...
1.3Crystal Structures.
| CCDC Number | 286524 |
|---|---|
| Associated Article | DOI:10.1021/cg0701877 |
What does CH3OH stand for?
There is no molecule with the formula CH2OH. The chemical you may be looking for is CH3OH, which is known as methanol. In organic Chemistry however, the group –R-OH have a name: Hydroxymethyl. – (Do search on it) The hydroxymethyl group consists of a methylene bridge (-CH2- unit) bonded to a hydroxy (-OH) group.
Is CH3OH a salt or base or acid?
This is because NaOH is a strong base while CH3COOH is a weak acid. The acetate anion may accept a proton from water to revert back to acetic acid. This leaves an hydroxide anion which you know is basic. On the other hand, if you react a weak base with strong acid, you get an acidic salt. MgOH is a weak base while HCl is a strong acid.
Which is more basic, CH3OH or CH3CH2OH?
In case of alcohol and acid compound CH3COOH is more acidic than CH3CH2OH becuase anion of acid group are more stable than alchoholic compound due to resonating structure. And in case of CH3NH2 it is less acidic but more basic in nature because of lone pair present on the N atom.
What type of compound is CH3COOH?
what type of compound is ch3 ch2 ch3
- IUPAC naam CH3-CH2-OH , CHCl3 , CH3COOH , CH3-CO-CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3
- O Br C6H4 CH (CH3) CH2 CH3
- The IUPAC name of following compound is ______. ` {: (CH_ (3) -CH_ (2) -CH-CH_ (2) -CH_ (3)), (
Is CH3OH an ionic or covalent compound?
0:011:35Is CH3OH (Methanol) Ionic or Covalent/Molecular? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipRight here that's a nonmetal. So when we have nonmetals bonded together we have a covalent compoundMoreRight here that's a nonmetal. So when we have nonmetals bonded together we have a covalent compound we have covalent bonds it's also called a molecular compound.
What type of organic compound is CH3OH?
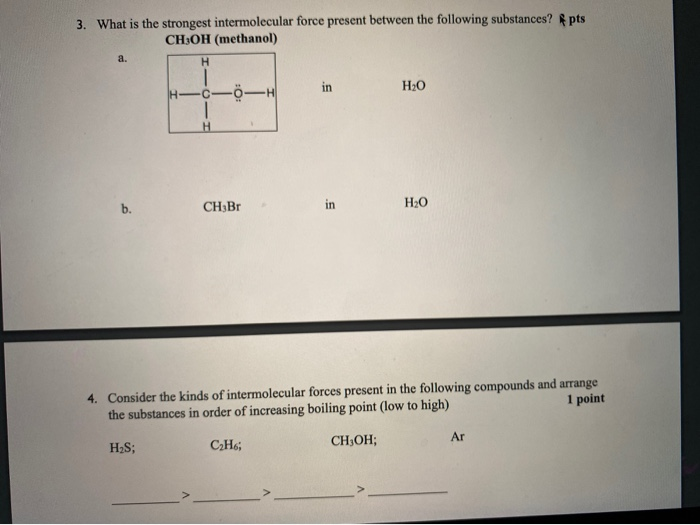
methanolmethanol (CH3OH), also called methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, or wood spirit, the simplest of a long series of organic compounds called alcohols, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) linked with a hydroxy group (OH).
Is methanol ionic compound?
Methanol is not an ionic molecule and will not exhibit intermolecular ionic bonding. Methanol is polar, and will exhibit dipole interactions. It also contains the -OH alcohol group which will allow for hydrogen bonding.
What type of bond does CH3OH have?
Ch3oh intermolecular forces has hydrogen bonding, dipole dipole attraction and London dispersion forces.09-Mar-2021
Is ch3cooh ionic or covalent?
Though acetic acid is covalent it dissociates into acetate ions and hydrogen ions.12-Apr-2021
Is CH3OH hydrocarbon?
Methanol is a simplest alcohol with a chemical formula CH3OH. It is not a hydrocarbon since the hydroxyl group is chemically bonded to the carbon atom. It consists of a methyl group linked with a hydroxy group. It is also known as Wood alcohol or Methyl alcohol.
Is cac2 an organic compound?
