KEY TAKEAWAYS
- In the moss life cycle, fertilization takes place in the archegonium of the gametophyte.
- Mosses have diploid and haploid generations.
- Gametophytes, spores, sperm, and eggs are all haploid.
- Zygotes and their resulting sporophytes are diploid.
- Mosses can reproduce sexually or asexually.
Where does fertilization take place in mosses?
In the moss life cycle, fertilization takes place in the archegonium of the gametophyte. Mosses have diploid and haploid generations. Gametophytes, spores, sperm, and eggs are all haploid.
What is the life cycle of a moss?
In the moss life cycle, fertilization takes place in the archegonium of the gametophyte. Mosses have diploid and haploid generations. Gametophytes, spores, sperm, and eggs are all haploid. Zygotes and their resulting sporophytes are diploid. Mosses can reproduce sexually or asexually.
What is the mode of reproduction in mosses?
Mosses have two forms of reproduction: sexual reproduction and asexual / vegetative reproduction. This is true for all bryophytes. Practically all flowering plants are diploid, but for mosses, this is different.
Do mosses produce sperm or eggs?
A single gametophyte moss plant can produce both sperm and eggs. This can occur on different parts of the same plant, one part producing sperm and another part producing eggs. However, a plant usually produces either all sperm-producing organs or all egg-producing organs at any one time.
What is the process of fertilization in mosses?
In all bryophytes fertilization is dependent on water—usually a film of water or the splashing of raindrops—for the transfer of sperm to the egg. Chemical stimuli direct the motile flagellate sperm to the archegonium. The fertilized egg (zygote) grows out of the gametophyte, which is also the source of its nourishment.
Where do meiosis and fertilization occur in moss?
Life cycle of a moss (genus Polytrichum). The sporophyte generation is dependent on the photosynthetic gametophyte for nutrition. Cells within the sporangium of the sporophyte undergo meiosis to produce male and female spores, respectively.
What are the stages in the life cycle of moss?
There are two stages that mosses go through in their life cycle. The first stage is haploid (gametophyte) and the second stage is diploid (sporophyte), change is known as the alternation of generations. This unique reproductive cycle starts when two male and female gametophytes, sexually reproduce.
Where is the sperm in the moss life cycle?
Sperm, which are released by the mature antheridium (the male reproductive organ), are attracted into the neck of an archegonium (the female reproductive organ). Here, one sperm fuses with the egg to produce the zygote.
What part of the moss plants helps them to reproduce?
In mosses, as in liverworts and hornworts, the leafy shoots belong to the gametophytic phase and produce sex organs when they mature. The leafy shoots (often called gametophores, because they bear the sex organs) arise from a preliminary phase called the protonema, the direct product of spore germination.
Where in mosses are zygotes and embryos formed?
Beginning with the bryophytes (e.g., mosses), however, the gametes are produced in gametangia that are composed of many cells; the zygote, through mitosis, develops into an embryo that, in turn, develops into a diploid sporophyte. Spores are produced by meiosis within a specialized part of the sporophyte.
How does fertilization of gametes occur in moss life cycle *?
Some successfully end up on female gametophyte moss plants and are chemically attracted to the archegonium. Each archegonium holds one egg, in a swollen section called the venter. The sperm enter the archegonium through the narrow channel in its neck. Fertilization occurs in the archegonium to form a diploid zygote.
Where do mosses reproduce?
Moss reproduces in two ways: sexually and asexually. Moss sexually reproduces by transmitting sperm (in the presence of water) from the male plant to the female. The zygote forms a stalk (called seta) which hold spores in a small pod at its top.
What are mosses and how do they reproduce?
Mosses are bryophytes and they can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Mosses can be monoecious or dioecious. They depend on moisture to produce sexually. MOsses reproduce by spores which are analogous to the flowering plants.
How do true mosses reproduce?
Mosses reproduce using spores, not seeds, and have no flowers. Moss gametophytes have stems which may be simple or branched and upright or prostrate. Their leaves are simple, usually only a single layer of cells with no internal air spaces, often with thicker midribs.
Where is the gametophyte and sporophyte in mosses?
page noted that bryophytes have a gametophyte stage and a sporophyte stage. The spore capsule, often with a supporting stalk (called a seta), is the sporophyte and this grows from the gametophyte stage. You will commonly see the statement that a moss gametophyte consists of leaves on stems.
How does the sperm reach the egg in mosses?
Their flagellated sperm must swim through water to reach the egg. So mosses and liverworts are restricted to moist habitats. There are no mosses in the desert. But mosses are surprisingly resistant to drying up, and can survive under very harsh conditions.
What is the name of the sperm that enters the female gametophyte and fuses with?
A. A diploid sperm from pollen enters the female gametophyte and fuses with a diploid egg.
Which pollen grain is produced by the male sporophyte?
D. A haploid pollen grain produced by the male sporophyte enters the female sporophyte and fuses with a haploid megasporangium.
Which generation is larger, sporophyte or gametophyte?
A. The sporophyte generation is much larger than the gametophyte generation and the two generations grow as independent structures.
