Which substances are the subunits of proteins?
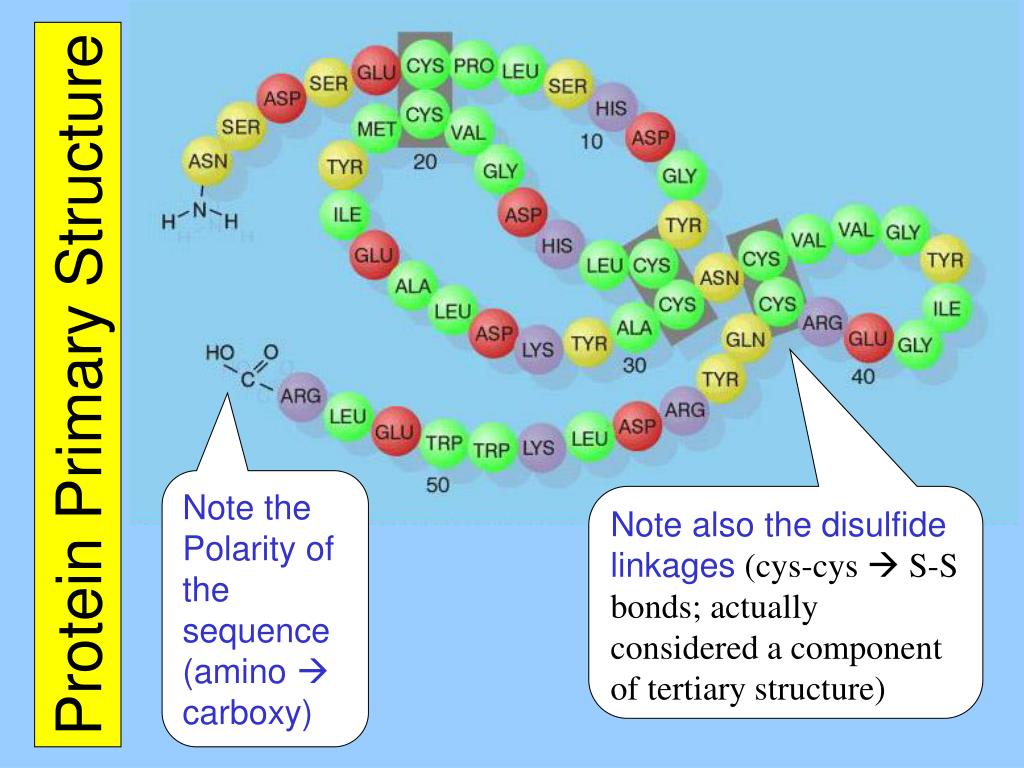
Proteins are large molecules made of amino acid, subunits composed an alfa carbon, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain, these amino acids are bonded by peptide bonds, covalent bonds formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid.
What does protein subunit mean?
With protein subunits, they are actually using what they call nanoproteins, which are just small amounts of protein, and what they call an adjuvant. They are using essentially the entire protein subunit, as I understand it, from the spike protein of the coronavirus. And so, in that way, it's a bit different.
What are proteins and what do they do?
Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains.
What are the four types of protein structure?
The α-carbon always has the following four groups attached to it:
- –NH2 a basic amino group
- –COOH an acidic group (known as a carboxyl group)
- –H a hydrogen atom
- –R a side chain
What subunits are found in proteins?
Single chains of amino acids that are the units of multimeric PROTEINS. Multimeric proteins can be composed of identical or non-identical subunits. One or more monomeric subunits may compose a protomer which itself is a subunit structure of a larger assembly.
What subunits make up proteins quizlet?
What subunits make up proteins? Nucleotides.
What are the subunits that make up lipids?
Lipids are made up of glycerol and fatty acids with a long chain hydrocarbon. Triglycerides are the most common type of fats. They have three fatty acids attached to one glycerol molecule.
What are the subunits that make up carbohydrates?
MONOSACCHARIDES. The monosaccharides (mono = one, saccharide = sugar) are the basic subunits of carbohydrates.
