Where is the electron transport chain located?
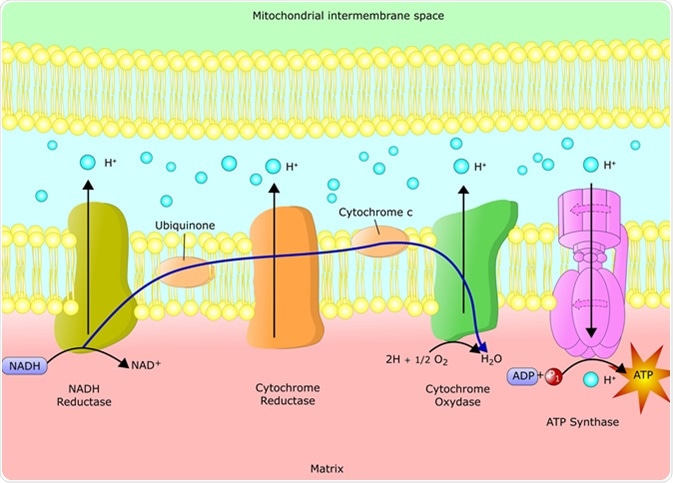
Electron Transport Chain Location. The electron transport chain is located within mitochondria, and the proteins of the electron transport chain span the inner mitochondrial membrane. This can be seen in the image below. The electron transport chain consists of 4 main protein complexes.
What happens along an electron transport chain?
what is the role of oxygen in the electron transport chain
- Electron Transport Chain (Oxidative Phosphorylation)
- The True Reason Why We Breath Oxygen – The Electron Transport Chain
- The Electron Transport Chain Explained (Aerobic Respiration)
- Electron Transport Chain ETC Made Easy
Where does electron transport happen?
What are the four steps of the electron transport chain?
- Step 1: Generating a Proton Motive Force.
- Step Two: ATP Synthesis via Chemiosmosis.
- Step Three: Reduction of Oxygen.
- Summary: Oxidative Phosphorylation.
What are the steps of electron transport chain?
The three main steps in the electron transport chain are:
- Generation of a proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane. Proton accumulation occurs in the intermembrane space of mitochondria.
- Reduction of molecular oxygen and formation of water.
- ATP synthesis by chemiosmosis.
Where is the electron transport chain found in a prokaryotic cell?
In prokaryotes, the electron transport chain components are found in the plasma membrane. As the electrons travel through the chain, they go from a higher to a lower energy level, moving from less electron-hungry to more electron-hungry molecules.
Where is the electron transport chain in eukaryotes vs prokaryotes?
1 Answer. In Eukaryotes it occurs in inner membrane of mitochondria while in prokaryotes it occurs in cell plasma membrane.
Where does the electron transport chain take place in the eukaryotic cell?
Since the electron transport chain is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes, and since NADH cannot be transported from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix, NADH formed in the cytosol needs to be oxidized by another route.
Where does the electron transport chain take place?
mitochondriaThe electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
How is the electron transport chain different in prokaryotes?
Explanation: In eukaryotes the electron transport chain (ETC) is situated in the mitochondiral membrane. Prokaryotes do not have organelles such as mitochondria, but they do have an ETC. A membrane is required for the ETC to work, otherwise it would not be possible to build a gradient of hydrogen atoms.
Where is ETS located in aerobic prokaryotes?
The ETS is embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane of prokaryotes and the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes. Each ETS complex has a different redox potential, and electrons move from electron carriers with more negative redox potential to those with more positive redox potential.
Where does electron transport chain occur in the mitochondria?
Electron transport chain (ETC) occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where the OXPHOS takes place through the action of ATP synthase, [37].
Where in the mitochondria is the electron transport chain?
inner mitochondrial membraneIn eukaryotic organisms the electron transport chain, and site of oxidative phosphorylation, is found on the inner mitochondrial membrane.
