See more
Is Phrygia a place?
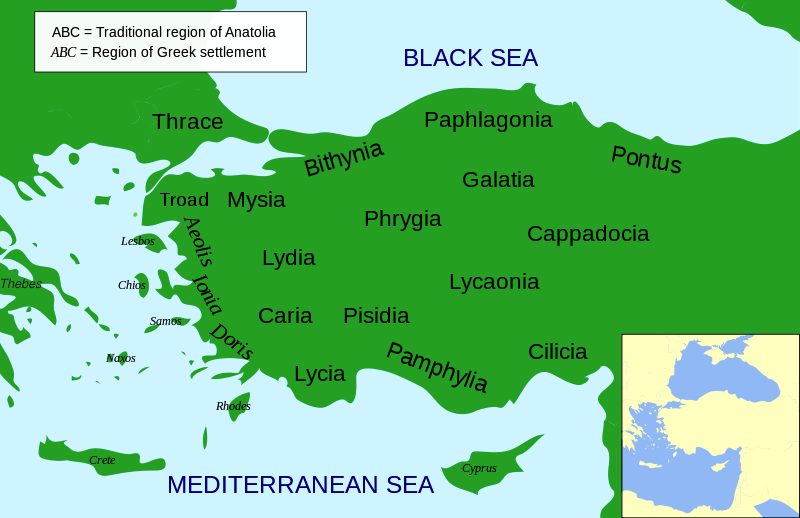
Phrygia, ancient district in west-central Anatolia, named after a people whom the Greeks called Phryges and who dominated Asia Minor between the Hittite collapse (12th century bc) and the Lydian ascendancy (7th century bc).
What race were Phrygians?
Indo-European speakingThe Phrygians (Greek: Φρύγες, Phruges or Phryges) were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks.
Where is modern day Phrygia and Galatia?
TurkeyGalatia (/ɡəˈleɪʃə/; Ancient Greek: Γαλατία, Galatía, "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey....GalatiaAchaemenid satrapyCappadociaRoman provinceGalatia5 more rows
Who ruled Phrygia?
Midas, (flourished 700 bc?), king of Phrygia (an ancient district in west-central Anatolia), first mentioned in extant Greek literature by Herodotus as having dedicated a throne at Delphi, before Gyges—i.e., before or little after 700 bc.
What language did the Phrygians speak?
The Phrygian language (/ˈfrɪdʒiən/) was the Indo-European language of the Phrygians, spoken in Anatolia (modern Turkey), during classical antiquity (c. 8th century BC to 5th century AD).
Are Armenians Phrygians?
Ancient Greek historian Herodotus stated that Armenians were colonists from Phrygia ("the Armenians were equipped like Phrygians, being Phrygian colonists" (Ἀρμένιοι δὲ κατά περ Φρύγες ἐσεσάχατο, ἐόντες Φρυγῶν ἄποικοι)(7.73). Phrygia encompassed much of western and central Anatolia during the Iron Age.
Are Phrygia and Galatia in Asia?
In classical antiquity, Phrygia (/ˈfrɪdʒiə/; Ancient Greek: Φρυγία, Phrygía [pʰryɡía]; Turkish: Frigya) (also known as the Kingdom of Muska) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River....PhrygiaRoman provinceGalatia, Asia7 more rows
What country is Galatia now?
TurkeyGalatia was a region in north-central Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) settled by the Celtic Gauls c. 278-277 BCE. The name comes from the Greek for “Gaul” which was repeated by Latin writers as Galli.
What nationality were the Galatians?
The Galatians were descended from Celts who had invaded Greece in the 3rd century BC. The original settlers of Galatia came through Thrace under the leadership of Leogarios and Leonnorios c. 278 BC.
What is the meaning of Phrygia?
Phrygia. / (ˈfrɪdʒɪə) / noun. an ancient country of W central Asia Minor. Slang.
How do you say Phrygia in the Bible?
0:051:00How To Say Phrygia - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFeria feria feria feria feria fecha.MoreFeria feria feria feria feria fecha.
When did Rome conquer Phrygia?
Phrygia became a part of the Roman province of Asia in 116 BCE & the region now grew in scope, at least as a geographical term. After the campaigns of Alexander the Great, the region of Phrygia/Lydia came under the control of one of Alexander's successors, Antigonus I (382-301 BCE).
What was the name of the Roman province of Asia?
In Roman times, however, when Paul journeyed there, the country was divided into two parts, one of which was known as Galatian Phrygia, and the other as Asian Phrygia, because it was a part of the Roman province of Asia, but the line between them was never sharply drawn.
What is the name of the region in Asia Minor?
PHRYGIA, a central district of Asia Minor, in the N.T. times, but very irregularly bounded, see map No. 7. It was on high tableland and at one time surrounded and touched by all the other provinces, with exception of Pontus. Strong's Greek. G5435: Phrugia. Phrygia, a region of Asia Minor.
What is the Phrygia?
