Are there any gods in Chinese mythology?
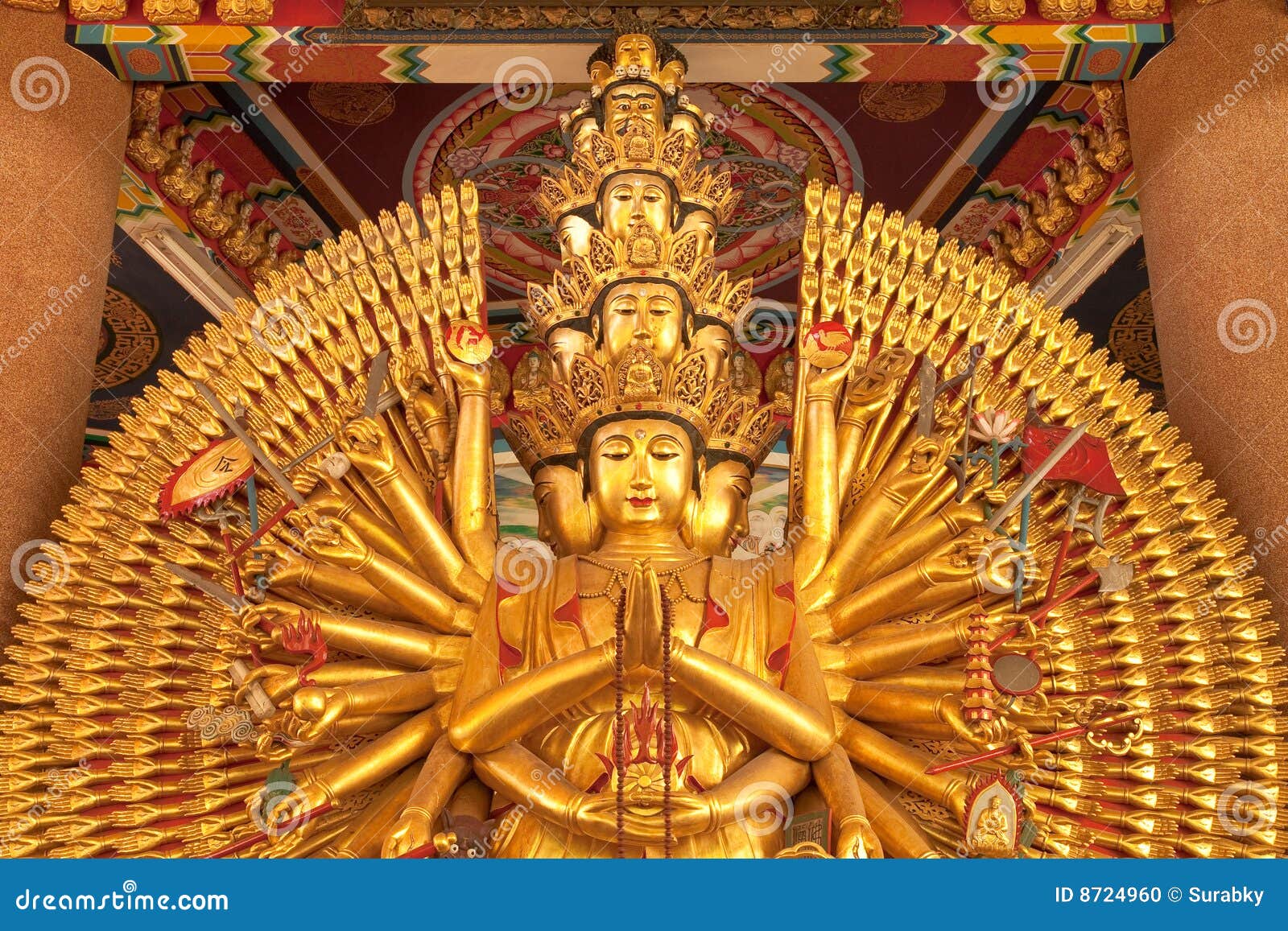
There are various important deities, spirits, and mythological people in Chinese mythology and folk religion. Some are clearly divine, such as the Jade Emperor (and even he is sometimes said to have begun life as a mortal). However, in Chinese language many beings are referred to as shen.