In which part of the mitochondria does the electron transport chain take place?
inner membraneThe electron transport chains are on the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. As the high-energy electrons are transported along the chains, some of their energy is captured. This energy is used to pump hydrogen ions(from NADH and FADH2) across the inner membrane, from the matrix into the intermembrane space.
What is the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain involves a series of redox reactions that relies on protein complexes to transfer electrons from a donor molecule to an acceptor molecule. As a result of these reactions, the proton gradient is produced, enabling mechanical work to be converted into chemical energy, allowing ATP synthesis.
How do electrons move in the electron transfer chain?
In the electron transfer chain, electrons move along a series of proteins to generate an expulsion type force to move hydrogen ions, or protons, across the mitochondrial membrane. The electrons begin their reactions in Complex I, continuing onto Complex II, traversed to Complex III and cytochrome c via coenzyme Q, and then finally to Complex IV. The complexes themselves are complex-structured proteins embedded in the phospholipid membrane. They are combined with a metal ion, such as iron, to help with proton expulsion into the intermembrane space as well as other functions. The complexes also undergo conformational changes to allow openings for the transmembrane movement of protons.
What is the name of the complex that the electrons are transferred to?
The cytochromes then extend into Complex IV, or cytochrome c oxidase. Electrons are transferred one at a time into the complex from cytochrome c. The electrons, in addition to hydrogen and oxygen, then react to form water in an irreversible reaction.
How many electrons does NADH have?
The NADH now has two electrons passing them onto a more mobile molecule, ubiquinone (Q), in the first protein complex (Complex I). Complex I, also known as NADH dehydrogenase, pumps four hydrogen ions from the matrix into the intermembrane space, establishing the proton gradient.
What is the mechanism that drives ATP synthesis?
Often, the use of a proton gradient is referred to as the chemiosmotic mechanism that drives ATP synthesis since it relies on a higher concentration of protons to generate “proton motive force”. The amount of ATP created is directly proportional to the number of protons that are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane. ...
Which protein transfers electrons to the last complex?
ISP and cytochrome b are proteins that are located in the matrix that then transfers the electron it received from ubiquinol to cytochrome c1. Cytochrome c1 then transfers it to cytochrome c, which moves the electrons to the last complex. (Note: Unlike ubiquinone (Q), cytochrome c can only carry one electron at a time).
What is the name of the protein that is oxidized into fumarate?
In the next protein, Complex II or succinate dehydrogenase, another electron carrier and coenzyme, succinate is oxidized into fumarate, causing FAD (flavin-adenine dinucleotide) to be reduced to FADH 2. The transport molecule, FADH 2 is then reoxidized, donating electrons to Q (becoming QH 2 ), while releasing another hydrogen ion into the cytosol.
Where is the electron transport chain located?
In eukaryotes the electron transport chain (ETC) is situated in the mitochondiral membrane. Prokaryotes do not have organelles such as mitochondria, but they do have an ETC.
Where is the ETC located in prokaryotes?
The only membrane in prokaryotes is the cellular membrane, that is where the ETC is located. On the top left corner the location of the ETC in prokaryotes, on the top right corner the situation in eukaryotes.
What is the electron transport chain in bacteria?
Bacterial electron transport chains vary in their electron carriers (e.g., in their cytochromes) and are usually extensively branched. Electrons often enter at several points and leave through several terminal oxidases. Bacterial electron transport chains are usually shorter and possess lower phosphorus to oxygen ...
Why is the cytochrome O branch not as efficient as the cytochrome O branch?
This branch is not as efficient as the cytochrome o branch because it does not actively pump protons to periplasmic space. The cytochrome o branch shows moderately high efficiency for oxygen and operates at high oxygen concentrations (high aeration).
How many complexes does an aerobic bacterium have?
When this bacterium grows aerobically, its electron transport chain possesses four complexes that correspond to the mitochondrial chain. But, when this bacterium grows anaerobically with nitrate as its electron acceptor, the chain is structured quite differently. Since most bacteria grow anaerobically using different variety ...