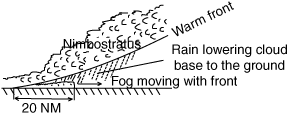
The correct answer is C. Fog is a cloud that begins within 50 feet of the surface. Both advection and upslope fog require wind to form. (Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge, page 11-15)
What are the two types of fog?
Advection fog forms due to moist air moving over a colder surface, and the resulting cooling of the near-surface air to below its dew-point temperature. Advection fog occurs over both water (e.g., steam fog) and land. (2) Radiation fog (ground or valley fog). Radiational cooling produces this type of fog.
What type of weather causes fog to form?
This saturation forms fog. Advection Fog:This type of fog forms from surface contact of horizontal winds. This fog can occur with windy conditions. Warm air, moist air blows in from the south and if there is snow or cool moisture on the ground it will come in contact with the warm, moist winds.
What type of air is involved in sea fog?
Warm, moist air that is cooled to saturation as it moves over cold water forms sea fog: • If the initial dew point is less than the coldest water temperature, sea fog formation is unlikely. In poleward-moving air, or in air that has previously traversed a warm ocean current, the dew point is usually higher than the cold water temperature.
What is the difference between freezing fog and valley fog?
Valley Fog:Valley fog forms in the valley when the soil is moist from previous rainfall. As the skies clear solar energy exits earth and allow the temperature to cool near or at the dew point. This form deep fog, so dense it's sometimes called tule fog. Freezing Fog:Freezing fog occurs when the temperature falls at 32°F (0°C) or below.
How does wind affect fog?
Fog requires a mixing action by wind; without wind, dew will appear instead of fog. If the surface is near saturation, a light wind will allow for the layer of air near the surface to remain near saturation. High wind speeds cause a mixing of air at the surface and higher into the atmosphere.
What are the 6 types of fog?
6 Different Names For FogRadiation Fog. Radiation fog needs clear skies and calm winds to form. ... Advection Fog. Advection fog looks like ground fog, but it forms a little bit differently. ... Evaporation Fog. Evaporation fog is relatively common, and it forms in one of two ways. ... Upslope Fog. ... Freezing Fog. ... Hail Fog.
What are the 4 types of fog?
There are several different types of fog, including radiation fog, advection fog, valley fog, and freezing fog. Radiation fog forms in the evening when heat absorbed by the Earth's surface during the day is radiated into the air.
What type of fog will persist until the direction of the wind changes?
Upslope fog often forms with moderate winds and it can persist for several days until there is a change to a drier air mass or the wind direction changes.
What are 5 types of fog?
This process is similar to how clouds at higher altitudes form as well. The different types of fogs we will discuss in this blog are: Radiation Fog, Advection Fog, Freezing Fog, Evaporation Fog and Mountain/Valley Fog. This type of fog is the one of most common in the country, especially in the fall and winter.
What is the most common type of fog?
Radiation FogRadiation Fog – This is the most common type of fog and is caused by clear and calm conditions, usually after a rainfall where the ground is fairly moist. With no clouds to prevent radiation from escaping, the temperature quickly falls to the dew point, saturates, and forms fog.
Where does advection fog occur?
Advection fog occurs when moist, warm air passes over a colder surface and is cooled. A common example of this is when a warm front passes over an area with snow cover. It is also common at sea when moist tropical air moves over cooler waters.
How is advection fog formed?
Advection fog forms as warmer, moist air moves over a cold ground. The air is cooled to saturation by the cold from the ground below cooling the air above. Unlike radiation fog, advection fog may form under cloudy skies and with moderate to strong winds.
What is an evaporation fog?
Evaporation fog (or cold advection fog) is formed when cold, stable air moves over a much warmer body of water. Evaporation from the warm body of water saturates the cold air above; water vapour condenses in the cold air producing “steam fog” or “sea smoke”, or, in polar regions, “Arctic sea smoke”.
What is a radiation fog?
Radiation fog is a very common type of fog throughout the United States. It is most prevalent during the fall and winter. It forms overnight as the air near the ground cools and stabilizes. When this cooling causes the air to reach saturation, fog will form.
What two kinds of fog are the result of adding moisture to a layer of air?
What two kinds of fog are the result of adding moisture to a layer of air? Steam and frontal.
How is steam fog formed?
(4) Steam fog (arctic sea smoke). In northern latitudes, steam fog forms when water vapor is added to air that is much colder, then condenses into fog. It is commonly seen as wisps of vapor emanating from the surface of water.
What is the normal approach in calm wind?
The normal approach in calm wind is a left hand pattern to runway 08. There is no other traffic at the airport. A thunderstorm about 6 miles west is beginning its mature stage, and rain is starting to reach the ground. The pilot decides to.
What causes an airplane to become airborne?
c) frost may cause the airplane to become airborne with a lower angle of attack at a lower indicated airspeed. a) frost may prevent the airplane from becoming airborne at normal takeoff speed. An almond or lens-shaped cloud which appears stationary, but which may contain winds of 50 knots or more, is referred to as.