Where can I find the Chinese goddess of healing?
Bao Gu, the Chinese Goddess of Healing, was raised in a monastery where she learned how to heal via acupuncture and how to make magic. Her shrine is located in Guangzhou City. Call on Bao Gu for healing and if your career path is in natural medicine.
What is abundant mythology in Chinese culture?
Abundant mythology is associated with religious holidays and folk festivals. The Qingming festival is a good example of a Chinese holiday that involves family activities associated with a seasonally-recurring annual event; and, also, ancestor veneration. The seasonally-recurring annual holiday of Qixi involves love and romance.
Are there any simian gods in Chinese mythology?
Various beings with simian characteristics appear in Chinese mythology and religion. The Monkey King was a warder of evil spirits, respected and loved, an ancient deity at least influenced by the Hindu deity Hanuman. The Monkey god is still worshiped by some people in modern China.
Where do gods and goddesses live?
Mount OlympusTheir major gods and goddesses lived at the top of Mount Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece, and myths described their lives and actions.
Where do major gods goddesses dwell as a home?
They are named after their dwelling place Mount Olympus.Zeus.Poseidon.Hades.Hestia.Hera.Ares.Athena.Apollo.More items...
Who is the main God in China?
ShangdiShangdi (Chinese: 上帝; pinyin: Shàngdì; Wade–Giles: Shang Ti), also written simply, "Emperor" (Chinese: 帝; pinyin: Dì), is the Chinese term for "Supreme Deity" or "Highest Deity" in the theology of the classical texts, especially deriving from Shang theology and finding an equivalent in the later Tian ("Heaven" or " ...
Where does God meet?
Mount Olympus was the home and meeting place of all the gods and is an actual place in Greece.
Where do all gods live?
Mount OlympusGreek Mythology: The Olympians At the center of Greek mythology is the pantheon of deities who were said to live on Mount Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece. From their perch, they ruled every aspect of human life.
Where do gods stay?
The Greek mythology says that the Greek gods were living in Mount Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece. Like all gods, they were immortal.
How do Chinese call god?
Tianzhu (Chinese name of God)
Who is god of Japan?
Hachiman (八幡神) is the god of war and the divine protector of Japan and its people. Originally an agricultural deity, he later became the guardian of the Minamoto clan. His symbolic animal and messenger is the dove. Inari Ōkami (稲荷大神) The god or goddess of rice and fertility.
Does China believe god?
China has the world's greatest irreligious population, and the Chinese government and the ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP) is officially atheist.
What was the first God?
Brahma the Creator In the beginning, Brahma sprang from the cosmic golden egg and he then created good & evil and light & dark from his own person. He also created the four types: gods, demons, ancestors, and men (the first being Manu).
How much gods are there?
Anthropologists estimate that at least 18,000 different gods, goddesses, and various animals or objects have been worshipped by humans since our species first appeared. Today, it is estimated that more than 80 percent of the global population considers themselves religious or spiritual in some form.
What is Chinese mythology?
Chinese mythology ( simplified Chinese: 中国神话; traditional Chinese: 中國神話; pinyin: Zhōngguó shénhuà) is mythology that has been passed down in oral form or recorded in literature in the geographic area now known as " China " . Chinese mythology includes many varied myths from regional and cultural traditions.
What are the features of the mythology of China?