Compounds of carbon are classified as organic when carbon is bound to hydrogen. Carbon compounds such as carbides (e.g., silicon carbide [SiC2]), some carbonates (e.g., calcium carbonate [CaCO3]), some cyanides (e.g., sodium cyanide [NaCN]), graphite, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide are classified as inorganic.
Is CH3OH polar or nonpolar or ionic?
The total molecule in its non ionic form is not symmetrical therefore the O-H “end” would have a slightly more negative charge than the C-H3 +ve “end”. Making it a dipole, therefore polar!
Is CH3OH an electrolyte?
Methanol, CH3OH, is a nonelectrolyte; ammonia, NH3, is a weak electrolyte; and iron(III) sulfate, Fe2(SO4)3, is a strong electrolyte.
Is methanol a solvent?
Methanol (MeOH), the simplest alcohol, is widely used as a solvent, motor fuel, ethanol denaturant, and, most of all, a feedstock for manufacturing other chemicals. It was originally made by the destructive distillation of wood—hence, the once commonly used name “wood alcohol”.11-Mar-2013
Is caco3 an ionic compound?
Calcium carbonateCalcium carbonate / IUPAC ID
Is caco3 ionic or covalent?
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) has ionic bonding between calcium ion Ca2+ and a polyatomic ion, CO2−3, but within the carbonate ion (CO32-), the carbon and oxygen atoms are connected by covalent bonds (shown above).16-Jul-2020
Is CH3OH aqueous?
0:000:53CH3OH + H2O (Methanol + Water) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThat's methanol plus water methanol is a covalent compound it's made up of all nonmetals. As isMoreThat's methanol plus water methanol is a covalent compound it's made up of all nonmetals. As is water and they're both polar covalent. Because of that when you mix methanol.
Is NH4NO3 a covalent compound?
Ionic bond. NH4NO3 is a nitrate salt of the ammonium cation. Since ammonium is a cation and bonds with the anion nitrate, hence the compound is bonded by an ionic bond.
Is C12H22O11 ionic or covalent?
Sucrose (table sugar), C12H22O11 is MOLECULAR or COVALENT compound, while sodium chloride (table salt) is _ an IONIC compound. 6. Carbon monoxide, CO, is an example of a diatomic molecule, while ammonia and glucose, NH3 and C6H12O6, are examples of POLYATOMIC molecules.
Is NaHCO3 covalent or ionic?
Yes, baking soda is an ionic compound. Baking soda is composed of sodium ions, Na+ and bicarbonate ions HCO−3 (also called hydrogen carbonate ions), in a 1:1 ratio. The formula unit for sodium bicarbonate ( also called baking soda or sodium hydrogen carbonate) is NaHCO3 .20-Feb-2015
7 Drug and Medication Information
METHYL ALCOHOL is an active ingredient in 3 products including: ' Aspartame /MSG Detox', Enviroclenz, and N02.
10 Pharmacology and Biochemistry
Liquids that dissolve other substances (solutes), generally solids, without any change in chemical composition, as, water containing sugar. (Grant and Hackh's Chemical Dictionary, 5th ed) (See all compounds classified as Solvents .)
11 Use and Manufacturing
Methanol is primarily used as an industrial solvent for inks, resins, adhesives, and dyes. It is also used as a solvent in the manufacture of cholesterol, streptomycin, vitamins, hormones, and other pharmaceuticals.
12 Identification
Method: EPA-RCA 8015C; Procedure: gas chromatography with flame ionization detection; Analyte: methanol; Matrix: surface water, ground water, and solid matrices; Detection Limit: 21 ug/L.
22 Information Sources
CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data.
CH3OH Lewis Structure
The Lewis Structure of a molecule gives the simplest representation of valence shell electrons around itself.
Steps to Draw the Lewis Structure of Methanol (CH3OH)
The total no. of valence electrons in a molecule is the sum of valence shell electrons of each element in the molecule.
CH3OH Molecular Geometry
The molecular geometry of a compound can be very well explained by the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory which is based on the assumption that a molecule stabilizes itself in a particular shape in which it experiences a minimum amount of electron-electron repulsions.
CH3OH Molecular Shape
A compound having tetrahedral geometry can have four types of molecular shapes depending on the no. of lone pairs present in the molecule.
