originates from soft rot, a fungal infection that occurs when products are stored at nonoptimal temperatures or extended periods of time at cold temperatures.
How to classify fungi?
24.2: Classifications of Fungi 1 Classify fungi into the five major phyla 2 Describe each phylum in terms of major representative species and patterns of reproduction
How many phyla are there in the kingdom of fungi?
The kingdom Fungi contains five major phyla that were established according to their mode of sexual reproduction or using molecular data. Polyphyletic, unrelated fungi that reproduce without a sexual cycle, are placed for convenience in a sixth group called a “form phylum”. Not all mycologists agree with this scheme.
What are the five phyla of fungi?
The five true phyla of fungi are the Chytridiomycota (Chytrids), the Zygomycota (conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), the Basidiomycota (club fungi) and the recently described Phylum Glomeromycota. An older classification scheme grouped fungi that strictly use asexual reproduction into Deuteromycota, a group that is no longer in use.
What is a conjugated fungus?
Zygomycota: The Conjugated Fungi. The zygomycetes are a relatively small group of fungi belonging to the Phylum Zygomycota. They include the familiar bread mold, Rhizopus stolonifer, which rapidly propagates on the surfaces of breads, fruits, and vegetables.
Where do chytrids live?
Chytrids usually live in aquatic environments , although some species live on land. Some species thrive as parasites on plants, insects, or amphibians (Figure 24.2. 1 ), while others are saprobes. The chytrid species Allomyces is well characterized as an experimental organism.
Where are basidia found?
The basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields after rain, on the supermarket shelves, and growing on your lawn (Figure 24.2. 6 ).
Description and Natural Habitats
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. They are multicellular. Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic human pathogens that often cause fatal disease called mucormycosis. This widespread genus includes at least eight species.
Species
Pathogenicity and Clinical Significance
Macroscopic Features
Microscopic Features
Histopathologic Features
- The genus Rhizopus contains several species. The most common ones are Rhizopus arrhizus, Rhizopus azygosporus, Rhizopus microsporus, Rhizopus schipperae, and Rhizopus stolonifer. Some morphological features, such as the length of rhizoids and sporangiophores, the diameter of sporangia, the shape of columellae, and the size, shape and surface texture of sporangiospor…
Compare to
- Rhizopus spp. are among the fungi causing the group of infections referred to as zygomycosis. Although the term mucormycosis has often been used for this syndrome, zygomycosis is now the preferred term for this angio-invasive disease. Rhizopus arrhizus is the most common cause of zygomycosis [408] and is followed by Rhizopus microsporus var. rhizop...
Susceptibility
- Colonies of Rhizopus grow very rapidly, fill the Petri dish, and mature in 4 days. The texture is typically cotton-candy like. From the front, the color of the colony is white initially and turns grey to yellowish brown in time. The reverse is white to pale. Pathogenic species of Rhizopus can grow well at 37°C [531, 1295, 2144, 2202].