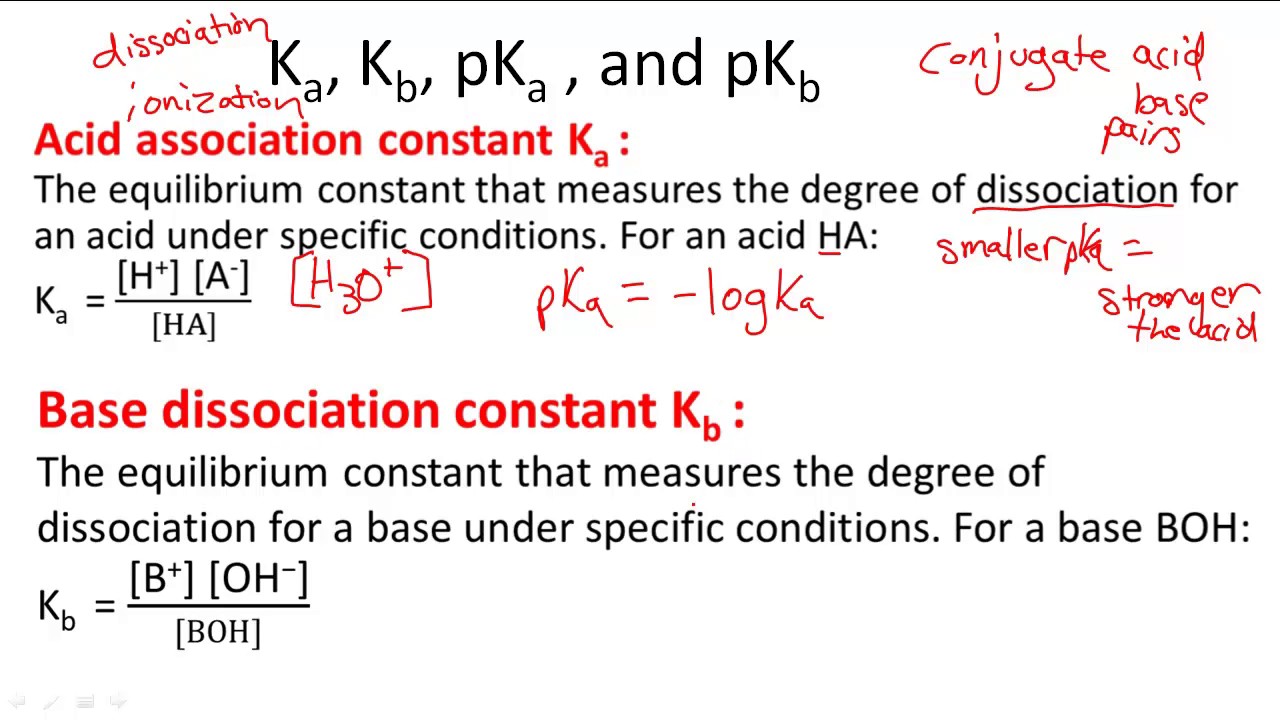
- Ka = [H+] [A-]/ [HA]
- pKa = - log Ka
- at half the equivalence point, pH = pKa = -log Ka
How do you calculate pKa from Ka?
- The [H30+] ion concentration for a solution with pH= 4.7is
- = 10^-4.7 =1.9957 x 10^ -5
- ~= 2 x 10^-5
- The [OH-] ion concentration for the above solution
- [OH-] = 1 x 10^-14) ÷ (1.9957 x 10^-5)
- [OH-] = 5.0119 x 10^-10
- ~= 5 x 10^-10
How to find pKa from Ka?
pH, pKa, and Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- The pKa is the pH value at which a chemical species will accept or donate a proton.
- The lower the pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater the ability to donate a proton in aqueous solution.
- The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates pKa and pH. ...
How are ka and pKa related?
Ka is acid dissociation constant and represents the strength of the acid. pKa is the -log of Ka, having a smaller comparable values for analysis. They have an inverse relationship. Larger the Ka, smaller the pKa and stronger the acid. Click to see full answer. Just so, is pKa the same as ka?
How do you calculate pKa?
pKa: pKa is the negative value of the logarithmic of Ka. pH: pH is the logarithmic value of the inverse of H+ concentration. pKa: pKa indicates whether an acid is a strong acid or a weak acid. pH: pH indicates whether a system is acidic or alkaline.
What is relation between Ka and pKa?
More precisely – pKa is the negative log base ten of the Ka value (acid dissociation constant). It measures the strength of an acid — how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid. The lower the value of pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater its ability to donate its protons.
What is the difference between pH and Ka and pKa?
A “p” in front of a value also indicates the -log of the value. So, pH is the negative log of hydrogen ion concentration, while pKa is the negative log of the Ka value. The capital letter “K” stands for a constant. In this case, it refers to the equilibrium constant.
