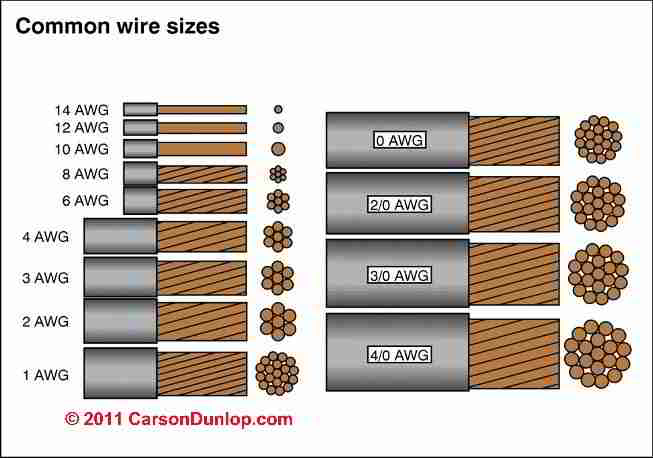
AWG chart
| AWG # | Diameter (inch) | Diameter (mm) | Area (kcmil) | Area (mm 2) |
| 0000 (4/0) | 0.4600 | 11.6840 | 211.6000 | 107.2193 |
| 000 (3/0) | 0.4096 | 10.4049 | 167.8064 | 85.0288 |
| 00 (2/0) | 0.3648 | 9.2658 | 133.0765 | 67.4309 |
| 0 (1/0) | 0.3249 | 8.2515 | 105.5345 | 53.4751 |
| AWG | Diameter | Turns of wire, no insulation |
|---|---|---|
| 000 (3/0) | 0.4096 | 2.44 |
| 00 (2/0) | 0.3648 | 2.74 |
| 0 (1/0) | 0.3249 | 3.08 |
| 1 | 0.2893 | 3.46 |
What is 3 0 electrical wire used for?
Multiconductor cables are used behind the walls of your home and to connect heavy appliances, such as washing machines and dishwashers. Commonly called type NM, or nonmetallic, these electric cables consist of a live, or hot, wire; ground wire; and neutral wire, which are encased in a plastic sheath.
What wire size to use?
Wire Gauge (AWG) Calculator
- Choosing the correct wire size is essential for SAFETY (fire hazard due to max current capacity) and PERFORMANCE (intermittent problems due to voltage drop) of your electrical system.
- Wire gauge depends on CURRENT and LENGTH of the wire. ...
- Wire sizing per ABYC standards for 12V DC, 105°C copper wire conductor. ...
How to select the correct size automotive wire?
- A Locate the CURRENT IN AMPS. Most electrical products include a rating label, or you can find the amperage rating in the documentation that came with the product.
- B Find circuit LENGTH IN FEET. ...
- C Select the CIRCUIT TYPE. ...
- Click the image below to enlarge. ...
What are the different sizes of electrical wire?
Wire size calculation formulas
- Explanation of the components
- Derivation of the required values. Nominal current \mathbf {I} and efficiency \mathbf {\cos \varphi} can be found in the manual or on the type plate of the machine.
- Wire size calculator tool. The online calculator helps you to determine the wire size for the desired parameters. ...
What is the diameter for 3 0 Thhn wire?
0.600 inchesSpecifications: Size AWG: 3/0. Weight per 1,000 ft: 570 lbs. Outside Diameter: 0.600 inches.
What size wire do I need for 100 amp service?
Size Wire for 100 Amp Service Wiring a 100 amp breaker panel requires either #4 copper wiring or #2 aluminum or copper-clad wiring. Which wire used is determined by the voltage drop and length of the wiring. Many licensed electricians use #2 copper-clad or aluminum wire size.
What size wire do I need for a 200 amp service?
The Short Answer: Like with aluminum, you'll need a #4/0 copper-clad aluminum wire for a 200 amp service.
What is 3 0 wire rated?
Table 310.15(B)(17)SizeTemperature Rating of Copper Conductor(AWG or kcmil)60°C (140°F)75°C (167°F)3/0 AWG2603104/0 AWG300360250 KCMIL34040527 more rows
What size wire do I need to run 100 amp Service 150 feet?
#00 AWG wireWire Size For 100 Amp Sub Panel 150 Feet Away 100 amp service 150 feet away from the sub panel requires #00 AWG wire (also known as 2/0 AWG wire). This wire has a median ampacity of 175 amps; more than enough than the required minimum 162.5 ampacity.
