Which economic system is used in Brazil?
The main countries to which Brazil exports in 2019 were:
- China - U $63.4 billion
- United States - U $29.7 billion
- Netherlands - U $10.1 billion
- Argentina - U $9.8 billion
- Japan - U $5.4 billion
- Chile - U $5.2 billion
- Mexico - U $4.9 billion
- Germany - U $4.7 billion
- Spain - U $4 billion
- South Korea - U $3.4 billion.
What type of economic system does Brazil have?
The Economy Of Brazil
- Overview Of The Economy Of Brazil. Brazil has a GDP of $3.2 trillion and a nominal GDP of $2.0 trillion. ...
- Leading Industries Of Brazil. ...
- Top Exports And Export Partners Of Brazil. ...
- Top Imports And Import Partners Of Brazil. ...
- Challenges To Brazil’s Economy. ...
What type of economy is Brazil's like?
Brazil is one of the countries referred to as BRICS, together with Russia, Indian, China, and South Africa, which are regarded as the five primary emerging global economies. The country's economy is inward-oriented, and it is marked by moderate free markets. Overview Of The Economy Of Brazil
Is Brazil a traditional economy?
Yet within many countries – be they classified as communist, capitalist, or socialist in terms of their economic systems – have pockets inside them that operate as traditional economies. One example is Brazil, a country whose primary economy is a mix of state-run and market-determined forces.
Is Brazil a command or market economy?
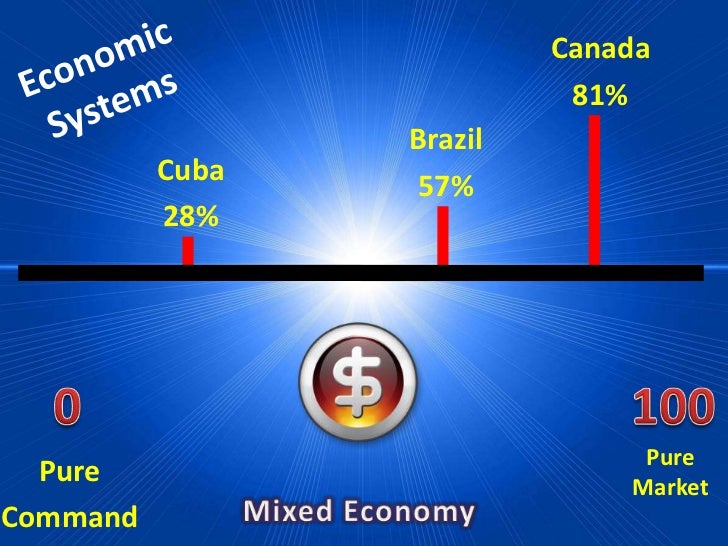
Brazil's economy is classified as a mixed economy, showing aspects of a command system and a market system.
Is Brazil a capitalist economy?
By Juan de Onís. In the past decade, Brazil has entered the first stages of a modern capitalist reorganization. Its economic transition has been gradual, but the country has avoided crippling setbacks.
What type of capitalism is Brazil?
Brazil's bursting economy may be under tighter state control than any economy outside the Communist countries. It is capitalism, sure enough—in some respects even “buccaneer capitalism,” as one of its architects has described it—but it is increasingly a state‐directed capitalism.
Is Brazil a capitalist state?
Brazil is a main exemplar of contemporary pursuit of state capitalism by a Western economy. Major SOEs have survived the prior wave of privatizations, but they are by no means the only avenue for state influence over corporate governance in Brazil.
What is the economy of Brazil?
Brazil has the largest economy in Latin America and the world’s ninth largest economy by nominal GDP and the seventh largest by Purchasing Power Parity (PPP).
What is the GDP of Brazil?
Brazil has a GDP of $3.2 trillion and a nominal GDP of $2.0 trillion. The nominal GDP is ranked 9th and 7th by PPP. The country recorded a GPD growth rate of -3.7% in 2015 and -4.0% in 2016 and it is projected to grow by -0.2% in 2017.
What was the inflation rate in Brazil in 2015?
Brazil experienced an inflation rate of 7.27% in 2015, while 15.4% of the population lives below the poverty line. The country’s unemployment rate is 7.5%, and it ranked 126th in regards to ease of doing business.
Why is unemployment so high in Brazil?
Unemployment has also risen significantly in the country as the cost of living continues to increase. The wealth gap has become a reality in Brazil as 10% of the population control over 40% of the country’s wealth. This situation has led to the sprawling of favelas (slums) in metropolises. Inadequate infrastructure in the country makes it difficult ...
Which countries are part of the BRICS?