What does Ka and pKa tell you about an acid?
3:095:49pKa, Ka, and Acid Strength - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe said that as the pKa decreases in value the acid strip which I'm going to write a s increases inMoreWe said that as the pKa decreases in value the acid strip which I'm going to write a s increases in value now what about the relationship between ka. And acid strength it turns out that there is a
What does Ka value mean?
acid dissociation constantThe acid dissociation constant (Ka) is used to distinguish strong acids from weak acids. Strong acids have exceptionally high Ka values. The Ka value is found by looking at the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the acid. The higher the Ka, the more the acid dissociates.
How do you go from pKa to Ka?
To create a more manageable number, chemists define the pKa value as the negative logarithm of the Ka value: pKa = -log Ka. If you already know the pKa value for an acid and you need the Ka value, you find it by taking the antilog. In practice, this means raising both sides of the equality to exponents of 10.
What is the relationship between Ka and pH?
In other words, Ka provides a way to gauge the strength of an acid. Larger values signify stronger acids. The pH (power of hydrogen) of a solution is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions and is also a measure of acidity, but it isn't the same as Ka.
How does Ka determine strength of acid?
The higher Ka is, the more easily the acid dissociates, and the stronger it is (i.e. the weaker the base it is, and the less strongly its bonds are held together by electron donation).
What does the pKa tell you?
The pKa measures how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid. A pKa may be a small, negative number, such as -3 or -5. It may be a larger, positive number, such as 30 or 50. The lower the pKa of a Bronsted acid, the more easily it gives up its proton.
What does the pKa of an indicator tell you?
Consequently, the pKa of an indicator corresponds to the pH of the solution at the inflection point in a plot of absorbance as a function Page 2 of pH as shown in Figure 1. Note, however, that it is critical that the absorbance at each wavelength corresponds to the absorbance of only HIn at λ1 and only In- at λ2.
What does pKa stand for?
PKAAcronymDefinitionPKAPreviously Known AsPKAProtein Kinase APKAIonization Constant (chemistry, kinetics)PKAPainkiller Already18 more rows
Is pK and pKa the same?
pKa does not mean the same thing as pK: pKa is just one of three measures of pK. In chemistry, K is the dissociation constant (for acids ...
How do you calculate Ka from pH?
2:104:48Find the Ka of an acid (Given pH) (0.1 M Hypochlorous acid) EXAMPLEYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBecause you're given the pH. You already know what the concentration of h+ is the way you can getMoreBecause you're given the pH. You already know what the concentration of h+ is the way you can get the concentration of h+ is that it's 10 to the power of the negative ph in this case 10 to the power
How do you calculate the Ka of an acid? + Example - Socratic
K_a applies to weak acids in aqueous solution For a hypothetical weak acid HA rightleftharpoons H^+ + A^- K_a = (([H^+][A^-])/[HA]) where [H^+], [A^-] & [HA] are ...
7.12: Relationship between Ka, Kb, pKa, and pKb
The magnitude of the equilibrium constant for an ionization reaction can be used to determine the relative strengths of acids and bases. For example, the general equation for the ionization of a weak acid in water, where HA is the parent acid and A− is its conjugate base, is as follows:
What is the difference between pKa and Ka?
I know that pKa= -log Ka and Ka= 10^ (-pKa), but when do we use pKa and Ka?
Re: What is the difference between pKa and Ka?
Ka is most frequently used in problems in which you are asked to calculate pH and pOH because Ka = [H30+] [A-] / [HA], where HA is an acid and A- is the conjugate base. pKa is simply another way of reporting Ka but is not often used in problems. The same goes for Kb and pKb.
What does pKa mean?
So, pKa is the -log of (Ka). A larger Ka means a smaller pKa. For pH, we are taking the -log of the [H+] concentration. A greater concentration of protons means a smaller pH.
What does ka mean in water?
Ka = dissociation value for a compound in water; relationship with pKa is: high Ka value indicates that something dissociates in H20 well, inversely, a low pKa value indicates that the compound in question dissociates in H20 well.
What does PI mean in chemistry?
pI is the isoelectric point of a molecule, usually a protein or amino acid. the pI of a molecule indicates that the compount carries no net charge. for something to have a defined pI, the compound must have negative and positive functional groups (amphoteric). hope this helps.
What does Ka measure?
Ka is the only true "measurement". It measures the strength of an acid. A stronger acid will have a greater [H+] concentration and hence a greater Ka. Any time you see a "p" in terms of acid-base chemistry, it automatically signifies -log (whatever is after p).
Is an amino acid acidic or basic?
Heres a little side note that I found useful, for amino acids when the pH of the surrounding is lower than the pI of the amino acid, then the substance is acidic (holds + charge), if the pH is higher than the PI then the substance is basic.