Which structure contains the genetic material needed for protein synthesis?
The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell's genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Click to see full answer. Herein, which structure contains information needed for protein synthesis?
Where does protein synthesis take place in a cell?
From DNA to RNA: Transcription DNA is housed within the nucleus, and protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm, thus there must be some sort of intermediate messenger that leaves the nucleus and manages protein synthesis.
Why are proteins important to the structure of the cell?
Most structural components of the cell are made up, at least in part, by proteins and virtually all the functions that a cell carries out are completed with the help of proteins. One of the most important classes of proteins is enzymes, which help speed up necessary biochemical reactions that take place inside the cell.
What is the structure of the cell membrane?
Cell membrane structure -plasma membrane -also a membrane around organelles -Composed primarily of a double layer of phospholipids -Non-polar FA chains in the middle (NO water in the middle) -Few chemical bonds link the phospholipids create fluid structure -Cholesterol adds stability to the cell membrane inside the membrane,
Where is the information for protein synthesis stored in the cell?
Information about protein synthesis is stored in the RNA. Information about protein synthesis is stored in the tRNA.
Which structure is responsible for synthesizing proteins?
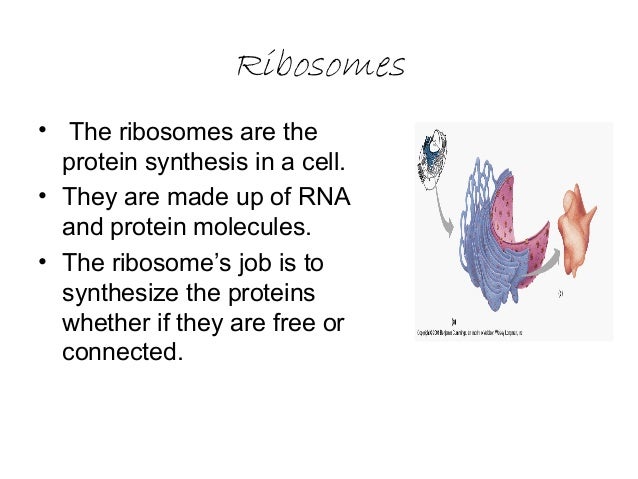
The ribosome is universally responsible for synthesizing proteins by translating the genetic code transcribed in mRNA into an amino acid sequence. Ribosomes use cellular accessory proteins, soluble transfer RNAs, and metabolic energy to accomplish the initiation, elongation, and termination of peptide synthesis.
What cell structure is responsible for protein synthesis quizlet?
Ribosomes are Responsible for Protein Synthesis and are often Associated with the Endoplasmic Reticulum 3.5.
Where does DNA synthesis take place?
From DNA to RNA: Transcription. DNA is housed within the nucleus, and protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm, thus there must be some sort of intermediate messenger that leaves the nucleus and manages protein synthesis.
What is the full complement of proteins in a cell?
Whatever the cellular process may be, it is almost sure to involve proteins. Just as the cell’s genome describes its full complement of DNA, a cell’s proteome is its full complement of proteins. Protein synthesis begins with genes. A gene is a functional segment of DNA that provides the genetic information necessary to build a protein.
Why is transcription called transcription?
This process is called transcription because the mRNA is like a transcript, or copy, of the gene’s DNA code. Transcription begins in a fashion somewhat like DNA replication, in that a region of DNA unwinds and the two strands separate, however, only that small portion of the DNA will be split apart.
What is triplet DNA?
A triplet is a section of three DNA bases in a row that codes for a specific amino acid. Similar to the way in which the three-letter code d-o-g signals the image of a dog, the three-letter DNA base code signals the use of a particular amino acid.
What are the stages of transcription?
Like DNA replication, there are three stages to transcription: initiation, elongation, and termination. Transcription: from DNA to mRNA. In the first of the two stages of making protein from DNA, a gene on the DNA molecule is transcribed into a complementary mRNA molecule. Stage 1: Initiation.
Where does transcription take place?
Transcription within the cell nucleus produces an mRNA molecule, which is modified and then sent into the cytoplasm for translation. The transcript is decoded into a protein with the help of a ribosome and tRNA molecules. Commonly, an mRNA transcription will be translated simultaneously by several adjacent ribosomes.
What is the purpose of DNA in learning objectives?
Learning Objectives. It was mentioned earlier that DNA provides a “blueprint” for the cell structure and physiology. This refers to the fact that DNA contains the information necessary for the cell to build one very important type of molecule: the protein.