Brazil is one of the countries referred to as BRICS, together with Russia, Indian, China, and South Africa, which are regarded as the five primary emerging global economies. The country’s economy is inward-oriented, and it is marked by moderate free markets.
Is Brazil in recession?
Brazil has been undergoing a recession since 2014, before which it was the sixth largest economy in the world. The country’s exports have been decreasing in key markets such as China. As Brazil’s budget deficit increases so does public spending which remains a challenge to be reduced.
What are the main exports of Brazil?
In 2019, Brazil exported close to U $ 225 billion and imported U $ 177 billion, with a surplus of U $ 48 billion. The country's top ten export products were: 1 Soy - represented 12% of the country's exports, at a value of U $ 26 billion. 2 Oil - 11% of exports, at a value close to U $ 24 billion. 3 Iron ore - Almost 10% of Brazil's exports, at a value of U $ 22 billion. 4 Pulp - 3.4% of exports, at a value of U $ 7.5 billion. 5 Corn - 3.3% of national exports, worth U $ 7.3 billion. 6 Beef - Almost 3% of Brazilian exports, totaling U $ 6.5 billion. 7 Chicken meat - 2.8% of the country's exports, at a value of U $ 6.3 billion. 8 Soybean meal - 2.6% of Brazilian exports, worth U $ 5.8 billion. 9 Sugar - 2% of exports, at a value of U $ 4.6 billion. 10 Coffee - 2% of exports, at a value of U $ 4.5 billion.
What was the economy of Brazil during the Stone Age?
When the Portuguese explorers arrived in the 16th century, the native tribes of current-day Brazil totaled about 2.5 million people and had lived virtually unchanged since the Stone Age. From Portugal's colonization of Brazil (1500–1822) until the late 1930s, the Brazilian economy relied on the production of primary products for exports. In the Portuguese Empire, Brazil was a colony subjected to an imperial mercantile policy, which had three main large-scale economic production cycles – sugar, gold and from the early 19th century on, coffee. The economy of Brazil was heavily dependent on African slave labor until the late 19th century (about 3 million imported African slaves in total). In that period Brazil was also the colony with the largest number of European settlers, most of them Portuguese (including Azoreans and Madeirans) but also some Dutch (see Dutch Brazil ), Spaniards, English, French, Germans, Flemish, Danish, Scottish and Sephardic Jews .
How does agribusiness contribute to Brazil's trade balance?
Agribusiness contributes to Brazil's trade balance, in spite of trade barriers and subsidizing policies adopted by the developed countries. In the space of fifty five years (1950 to 2005), the population of Brazil grew from 51 million to approximately 187 million inhabitants, an increase of over 2 percent per year.
What countries did Brazil come from?
Subsequently, Brazil experienced a period of strong economic and demographic growth accompanied by mass immigration from Europe, mainly from Portugal (including the Azores and Madeira), Italy, Spain, Germany, Poland, Ukraine, Switzerland, Austria and Russia.
How many kilometers of roads does Brazil have?
Brazil has at least 161,500 kilometers of paved roads, more than 150 gigawatts of installed electric power capacity and its real per capita GDP surpassed US$9,800 in 2017. Its industrial sector accounts for three-fifths of the Latin American economy's industrial production.
How much did poverty increase in Brazil in 2017?
According to data from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, extreme poverty had increased by 11 per cent in 2017, while inequalities also increased again (the Gini index rose from 0.555 to 0.567). The increase of informal work would be the leading cause, according to economists.
What is the GDP of Brazil in 2020?
According to International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimates, Brazil's 2020 nominal GDP was R$7.348 trillion or US$1.363 trillion. Brazil is the 83rd country in the world in GDP per capita, with a value of US$6,450 per inhabitant. The country is rich in natural resources .
What is Brazil's economic freedom score?
Brazil’s economic freedom score is 53.4, making its economy the 143rd freest in the 2021 Index. Its overall score has decreased by 0.3 point, primarily because of a decline in trade freedom. Brazil is ranked 24th among 32 countries in the Americas region, and its overall score is below the regional and world averages.
What is the largest rain forest in Brazil?
Brazil, the world’s fifth-largest country, has a mostly coastal population of more than 200 million and is dominated geographically by the Amazon River and the world’s largest rain forest. In 2018, after a long period of political chaos prompted by massive public corruption scandals and economic crises, voters elected Jair Bolsonaro of the Social Liberal Party to serve as president. Bolsonaro has generally pursued a free-market agenda, including an overhauling of the public pension system and privatization of government assets. However, his fractious relationships with many parties in Congress could delay enactment of his proposal to reform Brazil’s complex tax system, which is one of the most burdensome among emerging economies, consuming about 33 percent of gross domestic product.
