Is federalism really working after 200 years?
We have not seen any practical application of it for years. “Restoring the Constitution” is a phrase that is catching on with people as the influence of the tea party has grown. So is “federalism,” as people lament a national government that seems to have become out of control and is spiraling our nation into a downfall.
Why federalism is bad?
Federalism is not all bad, of course. In fact, it may help decrease partisan warfare. For Gerken, “federalism is a way to soften the problem of polarization by creating incentives for compromise ...
What was the era of dual federalism?
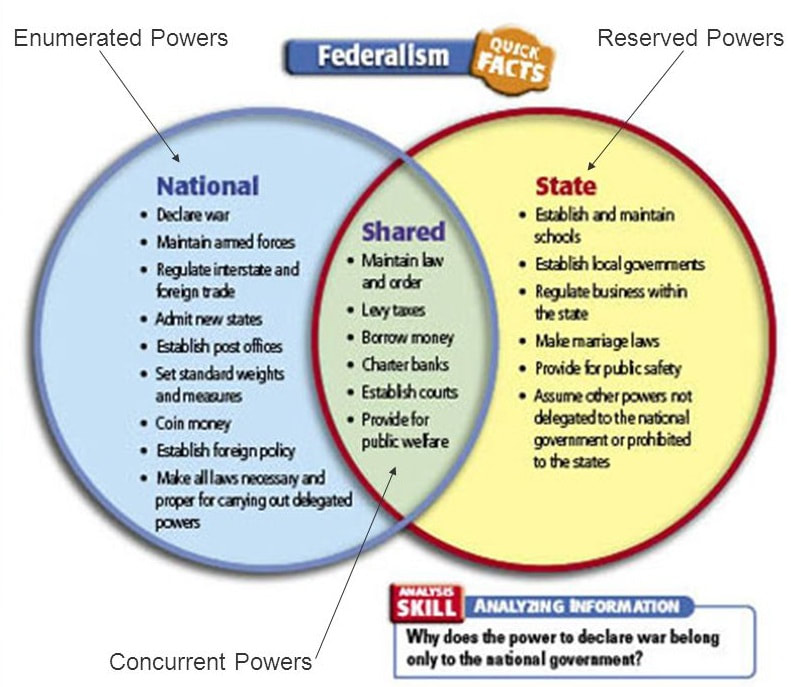
- Regulation of intrastate commerce
- Conduct elections
- Ratification of amendments to the U.S. Constitution
- To exercise powers neither delegated to the national government nor prohibited from the states by the Constitution as per Amendment X
- Property laws
- Inheritance laws
- Commercial laws
- Banking laws
- Corporate laws
- Insurance
What does dual federalism emphasize?
- dual federalism
- cooperative federalism
- pragmatic federalism
- non-centralized federalism
- nation-centered federalism
How long did dual federalism last?
The period from 1789 to 1901 has been termed the era of Dual Federalism. It has been characterized as an era during which there was little collaboration between the national and state governments.
Do we still have dual federalism?
As a direct result of American federalism, a dual court system exists within the United States today. There is a complete and independent federal court system, and there is a complete and somewhat independent state court system in every state.
Why did we move from dual federalism to cooperative federalism?
The United States moved from dual federalism to cooperative federalism in the 1930s. National programs would increase the size of the national government and may not be the most effective in local environments. Cooperative federalism does not apply to the Judicial branch of the government.
Which decade saw the shift from dual to cooperative federalism?
By the end of the second New Deal (1940), the era of dual federalism had clearly ended and the nation had moved into the era of cooperative federalism.
What ended dual federalism?
End of dual federalism The general consensus among scholars is that dual federalism ended during Franklin Roosevelt's presidency in 1937 when the New Deal policies were decided constitutional by the Supreme Court.
What type of federalism is the US today?
The United States operated under a Dual Federalism model from 1787 until about 1937 when the federal and state governments began to intersect, and sometimes conflict with one another. From about 1937 to the present, the United States has operated under a Cooperative Federalism model.
What type of federalism has been most common in the US since 1980?
New Federalism This form of federalism came about in the 1980s after Ronald Reagan was elected. In it, more power was returned to the states because the national government wanted to even out the balance of strength between state governments and the national government.
Why did cooperative federalism emerge in the 1930s?
Why did cooperative federalism emerge in the 1930s? The Great Depression forced the federal and state governments to work together for economic recovery.
Does cooperative federalism continue to exist today?
Yet cooperative subfederalism programs do exist. Particularly (but not only) in the realms of land use, environmental, and natural resources law, which are the primary focuses of this article, states often delegate authority to local governments while mandating state-level administrative oversight and review.
During which period of time has the United States had a system of dual federalism?
1789 to 1901Almost immediately upon its adoption, issues concerning state sovereignty and the supremacy of federal authority were hotly debated and ultimately led to the Civil War. The period from 1789 to 1901 has been termed the era of Dual Federalism.