CH3OH Hybridization
Hybridization is a concept that describes the formation of hybrid orbitals upon the mixing of pure atomic orbitals which are identical in both energy and shape.
CH3OH Polarity
If the charge distribution between two atoms is unequal or there occurs an electronegativity difference between them, then the bond between the two atoms is said to be polar.
Conclusion
To summarise, CH3OH is a polar and a neutral compound that has a tetrahedral geometry and bent and tetrahedral shapes with respect to the oxygen and carbon atoms respectively.
What is the pKa of methanol?
The pKa value for Methanol is 15.5, which is higher than water. pKa value is the constant used in chemistry to measure the number of acidic and basic ions present in the solution. On dissociation, the molecule gives CH3O- and H+ ions.
What is a Lewis base?
As per the definition, a compound or molecule that can donate electrons to form bonds is considered a Lewis base. Here in CH3OH, Oxygen has two lone pairs of electrons. These lone pairs of electrons are used by Lewis acids to complete their orbitals.
Is CH3OH a Lewis base?
Methanol, having the chemical formula of CH3OH, consists of a methane group and a hydroxyl functional group ( OH). One might argue how an OH group can be considered as a base. But it’s not the hydroxyl group; it is the OH- hydroxide ion that makes the compound a Lewis base. As per the definition, a compound or molecule that can donate electrons ...
Is methanol an acid or basic molecule?
Looking at all the chemical properties of Methanol and its pKa value, many biochemists consider this molecule amphoteric in nature as it has both basic and acidic properties. Depending upon the type of molecule it is reacting with, it exhibits its acidic or basic property. To answer in a nutshell, Methanol is as acidic and basic as water and is considered a weak acid.
Is methanol an acid or base?
A lot of students get confused when asked if Methanol is an acid or base. To be honest, it is a tricky question, but to answer it in one line, I would say it is as acidic or basic as water. Such compounds are also called amphoteric compounds as it exhibits properties of both – acids and bases.
Is methanol a weaker acid than water?
A compound that can donate protons are considered acids but here in Methanol; as a result, water is a better proton donor, which makes Methanol a weak acid. Hence, Methanol is a weaker acid than water.
Is alcohol an acid?
And according to the definition of acids, a compound that willingly loses a proton is considered acid. However, This alcohol exhibits weak acidic properties because the CH3 group and OH functional group leads to releasing negative ions in the aqueous solution.
How many bonds does CH3OH have?
While drawing the Lewis structure for CH3OH, you will notice that the Carbon atom will have three bonds with three hydrogen atoms and one bond with the Hydroxyl Group.
What is CH3OH Lewis?
CH3OH Lewis structure , Molecular Geometry and Shape. Methanol or Methyl alcohol is one of the compounds that are used to understand the molecular geometry, bonds, and much more in Organic chemistry. This compound has a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to the methyl group, and that is where it gets its name of “methyl alcohol.”.
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
Carbon has a steric number of 4 as it has four valence electrons in its outer shell. In Methanol, Carbon is the central atom, and all the other atoms are placed around it. For drawing the structure, you can place four electrons ( as dots ) around the central carbon atom in all four directions.
What is the name of the compound that has a hydroxyl group?
This compound has a hydroxyl group ( OH) attached to the methyl group, and that is where it gets its name of “methyl alcohol. ”. To make it easier for you to understand, assume that one hydrogen atom of methane or CH4 is substituted by a hydroxyl group, resulting in Methanol having the chemical formula of CH3OH.
Which atom has a sp3 hybridization?
The atom shares three of its four valence electrons with Hydrogen atoms and rests one electron with the hydroxyl group. Central Carbon atom has sp3 hybridization and a bent molecular shape due to the repulsion between lone pairs on Oxygen and the bonded pairs in the molecule.
Which atoms form sigma bonds?
The central carbon atoms form four sigma bonds and have no lone pairs, which results in the formation of a tetrahedron. Simultaneously, the Oxygen atom forms two sigma bonds and two lone pairs of electrons, which causes a bent in the bond angle due to the repulsion forces.
Is methyl alcohol a liquid?
Methyl alcohol is a light, colorless, and volatile liquid with an alcoholic odor similar to ethanol. The molecule’s structure is easy to understand, and one can also use this example to study more complex structures in organic chemistry.