Why should the government improve its judicial effectiveness?
In addition to reining in the budget deficits that are driving up debt and have led to one of the world’s lowest fiscal health scores, the government must improve in the areas of judicial effectiveness and government integrity if it hopes to get back on the path to greater economic freedom.
What percentage of GDP is public debt?
Public debt is equivalent to 89.5 percent of GDP.
Is electricity more expensive in Brazil?
Obtaining electricity has become more expensive and complicated. It also takes longer to obtain a connection. The cost of dealing with construction permits has increased. Reforming Brazil’s onerous labor laws is one of the Bolsonaro government’s objectives. The government provides massive subsidies for the production of sugar and other agricultural products in addition to subsidies for hundreds of state-owned enterprises.
What is the largest economy in South America?
Brazil is the largest economy in South America. It is also the eighth largest in the world. 1 In 2019, it produced $3.22 trillion in goods and services, as measured by purchasing power parity. 2 It allows you to compare the gross domestic product of countries that use different exchange rates.
How did Lula strengthen Brazil's economy?
Despite his corruption, Lula played a critical role in strengthening Brazil's economy. He helped build a left-wing party that governed Brazil for over 13 years. He is the son of illiterate farm workers. He became a union leader who stood up to Brazil’s military dictators.
What was the effect of the stop go monetary policy on the economy in the 1970s?
As a result, consumers cut back their spending. This is the same type of stop-go monetary policy combined with wage-price controls that caused U.S. stagflation in the 1970s.
What happened to Brazil during the recession?
Brazil's Recession. When Dilma Rousseff became president in 2011, she increased public spending. She raised the minimum wage and forced the state-run banks to lend more. At the same time, the central bank lowered the discount rate near the end of 2011. 9 This triggered inflation, which Rousseff aggravated by cutting sales taxes ...
How did Lula's spending affect the economy?
Lula's spending aggravated some of the economy's fundamental flaws. The public sector needed to be streamlined to allow public debt to be further lowered without losing services. Education needed to be both more of a priority and more evenly distributed.
When did Brazil pay off its debt?
Brazil's final payment of $15.46 billion was made in December 2005. 14 The funds came from Brazil's monetary reserves.
Who was the president of Brazil in 2018?
In 2018, frustration with the liberal government led to the election of conservative Jair Bolsonaro as president. He promised to allow police to kill suspected criminals. He agreed civilians should be armed for self-defense. 5 In 2017, Brazil had 64,000 murders. 6
What is Brazil's economy?
Brazil Economy at a Glance. Brazil has a moderate free market and export-oriented economy. Measured nominally, its Gross Domestic Product surpasses a trillion dollars, the tenth in the world and the third in the Americas; measured by purchasing power parity, $3.8 trillion, making it the eighth largest economy in the world and ...
What are Brazil's economic organizations?
Brazil is a member of diverse economic organizations, such as Mercosur, SACN, G8+5, G-20 and the Cairns Group.
What are the natural resources of Brazil?
Brazil has abundant natural resources and its economy is relatively diversified. Brazil is a huge agricultural power: it is the world’s largest producer of coffee, sugarcane and oranges; this attracts numerous international food processing groups. Agriculture accounts for 10% of GDP (30% when including agri-businesses) and 40% of Brazilian exports. Brazil has the world's largest commercial cattle herd (50% larger than the U.S.). Forests cover half of Brazil, with the largest rain forest in the world located in the Amazon Basin. Being a big industrial country, Brazil benefits from its abundant mineral resources: it is the 2nd largest exporter of iron in the world and one of the main aluminum producers. The country is now increasingly standing out in sectors like textile, aircraft, pharmaceuticals, cars, steel and chemicals. Most of the big automobile manufactures have established their production facilities in Brazil. The industrial sector contributes nearly 37% to the GDP, while as the service sector contributes around 52%.
What are Brazil's main trade partners?
[6] . Brazil's main trade partners are: the EEC (26% of trade), the United States (24%), Mercosur and Latin America (21%) and Asia (12%).
Is Brazil a pioneer in oil?
It is also a pioneer in many fields , including ethanol production. Brazil is also a pioneer in the fields of deep water oil research from where 73% of its reserves are extract ed.According to government statistics, Brazil was the first capitalist country to bring together the ten largest car assembly companies inside its national territory.
What is the legislative branch of Brazil?
The legislative branch of government is administered by the National Congress and is responsible for writing and approving new laws. The Federal Senate and the Chamber of Deputies make up the National Congress.
How long does the President of Brazil serve?