Why are mosses important?
Mosses are important components of many ecosystems and have even been shown to be important when they occur in freshwater habitats since they provide living space for many small invertebrate animals. As primary producers, moss-like other plants, are a source of food for primary consumers in food chains and food webs.
What is the division of moss?
The mosses are in the plant division known as the Bryophyta, which include non-vascular plants that produce spores. Besides moss, hornworts and liverworts are also included in this division of plants.
What is the name of the plant that is quite primitive?
In the archegonium of the gametophyte generation. The mosses are a type of plant that is quite primitive, and it is found in the division Bryophyta. This group of plants also contains the hornworts and liverworts. All of these plants live in shady and moist environments and are not large in size. Mostly the bryophytes are small, no longer ...
How are sporophytes produced?
The sporophyte generation is produced from the embryo of the gametophyte plant. A foot, stalk, and capsule are formed. Spores are produced in the capsule and are then dispersed by wind when the capsule breaks open. A spore germinates into a protonema which then forms a gametophyte plant once more. The entire life cycle then begins once more.
What is the root structure of moss?
A moss has a rootlike structure known as a rhizoid and stem-like and leaf-like structures. These form the gametophyte of the plant, and this is also the haploid (n) stage of the life cycle of the moss. The rhizoid attaches the plant to the soil and helps take up nutrients needed by the plant body.
Which stage of the plant produces antheridia?
The gametophyte stage produces antheridia which produce sperm, and archegonia, which produce eggs. Sperm is motile and transported by water. The sperm enters the archegonium of the plant where it fertilizes the egg cell and an embryo is formed. The sporophyte generation is produced from the embryo of the gametophyte plant.
How many spores does the sporangium produce?
The sporangium is a reproductive structure. In fact, each spore mother cell in the sporangium produces four (n) spores by meiosis. When the time is right the part of the capsule known as the calyptra and operculum become detached and the spores are able to be released.
Where does fertilization take place in moss?
In the moss life cycle, fertilization takes place in the archegonium of the gametophyte. Mosses have diploid and haploid generations. Gametophytes, spores, sperm, and eggs are all haploid. Zygotes and their resulting sporophytes are diploid. Mosses can reproduce sexually or asexually.
How do moss plants produce eggs?
A single gametophyte moss plant can produce both sperm and eggs. This can occur on different parts of the same plant, one part producing sperm and another part producing eggs. However, a plant usually produces either all sperm-producing organs or all egg-producing organs at any one time. This way it doesn't breed with itself, promoting genetic variation. The female structure for producing eggs is known as the archegonium, and the male structure for producing sperm is known as the antheridium. Antheridia are tiny, typically stalked, club-shaped or spherical structures. Archegonia are bottle-like containers, their wall just one cell thick. Archegonia are typically formed in groups. Archegonia and antheridia are usually bundled in leaf rosettes similar to flowers, called perichaetia. Elongated club-shaped cell filaments called Paraphyse are sometimes found on the gametophyte, storing water and protecting the archegonia sand antheridia from drying up.
How do archegonia get fertilized?
They swim using two threadlike tails. Some successfully end up on female gametophyte moss plants and are chemically attracted to the archegonium. Each archegonium holds one egg, in a swollen section called the venter. The sperm enter the archegonium through the narrow channel in its neck. Fertilization occurs in the archegonium to form a diploid zygote. Once one archegonium in a group has been fertilized, in many cases the others lose the ability to be fertilized. This is caused by an inhibitory hormone released from the fertilized archegonium.
What is the process of sexual reproduction?
Generally speaking, sexual reproduction is the process where genes from two different parents mix to produce offspring with a genetic makeup similar to, but different from, each parent. The sexual reproduction of the moss (bryophyte) life cycle alternates between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte phases.
What is the cause of a zygote in moss?
This is caused by an inhibitory hormone released from the fertilized archegonium. The formation of the zygote begins the second phase of the moss life cycle, where the zygote develops into a diploid sporophyte (spore-plant).
How many eggs does each archegonium hold?
Each archegonium holds one egg, in a swollen section called the venter. The sperm enter the archegonium through the narrow channel in its neck. Fertilization occurs in the archegonium to form a diploid zygote. Once one archegonium in a group has been fertilized, in many cases the others lose the ability to be fertilized.
What are the two forms of reproduction in mosses?
Mosses have two forms of reproduction: sexual reproduction and asexual / vegetative reproduction. This is true for all bryophytes.
Where does fertilization take place in the moss life cycle?
In the moss life cycle, fertilization takes place in the archegonium of the gametophyte. Mosses have diploid and haploid generations. Gametophytes, spores, sperm, and eggs are all haploid.
How does reproduction take place in moss?
Spores are housed in the brown capsule that sits on the seta. Pieces of the moss body can break off, move by wind or water , and start a new plant if moisture permits.
What happens in the life cycle of a moss?
A moss is a member of the plant phylum Bryophyta. The life cycle of a moss, like all plants, is characterized by an alternation of generations. A diploid generation, called the sporophyte, follows a haploid generation, called the gametophyte, which is in turn followed by the next sporophyte generation.