Various features of mythological terrain are described in myth, including a Heavenly world above the earth, a land of the dead beneath the earth, palaces beneath the sea, and various fantastic areas or features of the earth, located beyond the limits of the known earth. Such mythological features include mountains, rivers, forests or fantastic trees, and caves or grottoes . These then serve as the location for the actions of various beings and creatures. One concept encountered in some myths is the idea of travel between Earth and Heaven by means of climbing up or down the pillars separating the two, there usually being four or Eight Pillars or an unspecified number of these Sky Ladders.
What are some myths?
Many myths involve the creation and cosm ology of the universe and its deities and inhabitants. Some mythology involves creation myths, the origin of things, people and culture. Some involve the origin of the Chinese state.
How many immortals are there?
Main article: Eight Immortals. The Eight Immortals have an existence in mythology as well as developed a presence in religious Daoism, and art and literature. The standard group is He Xian'gu, Cao Guojiu, Li Tieguai, Lan Caihe, Lü Dongbin, Han Xiangzi, Zhang Guolao, and Han Zhongli (also known as Zhongli Quan).
Why were Yao and Shun important?
Yao and Shun were important mythological rulers, exemplars of propriety in rulership. The Great Flood began during the reign of Yao and continued through the time of Shun (the successor of Yao, who had passed over his own son and made Shun his successor because of Shun's ability and morality). Historically, when Qin Shi Huang united China in 221 BCE, he used propaganda to acclaim his achievements as surpassing those of mythological rulers who had gone before him. He combined the ancient titles of Huáng ( 皇) and Dì ( 帝) to create a new title, Huángdì ( 皇帝 ); thus, the Qin emperor used mythology to bolster his claims to be the legitimate and absolute ruler of the whole earth. This reflected what was to become a longstanding belief that all civilized people should have one government, and that it should be Chinese.
When did Buddhism come to China?
Buddhism was historically introduced to China, probably in the first century CE , accompanied by the import of various ideas about deities and supernatural beings including Kṣitigarbha who was renamed Dizang. the Four Heavenly Kings, the main Buddha himself Shakyamuni Buddha ( 釋迦牟尼 Shìjiāmóunífó), Avalokiteśvara who after a few centuries metamorphosized into Guanyin (also Kuanyin) a bodhisattva of compassion, and Hotei the Laughing Buddha. New Buddhist material continued to enter China, with a big spike in the Tang dynasty, when the monk Xuanzang brought over 600 texts from India. Over time, Guanyin also became a Daoist immortal and was the subject of much mythology.
Who is the goddess of agriculture?
Further information: Shennong, Yan Emperor, Agriculture in Chinese mythology, and Five Grains. Shennong is variously translated as "Divine Farmer" or "Divine Peasant", or "Agriculture God", and also known as the Wugushen (Spirit of the Five Grains) and Wuguxiandi "First Deity of the Five Grains".
What is the most unbelievable thing about Chinese eunuchs?
But the really unbelievable thing about Chinese eunuchs is that it was a volunteer workforce. Life outside the palace was so bad, apparently, that healthy men would volunteer to be parted from their bits and pieces (yes, the family jewels and the family scepter, as it were) in exchange for a life of luxury.
How many cats are there in the forbidden city?
China Daily reports that the Forbidden City is home to around 200 cats, and they aren't mere strays — they are practitioners of the cat's most noble and ancient occupation: rodent control. The Forbidden City's feline employees actually have it pretty good.
How many eunuchs were there at the end of the Ming Dynasty?
By the end of the Ming Dynasty there were 70,000 eunuchs living in the palace. That's right, men, if you ever visit the Forbidden City, you should cross your legs and give thanks to the North Star that it's not 500 years ago and you can walk out again with your junk still attached.
Is China a forbidden city?
China's "For bidden City" is no longer technically forbidden — in fact it welcomes millions of tourists annually, so it would really be more accurate to call it the "Allowed City," or maybe the "Permitted City.". No one would go there, though, because things that are allowed and permitted are totally boring. But the Forbidden City's forbidden past ...
Did Chinese emperors eat food?