The President of Brazil is elected by the general population to serve a 4-year term , limited to 2 consecutive terms. However, a President who has served two consecutive terms may run for office in the future with a lapse of 4 years. The person in this office is in charge of the executive branch of government and is the Commander-in-Chief of the military forces. The President appoints members to the Cabinet and judges to the Supreme Court. The judge appointments must be approved by the Senate. The President is also able to propose new laws to the National Congress or enact provisional laws in cases of emergency. These provisional laws are effective for between 60 and 120 days and Congress can vote to make them permanent laws. In addition to the domestic duties of the office, the President also represents Brazil in international affairs.
Who is the executive branch of government?
The executive branch of government is headed by the President and administered by the Cabinet of Ministers. These members are appointed by and can be dismissed by the President. The Cabinet consists of the Chief of Staff, Secretary of Government, Institutional Security Cabinet, Central Bank, and 21 Ministries.
Is Brazil a democratic country?
The government of Brazil is considered a federal representative democratic republic, under a presidenti al system. Under this system, the President is both the Head of State and the Head of Government. Multiple political parties are represented throughout the government and its administration.
Overview of The Economy of Brazil
Leading Industries of Brazil
- The service sector in Brazil is dominated by hospitality, retail sales, financial services, professional services, and information technology. The primary products dominating the agriculture industry in Brazil are soybeans, corn, beef, sugar, wheat, cocoa, rice, chicken, and citrus. The major industries in the country are textiles, cement, petroleum processing, aerospace…
Top Exports and Export Partners of Brazil
- Brazil is ranked 23rd largest export economy in the world. The leading export goods are transport equipment, soybeans, sugar, iron ore, crude petroleum, coffee, footwear, poultry meat, and automobiles. The top export partners are Chin, taking 18.6% of the total exports; US accounts for 12.7% of all exports while Argentina accounts for 6.7%, and the Netherlands 5.3%.
Top Imports and Import Partners of Brazil
- Brazil is the world’s 19th largest importing economy. The country’s top imports are machinery, refined and crude petroleum, chemicals, motor vehicle parts, transport equipment, and electronics. Brazil’s top import partners are China accounting for 17.9% of all imports, US accounts for 15.6 of imports, Germany accounts for 6.1%, while Argentina is 6...
Challenges to Brazil’s Economy
- Brazil has been undergoing a recession since 2014, before which it was the sixth largest economy in the world. The country’s exports have been decreasing in key markets such as China. As Brazil’s budget deficit increases so does public spending which remains a challenge to be reduced. The country’s debt is serviced by 7% of GDP, and the country has been unable to pay creditors since t…
Overview
The economy of Brazil is historically the largest in Latin America and the Southern Hemisphere in nominal terms. The Brazilian economy is the third largest in the Americas. The economy is a middle income developing mixed economy. In 2022, according to International Monetary Fund (IMF), Brazil is the 10th largest in the world by nominal gross domestic product (GDP) and 9th largest by purchasing …
History
When the Portuguese explorers arrived in the 16th century, the native tribes of current-day Brazil totaled about 2.5 million people and had lived virtually unchanged since the Stone Age. From Portugal's colonization of Brazil (1500–1822) until the late 1930s, the Brazilian economy relied on the production of primary products for exports.
In the Portuguese Empire, Brazil was a colony subjected to an imperial mercantile policy, which ha…
Components
The service sector is the largest component of the gross domestic product (GDP) at 67.0 percent, followed by the industrial sector at 27.5 percent. Agriculture represents 5.5 percent of GDP (2011). The Brazilian labor force is estimated at 100.77 million of which 10 percent is occupied in agriculture, 19 percent in the industry sector and 71 percent in the service sector.
Exports and imports
Brazil was the 25th largest exporter in the world in 2020, with 1.1% of the global total.
In 2021, Brazil exported US$280.4 billion and imported US$219.4 billion, with a surplus of US$61 billion.
The country's top ten export products were:
Economic status
Portuguese explorers arrived in 1500, but it was only in 1808 that Brazil obtained a permit from the Portuguese colonial government to set up its first factories and manufacturers. In the 21st century, Brazil became the eighth largest economy in the world. Originally, its exports were basic raw and primary goods, such as sugar, rubber and gold. Today, 84% of exports are of manufactured and semi-…
See also
• Economic history of Brazil
• List of economic crises in Brazil
• Brazilian Packaging Market
• Brazil and the World Bank
Further reading
• Furtado, Celso. Formação econômica do Brasil [1]
• Prado Junior, Caio. História econômica do Brasil[2]
External links
• Ministry of Finance (Brazil)
• IBGE : Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics
• World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Brazil
• Brazil profile at the CIA World Factbook