What are the most important components of a cell?
Most structural components of the cell are made up, at least in part, by proteins and virtually all the functions that a cell carries out are completed with the help of proteins. One of the most important classes of proteins is enzymes, which help speed up necessary biochemical reactions that take place inside the cell.
Where does DNA synthesis take place?
From DNA to RNA: Transcription. DNA is housed within the nucleus, and protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm, thus there must be some sort of intermediate messenger that leaves the nucleus and manages protein synthesis.
Why is transcription called transcription?
This process is called transcription because the mRNA is like a transcript, or copy, of the gene’s DNA code. Transcription begins in a fashion somewhat like DNA replication, in that a region of DNA unwinds and the two strands separate, however, only that small portion of the DNA will be split apart.
Where does transcription take place?
Transcription within the cell nucleus produces an mRNA molecule, which is modified and then sent into the cytoplasm for translation. The transcript is decoded into a protein with the help of a ribosome and tRNA molecules. Commonly, an mRNA transcription will be translated simultaneously by several adjacent ribosomes.
What is triplet DNA?
A triplet is a section of three DNA bases in a row that codes for a specific amino acid. Similar to the way in which the three-letter code d-o-g signals the image of a dog, the three-letter DNA base code signals the use of a particular amino acid.
How do genes work?
Recall that proteins are polymers, or chains, of many amino acid building blocks. The sequence of bases in a gene (that is, its sequence of A, T, C, G nucleotides) translates to an amino acid sequence.
What is the function of a gene?
A gene is a functional segment of DNA that provides the genetic information necessary to build a protein. Each particular gene provides the code necessary to construct a particular protein.
Where does DNA synthesis take place?
From DNA to RNA: Transcription. DNA is housed within the nucleus, and protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm, thus there must be some sort of intermediate messenger that leaves the nucleus and manages protein synthesis.
What is the full complement of proteins in a cell?
Whatever the cellular process may be, it is almost sure to involve proteins. Just as the cell’s genome describes its full complement of DNA, a cell’s proteome is its full complement of proteins. Protein synthesis begins with genes. A gene is a functional segment of DNA that provides the genetic information necessary to build a protein.
Why is transcription called transcription?
This process is called transcription because the mRNA is like a transcript, or copy, of the gene’s DNA code. Transcription begins in a fashion somewhat like DNA replication, in that a region of DNA unwinds and the two strands separate, however, only that small portion of the DNA will be split apart.
What is triplet in DNA?
A triplet is a section of three DNA bases in a row that codes for a specific amino acid. For example, the DNA triplet CAC (cytosine, adenine, and cytosine) specifies the amino acid valine.
What are the stages of transcription?
Like DNA replication, there are three stages to transcription: initiation, elongation, and termination. Figure 3.4.2 – Transcription: from DNA to mRNA: In the first of the two stages of making protein from DNA, a gene on the DNA molecule is transcribed into a complementary mRNA molecule.
How do genes work?
Recall that proteins are polymers, or chains, of many amino acid building blocks. The sequence of bases in a gene (that is, its sequence of A, T, C, G nucleotides) translates to an amino acid sequence.
What are the biochemical reactions that occur during DNA replication?
Some of these critical biochemical reactions include building larger molecules from smaller components (such as what occurs during DNA replication or synthesis of microtubules) and breaking down larger molecules into smaller components (such as when harvesting chemical energy from nutrient molecules).
Big Picture
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are the molecules that provide genetic directions to the cells of all organisms. Almost all organisms use DNA as their principle genetic material with the exception of certain RNA viruses. DNA contains instructions for making proteins, which determine the structure and function of the cells.
Key Terms
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Doctrine that genetic instructions in DNA are copied by RNA, which carries them to a ribosome where they are used to synthesize a protein.
Protein Synthesis
Protein molecules play a huge role in the body, as many of our structures are made of protein. The genetic instructions in DNA is carried by RNA to the ribosomes where the proteins are made. The relationship DNA → RNA → protein is known as the central dogma of molecular biology.
The Genetic Code
During protein synthesis, the protein is built up one amino acid at a time. DNA contains the information that determines which amino acid comes next. DNA is made up of four different nitrogen bases: adenosine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases make up the genetic code. All living things have the same genetic code.
Role of RNA
DNA always stays in the nucleus, yet the actual process of protein synthesis occurs in the ribosomes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Instructions coding for a specific protein from the DNA are transferred to the ribosomes in the form of RNA, a small molecule that can leave the nucleus.