How does the life cycle of a moss begin?
The life cycle of most mosses begins with the release of spores from a capsule, which opens when a small, lidlike structure, called the operculum, degenerates. After cell division, the zygote becomes the sporophyte, and, at the same time, the archegonium divides to form the protective calyptra.
What is unusual about the reproductive cycle of a moss?
The mosses (and all bryophytes) have an alternation of generations life cycle that is unusual for two reasons: The haploid form is the dominant generation (larger, long-lived, and photosynthetic) The diploid form is the lesser generation (smaller, short lived and nutritionally dependent on the haploid form).
What is the reproductive structure in moss and fern?
The ferns and fern allies germinate from spores. These plants are mostly homosporous – their spores are identical and you can’t differentiate which will grow into male or female plants. They are also monoecious – both the archegonia and antheridia (male and female reproductive structures) are borne on the same plant.
What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of a moss?
In bryophytes, such as mosses and liverworts, the gametophyte is the dominant life phase, whereas in angiosperms and gymnosperms the sporophyte is dominant. The haploid phase is also dominant among fungi.
The Bryophytes
- The mosses are in the plant division known as the Bryophyta, which include non-vascular plants that produce spores. Besides moss, hornworts and liverworts are also included in this division of plants. These plants grow in a shady area, which is also moist, and some species are also found in freshwater habitats. The bryophytes are generally consider...
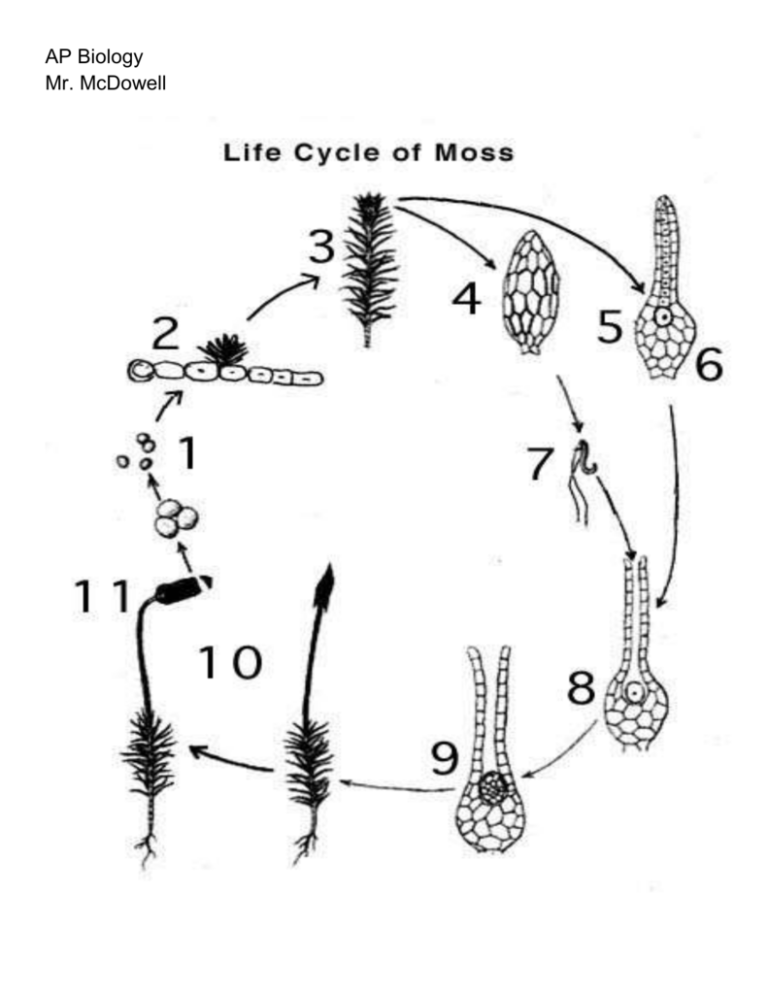
The Moss Life Cycle
- The mosses have an alternation of generations, with a haploid gametophyte stage alternating with a diploid sporophyte stage. Other types of plants also have an alternation of generations, but over time in the more advanced plants, it is the sporophyte generation that has become dominant. In the bryophytes though, the gametophyte is the dominant stage of the cycle and the sporophyte i…
Importance of Moss
- Mosses are important components of many ecosystems and have even been shown to be important when they occur in freshwater habitats since they provide living space for many small invertebrate animals. As primary producers, moss-like other plants, are a source of food for primary consumers in food chains and food webs. They are thus an important part of biological …
References
- PH Raven, RF Evert, SE Eichhorn (1987). Biology of Plants, 4th edition. New York: USA, Worth Publishers.
- Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica (2019). Moss. Retrieved from Encyclopedia Britannica.
- Walter K. Dodds, Matt R. While (2010). Nonvascular plants. Retrieved from sciencedirect.com.
- JW Kimball (2018). Moss life cycle. Biology libretexts. Retrieved from libretexts.org.