Chinese emperors lived in pretty ridiculous opulence, from the clothes they wore to the food they ate. Emperors living within the Forbidden City didn't eat just any food, they ate "Imperial cuisine.". According to Voice of America, Chinese imperial cuisine was forbidden to anyone who was not royalty.
Who is the goddess next to Guan Yin?
Call on Bao Gu for healing and if your career path is in natural medicine. 4. Wangmu Niangniang. Wangmu Niangniang is the most well-known Chinese goddess next to Guan Yin. Ruling the west from her magical palace on top of a mountain range, Wang Mu Niang Niang is the Chinese goddess of fertility, health and immortality.
Which ancient culture has its own goddess?
Nearly every ancient culture around the world had their own sacred deities. These deities were assigned or had domain over different aspects of nature and human life. In the past, we’ve covered goddesses from Egypt, Greece, Africa and the Celtic pantheon. In this article, we present our favorite Chinese goddesses including the Chinese Goddess ...
What is the Chinese goddess of love?
1. Guan Yin: Chinese Goddess of Love and Peace. Also called Kuan Yin or Quan Yin, this widely-known Chinese Goddess brings love, harmony and healing to any home or situation. The interesting thing about this Chinese goddess is that she crosses cultures and religions in the East and West.
What is the name of the Chinese snake goddess?
Trapped in a bowl with her snake spirit friend Lady White, Lady Blue is another Chinese snake goddess of legend. As opposed to Lady White, Lady Blue is blue in color and smaller when in snake form. When she manifests as a woman, she is known as Siu Ching.
Where is Bao Gu located?
Her shrine is located in Guangzhou City.
Where did Lady Xian live?
Beginning as a historical or mythical figure, Lady Xian once lived in Southern China. She was married to a chieftain of the Xian tribe and did wonders for her people over her lifetime. Even during a time when women weren’t as respected in China, Lady Xian earned the regard of the emperor himself.
Who is the snake spirit of China?
Lady White. Another interesting Chinese Goddess is Lady White, the snake spirit of China. Known well through Chinese plays, operas, and literature, Lady White sought to be venerated by humans and got her wish! A monk punished this Chinese goddess for coming to the human world and marrying a man.
Where are the Forbidden City treasures?
In the Chinese civil war that broke out after World War II, the retreating Nationalists moved about 600,000 treasures, originally from the Forbidden City, to Taiwan, where they are now part of a Palace Museum in Taipei.
How many emperors occupied the Forbidden City?
1420 to 1911. In total, 24 emperors occupied the Forbidden City, so named because it could only be accessed by the emperor, his immediate family, his women and thousands of eunuchs ...
How many artifacts are there in the Forbidden City?
Today, there are still many more stories waiting to be told about the Forbidden City. The Palace Museum in Beijing has more than 1.5 million artifacts from the city, including many which have yet to be published despite a program that has produced 60 volumes in the last few decades.
What is the roof of the Forbidden City decorated with?
The roof of the Hall of Supreme Harmony is decorated with dragons. (Image credit: Jorge Sanchez Shutterstock)
Where was the Emperor's retirement palace?
In doing so, he built a retirement palace called Ningshougong (Tranquility and Longevity Palace) in the northeast part of the Forbidden City, writes Nancy Berliner in an article published in the book "The Emperor’s Private Paradise: Treasures from the Forbidden City" (Peabody Essex Museum, 2010).
Who was the last emperor of the Ming Dynasty?
In that year, a rebel army attacked Beijing, forcing the last emperor of the Ming Dynasty, Zhu Youjian (the Chongzhen emperor) to commit suicide. A Manchu army from Manchuria was invited by the remaining Ming supporters to march on Beijing and kick the rebels out.
When did the Qing Dynasty retire?
An emperor’s retirement abode. The Qing Dynasty reached the height of its power under Hongli (the Qianlong emperor) who reigned 1736-1795. In 1795 , after ruling for 60 years, he officially retired as emperor so that the length of his rule would not surpass that of his grandfather.
