Eudicot roots lack xylem and phloem, whereas monocot roots have both xylem and phloem. c. In eudicots, the xylem and phloem are at the periphery, whereas in monocots
Monocotyledon
Monocotyledons, commonly referred to as monocots, are flowering plants, the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided, the rest of the flowerin…
Full Answer
What is the difference between monocot and dicot roots?
• Dicot roots have tap roots with lateral roots, whereas monocot root has adventitious root system, lacking a tap root. • Monocot roots do not have secondary growth, while dicot roots have two growth phases. • In secondary growth dicot roots have vascular cambium and cork cambium, which originate from the cells of pericycle and conjunctive tissues, whereas monocot roots lack those.
How many petals do dicots have?
The number of petals on a flower can give an indication of the classification of a plant. For example, the flowers of the eudicots (the largest group of dicots) usually have four or five petals, while the flowers of the monocots have three or six petals, although there are many exceptions to this rule.
What are the characteristics of a monocot?
The features of the monocotyledonous are the following:
- Embryo with a single cotyledan.
- Pollen with a single furrow or pore.
- Flower parts in multiple of three.
- Major leaf veins parallel.
- Stem vacular bundles scattered.
- Roots are adventitious.
- Secondary growth absent.
What are some examples of monocots and dicots?
The examples of dicot fruits are as follows:
- Apple (Malus pumila)
- Chinese date (Ziziphus mauritiana)
- Grape (Vitis vinifera)
- Guava (Psidium guajava)
- Java plum (Syzygium cumini)
- Litchi (Litchi chinensis)
- Mango (Mangifera indica)
- Papaya (Carica papaya)
- Pomegranate (Punica granatum)
- Sapodilla (Manilkara zapota)
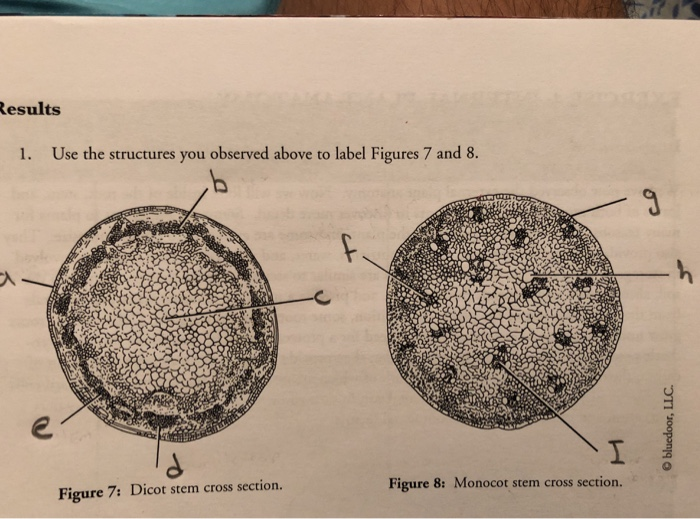
What was the major difference you observed between the monocot and dicot stem cross sections?
The main difference between monocot stem and dicot stem is that monocot stem contains scattered vascular bundles across the stem whereas dicot stem contains vascular bundles arranged in the form of one or two rings. Monocot stem and dicot stem are the two types of stem structures in flowering plants.
How do monocot and eudicot stems differ from one another?
The key difference between eudicot and monocots relies on the number of apertures in their pollens. Eudicots have three apertures in the pollen while monocots have one aperture in the pollen. Moreover, eudicots produce two cotyledons in their seedlings while monocots produce one cotyledon in their seedlings.
Which of the following is characteristic of a monocot stem cross section?
The answer is (a) Vascular bundles that are spread evenly among the parenchyma. (a) Vascular bundles that are spread evenly among the parenchyma.
What are the differences between monocots and eudicots quizlet?
A monocot means that there is only one seed leaf. In a dicot, it means there are two seed leaves in the embryo. In a monocot, there is only one cotyledon, and in a eudicot there is two.
Which of the following characteristics can be used to differentiate between monocots and eudicots?
The characters which distinguish the classes.MONOCOTSDICOTSEmbryo with single cotyledonEmbryo with two cotyledonsPollen with single furrow or porePollen with three furrows or poresFlower parts in multiples of threeFlower parts in multiples of four or fiveMajor leaf veins parallelMajor leaf veins reticulated6 more rows
What traits are characteristic of eudicots quizlet?
Eudicots: have two cotyledons, flower parts are in four or fives or multiples of four or fives, leaf veins form a net pattern, and vascular bundles arranged in a ring.
How are the xylem and phloem arranged in a eudicot root?
In dicot roots, the vascular structures are located in the middle of the root. The arrangement of xylem and phloem is different in dicots than it is in monocots. The xylem is all located in the middle of the dicot root, and bundles of phloem are arranged around it, separated from it by vascular cambium.
What is a characteristic of a monocot?
Monocot plants are marked by seeds with a single cotyledon, parallel-veined leaves, scattered vascular bundles in the stem, the absence of a typical cambium, and an adventitious root system.
What is a monocot stem?
Monocot stems are a circular-shaped stem with lateral branches and are bounded with a layer of dermis. It is mainly composed of hard, organised, rectangular cells coated with a waxy substance known as cutin.
What is the structure of a dicot stem?
Dicot stems have a well-defined epidermis with cuti cle, a layer of dermis along with multicellular stem hair. The internal structure of a dicot stem mainly consists of epidermis, hypodermis, cortex endodermis, pericycle, vascular strand and pith. Sunflower and Cucurbita are examples of dicot stems.
What are dicotyledons? What are some examples?
Dicotyledons or dicots are generally referred to the flowering plants or angiosperms in which the seeds typically contain two embryonic leaves or cotyledon. All legumes such as beans, lentils, pea, and peanuts are examples of dicotyledons. There are around 1.0 – 1.5 lakh species of dicot plants.
What are some examples of monocotyledons?
Monocotyledons or monocots commonly refer to the flowering plants or angiosperms in which the seeds typically contain only one embryonic leaf or cotyledon. Ginger, onions, wheat, and grass are the best examples of Monocotyledons.
Why are vascular bundles open?
The vascular bundles always remain open, due to the presence of cambium within phloem and xylem. The vascular bundles are closed. Dicot stem can feature secondary growth as a result of secondary vascular tissues and periderm formation. No secondary growth is witnessed in case of monocots.
Do vascular tissues stop working?
Usually, vascular tissues stop functioning when they get old. New vascular tissues replace the old ones. Vascular tissues remain the same throughout the plant’s life cycle. Learn more about Dicot and Monocot plants, the difference between monocot and dicot stem, or any other related topics only at BYJU’S Biology.
Does epidermal hair exist?
Epidermal hair may or may not exist. Presence of epidermal hair. Vascular bundles are less in number and are of uniform size. There are numerous vascular bundles of different sizes. The dicot stem does not have a bundle sheath on the outside of a vascular bundle.