What period of US history is commonly identified as the time when dual federalism gave way to cooperative federalism?
1954–78John Kincaid, for instance, has designated the time period of 1954–78 as the time frame for cooperative federalism in the United States. Since the late 1970's, there has been a swing toward the model of dual federalism, especially during Ronald Reagan's administration.
What model of federalism began in the 1930s?
Dual federalism was used in this country for a long time. However, by the 1930s, 'layer cake' federalism began to morph into 'marble cake' federalism. In the 1930s, the New Deal brought new federal legislation implementing several programs and policies geared toward reviving the economy.
What is dual federalism?
Dual federalism is both a theory of how a federal system should allocate governmental powers, responsibilities, and resources and an era of American political history. As a theory, dual federalism holds that the federal and state governments both have power over individuals but that power is limited to separate ...
What was the challenge of dual federalism?
Dual federalism faced a fatal challenge with the Industrial Recovolution. The Industrial Revolution allowed firms to amass great wealth and economic power, which some used to exploit workers and markets. Governments appeared to be the only force strong enough to counter these large firms.
What is the term for the period of American political history when the Constitution was interpreted as creating separate and distinct sphere
The era of dual federalism refers to the period of American political history when the Constitution was interpreted as creating separate and distinct spheres of authority between the federal and state governments. The practice of dual federalism was considerably messier than the theory of dual federalism.
What powers does the national government have over interstate commerce?
The national government’s authority over interstate commerce includes responsibility for currency, weights and measures, patents and copyrights, and bankruptcy laws. All other powers not defined in the Constitution or prohibited to the states, according to the Tenth Amendment, are reserved to the states.
Which convention was the first to recognize that states are sovereign entities?
Ogden (1824), Barron v. Baltimore (1833), and Dred Scott v. Sandford (1856). At the Hartford Convention of 1814 , New England representatives approved the idea that states exist as sovereign entities with rights that could not be violated by the national government.
Who was the first president to argue that the nation needed a stronger national government?
In 1901 President Theodore Roosevelt argued that national interests had become too decentralized and the nation needed a stronger national government to protect the common man. Roosevelt laid the foundation for ending dual federalism. Over the next three decades, dual federalism decayed. National government grants to state ...
Who is trying to restore dual federalism?
Some claim that the Supreme Court, under the direction of Chief Justice William Rehnquist, is trying to restore dual federalism, particularly in its reading of the Eleventh Amendment.
Overview
Dual federalism, also known as layer-cake federalism or divided sovereignty, is a political arrangement in which power is divided between the federal and state governments in clearly defined terms, with state governments exercising those powers accorded to them without interference from the federal government. Dual federalism is defined in contrast to cooperative federalism ("marble-cake federalism"), in which federal and state governments collaborate on pol…
United States
The system of dual/joint federalism in the United States is a product of the backlash against the Articles of Confederation, ratified in 1781, which established a very weak federal government with the powers to declare war, make treaties, and maintain an army. Fueled by Shays' Rebellion and an economy faltering under the inability of the federal government to pay the debt from the American Revolution, a group later known as the Federalists generated support for a strong central govern…
Outside the United States
The governments of Argentina, Austria, Australia, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Canada, Comoros, Ethiopia, Germany, India, Malaysia, Mexico, Micronesia, Nepal, Nigeria, Pakistan, Russia, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Spain, Switzerland, United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela also operate through federalism. The federations of Australia, Canada, and Switzerland most closely resemble the model of American dual federalism in which fundamental governmental powers are divided bet…
Origins of "layer cake" metaphor
In his second term, President Dwight D. Eisenhower organized the Commission on National Goals to broadly outline national objectives. Included in their 1960 report Goals for Americans: The Report of the President's Commission on National Goals was "The Federal System", a report by political scientist Morton Grodzins. In this report, Grodzins first coined the terms "layer cake federalism" and "marble cake federalism." He used the metaphor of a layer cake to describe the system of d…
See also
• Federalism
• Federalism in the United States
• Anti-Federalism
• Cooperative federalism
Footnotes
1. ^ Boyd, Eugene; Michael K. Fauntroy (2000). "American Federalism, 1776 to 2000: Significant Events". Congressional Research Service. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
2. ^ Articles of Confederation : March 1, 1781. The Avalon Project. http://avalon.law.yale.edu/18th_century/artconf.asp
3. ^ Lowi, et al. (2012) American Government: Power and Purpose -- Brief Twelfth Edition. W.W. Norton and Company p.26-27
Further reading
Elazar, Daniel J. The American Partnership: Intergovernmental Cooperation in the Nineteenth-Century United States. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1962.
Mallat, Chibli Federalism in the Middle East and Europe 35 Case W. Res. J. Int'l L. 4 (2003).
Montinola, Gabriella, Qian, Yingyi and Weingast, Barry R. Federalism, Chinese Style: The Political Basis for Economic Success in China World Politics, Vol. 48, No. 1 (Oct., 1995), pp. 50–81.