What are some of the most famous Chinese myths?
Top 10 Chinese myths. To celebrate the Chinese new year, Moon Princess author Barbara Laban, shares her favourite mythological stories from China, from Sun Wukong the monkey king to how the Chinese zodiac began. Lin Hui the panda grabs traditional red packages to celebrate Chinese Lunar New Year which starts today and marks the year of the monkey. ...
What is the dragon in Chinese mythology?
The dragon. He clearly is a hero in Chinese mythology: the most powerful and divine creature, controller of the water. Dragons were the symbol of the emperor, bringing luck and good fortune. It is said that the legendary Yellow Emperor turned into a dragon and flew to heaven when he died.
How did Hou Yi become immortal?
Hou Yi had a potion to become immortal, but it was sufficient only for one. He did not want to part from his beloved wife Chang’e, so he made her look after the potion for him. One day when Hou Yi wasn’t home, his student Feng Meng tried to steal the potion from Chang’e. She knew she couldn’t defeat him, so she drank it. The potion made her fly all the way to the moon, where she is still today, watching the world. When the moon is the brightest, during the Chinese Moon Festival, you can try to spot her up there.
What is the name of the monster in Chinese New Year?
This is how the first Chinese New Year celebration started. The name of the monster, “Nian”, also means “year” in Chinese.
How were animals allocated to the Chinese zodiac?
Here is one popular version of how the animals were allocated to the Chinese zodiac: The Jade Emperor announced a race for all animals to compete for the twelve places in the Chinese zodiac. The rat was supposed to wake up her neighbour the cat in the morning, but simply forgot. The rat joined the other animals in the race to the palace, climbing on the ox , who was running in front, only to jump off when they had reached the palace to become the first animal of the zodiac. It was followed by the ox, the tiger, the rabbit, the dragon, the snake, the horse, the goat, the monkey, the rooster, the dog and the pig. The cat, however, arrived far too late and missed out. This is why the cat hates the rat so much that she will always try to kill her.
What is the name of the rabbit in the story of Chang'e?
3 The Jade rabbit. Many stories are told all over Asia about the Jade Rabbit. He became a companion of Chang’e and is often pictured next to her on the moon. He is closely associated with the medical profession, frequently shown carrying a mortar and pestle.
Why are guardian lions placed in temples?
7. Guardian lions. You might have seen them in front of houses, palaces or temples and they have been placed there because people believe in their protective powers. Often they come as a pair, the male holding a ball that represents the world under his paw, the female protecting a lion cub.
Where did Daoism originate?
Daoism is a philosophy, a religion, and a way of life that arose in the 6th century BCE in what is now the eastern Chinese province of Henan. It has strongly influenced the culture and religious life of China and other East Asian countries ever since.
What is the Daoist tradition?
For the article summary, see Daoism summary . Daoism, also spelled Taoism, indigenous religio-philosophical tradition that has shaped Chinese life for more than 2,000 years. In the broadest sense, a Daoist attitude toward life can be seen in the accepting and yielding, the joyful and carefree sides of the Chinese character, ...
What are the teachings of Daoism?
The Cosmic Dao, or the Way of the Cosmos, is an indeterminate force or principle that latently contains all things and spontaneously generates the universe through its constant rhythmic fluctuations.
What does "dao" mean in Chinese?
Its literal meanings include “way,” “path,” “road,” “course,” “speech,” and “method,” among others. Read more below: Dao: Meanings of dao.
What are the elements of the Chinese zodiac?
While Western astrology incorporates beliefs about the four elements of earth, air, fire, and water, the Five Elements of the Chinese zodiac are metal, water, wood, fire, and earth. An illustration of how the Five Elements interconnect with each other. The Five Elements impact the Chinese zodiac in several ways.
How long has Chinese astrology been around?