What wire size do I need to go 100 feet for a 100 amp service to a workshop?
For a 100 ampere circuit, the conductors will likely be required to be 3 AWG copper or 1 AWG aluminum.
What size wire do I need to run 200 amp Service 200 feet?
Installation of 200 amp electrical service needs a #2/0 AWG copper wire or #4/0 AWG for aluminum or copper-clad wire inside a minimum of 1.5 inches, schedule 40 or 80 PVC conduit for underground service. However, 2 or 2.5 inches is recommended if running 3 wires in the same conduit.
What size wire do I need for a 100 amp underground 300 ft run?
for 300 feet for 100 amp rated service I would use Aluminum direct burial 1/0-1/0-1/0-1/0, the forth can be as low as #4 for the ground (but also in conduit, even if in conduit must still be rated underground wire and required by code also) Also note the size wire the breaker can handle, cannot cut strands to make fit, ...
What size ground rod do I need for 200 amp service?
#4for 200 Amp services, a #4 grounding electrode conductor (ground wire) is required.
How many amps can 3 0 wire carry?
300 amps3/0 Gauge (AWG) Battery Cable has an amperage capacity of 300 amps at a cable length of around 15 feet.
What size wire do I use for 150 amp service?
SERVICE ENTRANCE CONDUCTORS SIZE AND RATINGService or Feeder RatingCopper ConductorsAluminum or Copper-Clad Aluminum100 Amps#4 AWG#2 AWG125 Amps#2 AWG#1/0 AWG150 Amps#1 AWG#2/0 AWG1 more row
What size wire is needed for 60 amps?
60 amp wire size is either 6 AWG or 4 AWG wire (AWG stands for American Wire Gauge; standard wire sizing is the US) for 220V voltage. An amateur will use a 6 AWG wire size for 60 amp 220V. A professional will always use 4 AWG wire size for 60 amp 220V.
AWG Wire Gauge Chart For All 44 Wires (Ampacity Chart)
AWG Wire Gauge Chart (1st Chapter) In this AWG wire gauge chart for a standard copper wire, you can find every AWG wire; from the biggest 10+ mm wires (such as 4/0 AWG and 3/0 AWG wires) to the smallest below 0.01 mm wires like 39 and 40 AWG wires.
AWG Wire Sizes (see table below)
UIUC Physics 436 EM Fields & Sources II Fall Semester, 2015 Supplemental Handout Prof. Steven Errede © Professor Steven Errede, Department of Physics, University of ...
American Wire Gauge Conductor Size Table - Solaris
conductor does not have to be type TW, it could have a higher temperature designation such as THW or THHN; however, the ampacity must be based upon a 60°C rated conductor.
AWG to MM2 Wire Gauge Size Chart - LEX Products
Request A Quote PowerFlex Subscribe To Email. AWG to MM2 Explained. Since 1857, wire gauge to MM2 made determining a wire’s current-carrying ratings easier. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi.
How to determine gauge wire size?
To determine the gauge wire you need, consider what carrying capacity and amount of current the wire needs to conduct to work for your application. Now consider the distance. The distance your wire needs to go can impact the gauge size you need. The longer the wire, the more voltage you can lose through resistance and heat.
What is AWG wire gauge?
American Wire Gauge (AWG) is the U.S. standardized wire gauge system used to note the diameter of rounded, non-ferrous electrical wiring. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. The table below illustrates the conversion ...
How to determine AWG?
AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. Oftentimes the term “circular mil” is used. Circular mil is the area of a 1/1000 (or 1 mil) diameter circle. Such measurements are made on only the wire and not on the wire’s jacketing or insulation. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller (or thinner) the wire will be.
What is AWG resistance?
Resistance acts upon both a direct current and alternating current to create a “skin effect.”. Simply put, as a signal frequency increases, the current flow of the wire concentrates toward the skin (outside) of the conductor.
Why use smaller gauges?
Since smaller gauge sizes are more durable and flexible, it’s common practice to use them with higher AWG numbers when stranding conductors for bending or vibration applications . While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands.
Is AWG a size determining factor?
Such measurements are made on only the wire and not on the wire’s jacketing or insulation. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller (or thinner) the wire will be.
How to tell the thickness of a wire?
The thickness of a cable or wire is defined by its gauge size. The general rule of thumb is that the smaller the gauge number, the thicker the cable. The standardized method of measuring the thickness of a cable was established in 1857 in the United States.
What is gauge wire?