Definition. Phrygia was the name of an ancient Anatolian kingdom (12th-7th century BCE) and , following its demise, the term was then applied to the general geographical area it once covered in the western plateau of Asia Minor. With its capital at Gordium and a culture which curiously mixed Anatolian, Greek, and Near Eastern elements, ...
Where did Phrygia expand?
Phrygia's territory expanded to reach Daskyleon in the north and the western edge of Cappadocia. Phrygia prospered thanks to the fertile land, its location between the Persian and Greek worlds, and the skills of the state's metalworkers and potters.
What were the towns in the Phrygian period?
Notable Phrygian towns in this period besides Gordium included Hierapolis , Laodikeia by the Lykos (aka Laodicea), Aizanoi, Apamea, and Synnada, although most of the region's population lived in small, agriculturally-based villages.
When did Phrygia become a Roman province?
Phrygia became a part of the Roman province of Asia in 116 BCE & the region now grew in scope, at least as a geographical term. After the campaigns of Alexander the Great, the region of Phrygia/Lydia came under the control of one of Alexander's successors, Antigonus I (382-301 BCE).
Who wrote Phrygia?
Written by Perrot And Chipiez, George Charles, published by Franklin Classics (2018) $27.95 $33.53. Phrygia: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Phrygian Kingdom in Anatolia... Written by Charles River Editors, published by CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (2017) $6.78 $8.41.
Who conquered Phrygia?
Phrygia was conquered by the Cimmerians in the 7th century BCE but the period of domination by Lydia and Persia has left an impoverished archaeological record. We know that Lydia expanded under the reign of the Mermnad dynasty (c. 700-546 BCE), and especially King Gyges (r. c. 680-645 BCE).
How tall is Phrygia?
The site is a tableland 3,000–5,000 feet (900–1,500 m) high, with mountains. Between the 12th and 9th centuries Phrygia formed the western part of a loose confederation of peoples (identified as “Mushki” in Assyrian records) that dominated the entire Anatolian peninsula.
What were the Phrygians known for?
After the Cimmerian invasion Phrygia lingered as a geographic expression under the successive rulers of Anatolia; its people were valued as slaves by the Greeks. The Phrygians excelled in metalwork and wood carving and are said to have originated the art of embroidery. Phrygian carpets were famous.
What were the Phrygian carpets?
Phrygian carpets were famous. Some magnificently carved stone tombs and shrines were uncovered after World War II by American archaeologists. Among the various Phrygian religious practices, the cult of the Great Mother ( Cybele) predominated and was passed on to the Greeks. Little else is known of Phrygian society.
Was Phrygia a centrally governed kingdom?
The early Phrygia ns probably were not organized in one strong and centrally governed kingdom. Their origins and the affiliations of their language are still enshrouded in mystery. Greek tradition—still in many cases the best source available—usually dates their…
Where did the Phrygians come from?
Strabo (12.4.4; 14.5.29) describes Phrygians as “barbarians and warriors” who had migrated to Central Asia from Macedonia and Thrace around the time of the Trojan War. According to Homer, during the Trojan War the kingdoms of the southeastern Balkans had fought on the side of the Trojans.
Where is Midas in Phrygia?
Phrygia. The Midas Monument in Phrygian Yazılıkaya about 50 km from Afyon includes on the right margin a Phrygian inscription whose last word can be deciphered as Midas. The Artemis of Ephesus probably represents a transitional form of the former Phrygian mother goddess Cybele to the Greek and later Roman goddess.
Why is Gordium not well known?
The Bronze Age settlement layers of Gordium, however, are not well known, because they are hidden under the foundations of the Phrygian era. Findings of Luwian hieroglyphic writing indicate to which civilization this place belonged. Gordium’s development as a city peaked only after the fall of the Hittite Empire.
What did Homer say about Phrygia?
A Homeric Hymn (no. 5, To Aphrodite) mentions that Phrygia possessed many fortresses. In the Iliad, Homer states that the Phrygians were “aggressive” (2.864) and riding on horses (10.432), which apparently was rare or even unique at the time.
What river did Midas bathe in?
When Midas bathed in the Pactolus River (today Sart Çayı), he transferred this gift to the river, thereby turning the Pactolus into the richest gold-carrying river and the kings of Sardis on its banks into the wealthiest rulers of Asia Minor at the time.
Where was the Phrygian kingdom of Dascylium located?
During the 8th century BCE, the Phrygian kingdom of Dascylium in northwestern Asia Minor extended to Tyana in Taurus. The kingdom’s central locations were Gordium and Midas city. Near Gordium, a royal necropolis with large tumuli went up, of which the most famous one, the so-called Midas Mound, was built around 740 BCE.
Who described the West Phrygian culture as “incredibly powerful”?
The American prehistorian Machteld Mellink described the west Phrygian culture as “incredibly powerful,” and expressed the opinion that many of its achievements rooted in the previous – almost unknown – Late Bronze Age culture. Behind these words, one might argue today, lies the hidden Luwian culture.