What is the hyvac4 subunit?
The vaccine is delivered with GSK proprietary adjuvant AS02. Like M72, HyVac4 is an adjuvant subunit vaccine. It was developed on the heels of Hybrid-1, a fusion molecule of the Ag85B and ESAT-6 antigens (Agger et al., 2006 ), which was abandoned because ESAT-6 had shown utility in diagnostic tests. HyVac4 is a recombinantly expressed fusion of Mtb antigens Ag85B and TB10.4 that is delivered in IC31, an Intercell proprietary adjuvant based on a cationic peptide KLKL 5KLK and immunostimulatory oligodeoxynucleotide ODN1a. It was developed by the Statens Serum Institute, Intercell, and Aeras (Aeras-404) and entered Phase I clinical trials in 2007.
How many CP subunits are in a helix?
CP subunits isolated either by acetic acid treatment of purified virus or expressed in E. coli formed 450kDa disks comprising about 20 subunits arranged in two turns of a helix (Erickson et al., 1978;
What are the functions of heterotrimeric G proteins?
Heterotrimeric G proteins (subunits Gαβγ) mediate a variety of physiological responses, including sensory perception, hormone action, polarization, chemotaxis, and growth control [1–3 ]. In the conventional paradigm for G-protein signaling, ligand-bound (or light-activated) heptahelical receptors catalyze release of GDP from the G α subunit, resulting in a complex between the receptor and the nucleotide free Gαβγ heterotrimer. Association of GTP with G α triggers release from the receptor and dissociation of G α GTP and G βγ. Depending on the particular signaling pathway, either Gα GTP or the released G βγ subunits interact with downstream effectors until the G α subunit is deactivated by GTP hydrolysis. Although the Gα subunit possesses an intrinsic GTP hydrolytic activity, regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) domains, present in a variety of modular proteins, accelerate the rate of GTP hydrolysis [4 ].
What is the coat protein of a small icosahedral virus?
The coat protein subunits of most small icosahedral viruses are in the range of 20- to 40-kDa; some are larger but fold to give effective “pseudomolecules” within this range (Section V, B, 6 ). In contrast to rod-shaped viruses, the subunits of most small icosahedral viruses have a relatively high proportion of β -sheet structure and a low proportion of α -helix ( Denloye et al., 1978; Odumosu et al., 1981) and have the same basic structure. This comprises an eight-stranded antiparallel β sandwich, often termed a β -barrel or “jelly-roll β -barrel”, which is shown schematically in Figure 3.20.
What are the disadvantages of a protein subunit?
Sometimes the production of a vaccine protein in a recombinant organism alters the conformation of the protein such that its stability is affected or protective conformational epitopes are no longer present.
What is recombinant DNA?
Recombinant DNA technology has greatly simplified the synthesis of vaccines for pathogens that are difficult or impossible to grow in vitro, and/or whose components are a challenge to purify in sufficient amounts from in vivo infections.
Is HyVac4 an adjuvant?
Like M72, HyVac4 is an adjuvant subunit vaccine. It was developed on the heels of Hybrid-1, a fusion molecule of the Ag85B and ESAT-6 antigens (Agger et al., 2006 ), which was abandoned because ESAT-6 had shown utility in diagnostic tests.
What is a protein subunit?
In structural biology, a protein subunit is a single protein molecule that assembles (or " coassembles ") with other protein molecules to form a protein complex. Some naturally occurring proteins have a relatively small number of subunits and therefore described as oligomeric, for example hemoglobin or DNA polymerase.
How many genes are in a polypeptide chain?
A polypeptide chain has one gene coding for it – meaning that a protein must have one gene for each unique subunit. A subunit is often named with a Greek or Roman letter, and the numbers of this type of subunit in a protein is indicated by a subscript. For example, ATP synthase has a type of subunit called α.
What is the difference between a catalytic and regulatory subunit?
In some protein assemblies, one subunit may be a "catalytic subunit" that enzymatically catalyzes a reaction, whereas a "regulatory subunit" will facilitate or inhibit the activity. Although telomerase has telomerase reverse ...