The practice of Chinese astrology dates back thousands of years . As authors Gerry Maguire Thompson and Shuen-Lian Hsaio write in The Guide to Chinese Horoscopes, for the first 2000 years of recorded Chinese history, there wasn’t really a line between what we consider astrology and the scientific study that we know as astronomy.
Who is the president of the Museum of the Chinese in America?
It’s the exact opposite,” Nancy Yao Maasbach, president of the Museum of the Chinese in America, tells OprahMag.com. You should actually be extra-careful during the year of your birth animal, Maasbach says, lest you attract an accident or other misfortune in what's believed to be a year of obstacles.
What is the Chinese legend 2020?
Lee write in the 2020 Pocket Chinese Almanac, an annual daily guide to our aforementioned collective fortune —such as which days are lucky and unlucky for weddings, planting seeds, and more. "They do, however, seem to agree on a couple of things: First, that a prominent Emperor (either Jade or Yellow, depending on your source) announced a great race, the order of 12 animals to be determined by their finishing time; and second, that the rat cheated.”
Overview
Important deities, spirits, and mythological people
There are various important deities, spirits, and mythological people in Chinese mythology and folk religion. Some are clearly divine, such as the Jade Emperor (and even he is sometimes said to have begun life as a mortal). However, in Chinese language many beings are referred to as shen. (Sometimes Chinese mythology is called 中國神話 – Mandarin Chinese: Zhōngguó Shénhuà). Due to the ambiguity of this word when translated into English, it is not always clear how to classify i…
Mythology and religion
There has been extensive interaction between Chinese mythology and Confucianism, Taoism, and Buddhism. Elements of pre-Han dynasty mythology such as those in Classic of Mountains and Seas were adapted into these belief systems as they developed (in the case of Taoism), or were assimilated into Chinese culture (in the case of Buddhism). Elements from the teachings and beliefs of these systems became incorporated into Chinese mythology. For example, the Taoist …
Mythology and philosophy
True mythology is distinguished from philosophical treatises and theories. Elaborations on the Wu Xing are not really part of mythology, although belief in five elements could appear. The Hundred Schools of Thought is a phrase suggesting the diversity of philosophical thought that developed during the Warring States of China. Then, and subsequently, philosophical movements had a complicated relationship with mythology. However, as far as they influence or are influenced by …
Mythology and ritual
Mythology exists in relationship with other aspects of society and culture, such as ritual. Various rituals are explained by mythology. For example, the ritual burning of mortuary banknotes (Hell Money), lighting fireworks, and so on.
A good example of the relationship of Chinese mythology and ritual is the Yubu, also known as the Steps or Paces of Yu. During the course of his activities in controlling the Great Flood, Yu was su…
Cosmology
Various ideas about the nature of the earth, the universe, and their relationship to each other have historically existed as either a background or a focus of mythologies. One typical view is of a square earth separated from a round sky by sky pillars (mountains, trees, or undefined). Above the sky is the realm of Heaven, often viewed of as a vast area, with many inhabitants. Often the heavenly inhabitants are thought to be of an "as above so below" nature, their lives and social arr…
Mythological and semi-mythological chronology
Mythological and semi-mythological chronology includes mythic representations of the creation of the world, population (and sometimes re-populations) by humans, sometimes floods, and various cultural developments, such as the development of ruling dynasties. Many myths and stories have been recounted about the early dynasties, however, more purely historical literature tends to begin with the Qin dynasty (for example, see Paladin 1998). On the other hand, accounts …
Creation myths
Various ideas about the creation of the universe, the earth, the sky, various deities and creatures, and the origin of various clans or ethnic groups of humans have circulated in the area of China for millennia. These creation myths may include the origins of the universe and everything, the origins of humans, or the origins of specific groups, such as a Han Chinese in descent from Yandi and Huangdi (as 炎黃子孫, "Descendants of the Flame and Yellow Emperors"). Various myths contai…