Where does mitosis actively take place in a plant?
Mitosis takes place actively in meristematic cells of plants, apical meristems of roots and stems which increases the length of roots and stems, vascular cambium which produces increase of diameter of roots and stems, and cork cambium which produces new bark cells as the plant increases in diameter.
What are three reasons cells go through mitosis?
- To grow and develop, you must form new cells. Imagine how often your cells must divide during a growth spurt.
- Cell division is also necessary to repair damaged cells.
- Your cells can also simply wear out.
Where does glycolysis occur in plants?
where is glycolysis located in the cell
- Cellular Respiration Part 1: Glycolysis
- Glycolysis Pathway Made Simple !! Biochemistry Lecture on Glycolysis
- Steps of glycolysis | Cellular respiration | Biology | Khan Academy
- Cellular Respiration (UPDATED)
What do plant cells undergo mitosis?
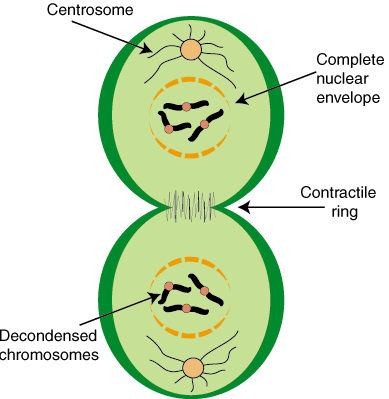
Plant mitosis is a part of plant cell division where the replicated chromosomes are separated into two, daughter nuclei. It occurs in four stages, same as animal mitosis. These stages are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What are the cells in plants called?
Most plants have several different zones where you’ll find these cells – these zones are called meristems. What Are Meristematic Cells? Meristematic cells have the same function in plants as stem cells have in animals – they divide themselves to create new cells. Meristems are essential to the growth of the plant.
Where are the apical meristems located?
Apical Meristems are located at the tip of roots and shoots. Lateral Meristems are located between the Xylem and phloem. Mitosis occurs exclusively in eukaryotic cells, but occurs in different ways in different species. For plants, it occurs in each individual plant cell.