The term “gauge” is used for wire up to 1 AWG. The term “aught” is used for wire 1/0 AWG and larger. This number of “0” in the size is the number of “Aught”. Staff writers at Sonic Electronix are experts in their field.
What is the purpose of wire gauges?
Wire Gauge Sizes and the American Wire Gauge (AWG) Although wire is available in many different sizes and colors, the purpose is still the same: To transfer an electrical current from one device to another.
What is the AWG gauge used for?
Commonly known as the American Wire Gauge (AWG), this form of measuring cable thickness is used for electrically conducting wire.
10 Amps Wire Size: AWG Gauge, Breaker, Suggestion For 110V-120V Circuit
If you’re looking for wire size for a 10 amp circuit (this can be for a 10 amp 120-volt circuit, breaker, battery output), you will need an AWG with at least 10 amp rated ampacity at 75°C.
15 Amps Wire Size: AWG Gauge, Breaker, Suggestion For 110V-120V Circuit
If you’re looking for wire size for a 10 amp circuit (this can be for a 15 amp 120-volt circuit, breaker, battery output), you will need an AWG with at least 15 amp rated ampacity at 75°C.
20 Amps Wire Size: AWG Gauge, Breaker, Suggestion For 220V-240V Circuit
If you’re looking for wire size for a 20 amp circuit (this can be for a 20 amp 220-volt circuit, breaker, battery output), you will need an AWG with at least 20 amp rated ampacity at 75°C.
25 Amps Wire Size: AWG Gauge, Breaker, Suggestion For 220V-240V Circuit
If you’re looking for wire size for a 25 amp circuit (this can be for a 25 amp 220-volt circuit, breaker, battery output), you will need an AWG with at least 25 amp rated ampacity at 75°C.
30 Amps Wire Size: AWG Gauge, Breaker, Suggestion For 220V-240V Circuit
If you’re looking for wire size for a 30 amp circuit (this can be for a 30 amp 220-volt circuit, breaker, battery output), you will need an AWG with at least 30 amp rated ampacity at 75°C.
40 Amps Wire Size: AWG Gauge, Breaker, Suggestion For 220V-240V Circuit
If you’re looking for wire size for a 40 amp circuit (this can be for a 40 amp 220-volt circuit, breaker, battery output), you will need an AWG with at least 40 amp rated ampacity at 75°C.
50 Amps Wire Size: AWG Gauge, Breaker, Suggestion For 220V-240V Circuit
If you’re looking for wire size for a 50 amp circuit (this can be for a 50 amp 220-volt circuit, breaker, battery output), you will need an AWG with at least 50 amp rated ampacity at 75°C.
How many feet per pound of wire?
Feet per pound refers to the number of feet of wire needed to reach one pound in weight. (e.g., AWG 4 wire requires 7.918 feet, while AWG 40 requires 34.364 feet.) Resistance (ohms per 1000 feet). A wire’s electrical resistance depends on its length and thickness. Longer wires provide greater resistance than shorter wires.
What is gauge wire?
What Are Wire Gauges? The gauge of a wire refers to its thickness. Each gauge is represented by a number, with smaller numbers representing thicker wire gauges and higher numbers signifying thinner wires.
What is the difference between AWG 40 and AWG 4 wire?
(e.g., At 25° C, AWG 4 wire has a resistance of .2485Ω for 1000 feet, while AWG 40 wire has a resistance of 1079Ω for 1000 feet.) Current capacity (amps).
What is AWG wire gauge?
American Wire Gauge (AWG) is a standard method of measuring and identifying cable thickness developed in the United States for electrically conductive wire. It is suitable for specifying gauges for round and solid conductive wires made from non-ferrous material.
Why do electrical wires need to be thicker?
For example, electrical circuits with higher amperage ratings require thicker wires to accommodate the load without experiencing excessive heat buildup. Using wires that are too thin for the specified circuit amperage can result in wire failure or ignition.
What gauge wire is used for wire wrapping?
The most commonly used sizes for wire wrapping are 20 to 24 gauge. Wire Temper: Measures the amount of spring in the wire. Soft – Has no spring when you bend it and is good for making wire beads. Half-Hard – Has some spring, but is still malleable. It is good for basic wire work because it holds its shape well.
What gauge wire is used for chainmaille?
18 Gauge – heavy – often good for chainmaille or when a heavier look is needed. 16 Gauge – heavy – often used as a base to wrap finer wires around. 14 Gauge – heavy – often used as a base to wrap finer wire around. 12 Gauge – very heavy – hard to work with – good for rings and buckles.