Can adenine pair with guanine or cytosine?
Under normal circumstances, adenine does not pair up with guanine or cytosine; any other mismatches cannot occur. What 2 factors prevent a mismatch? Hover for more information.
What is the correct base pairing for adenine?
Adenine correctly bonds to thymine, while guanine correctly bonds to cytosine. This pairing is referred to as "complementary base pairing". The other factor that preserves the correct pairing of the complementary base pairs is the use of the existing DNA strand as a template to build new strands of DNA.
Why is adenine-cytosine paring not possible?
Therefore an Adenine-Cytosine paring is not energetically favorable. It can only bond with a base with two hydrogen sites. This is the second factor. The only base that Adenine pairs with is Thymine which is a pyrimidine and has only two hydrogen bonding sites. Thus AT and GC paring rule comes into existence.
How many hydrogen bonds are in a guanine and cytosine base pair?
A corresponding arrangement can be drawn between a guanine and a cytosine, so that there is both hydrogen bonding and shape complementarity in this base pair as well. A G:C base pair has three hydrogen bonds, because the exocyclic NH, at C2 on guanine lies opposite to, and can hydrogen bond with, a carbonyl at C2 on cytosine.
Why does cytosine make pair with guanine and not with adenine?
Solution : Cytosine make pair with guanine and not with adenine because hydrogen bond forming functional groups are not complementary between C and A.
Can adenine pair with guanine?
In DNA, the code letters are A, T, G, and C, which stand for the chemicals adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine, respectively. In base pairing, adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine.
Why does adenine only pair with thymine?
Adenine cannot pair with Cytosine because the purine and pyrimidine bases pair only in certain combinations. Adenine pairs with thymine A:T and guanine with cytosine G:C. Adenine and thymine are joined by two hydrogen bonds through atoms attached to positions 6 and 1.
Why can't A and G pair?
Guanine and thymine are similarly incompatible. A always pairs with T and G always pairs with C because these are the only combinations that allow for hydrogen bonding to occur, given the spatial constraints of the double helix, which requires there to be one purine and one pyrimidine in each base pair.
Why can't A purine pair with A purine?
You already know that purines bond with pyrimidines, but why can't purines bond with purines or pyrimidines bond with pyrimidines? It's because there is not enough space for two purines to fit within the helix and too much space for two pyrimidines to get close enough together for hydrogen bonds to form between them.
What are the rules of complementary base pairing?
What is the complementary base pairing rule for DNA? Complementary base pairs refer to the nitrogenous bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. in a double strand of DNA, adenine will always pair with its complement thymine and cytosine will always pair with its complement guanine.
Why does adenine always pair with thymine and guanine with cytosine in DNA quizlet?
Adenine and Guanine are purines, and Thymine and Cytosine are pyrimidines. So, for a uniform diameter, a purine must always bond with a pyrimidine. Adenine pairs with only Thymine because they form two hyrdrogen bonds while Guanine forms three hydrogen bonds and can only bond with Cytosine.
Why does adenine always pair with thymine and guanine always pair with cytosine What two factors determine the base pairing rule?
The Four Bases Cytosine pairs with guanine, and adenine pairs with thymine. These are the base pairing rules that allow DNA replication and protein synthesis to happen. A and T are connected by two hydrogen bonds, while C and G are connected by three hydrogen bonds.
Why does adenine pair with thymine and guanine with cytosine in DNA?
Each nucleotide base can hydrogen-bond with a specific partner base in a process known as complementary base pairing: Cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine, and adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine.
Why does guanine pair with cytosine?
Guanine and cytosine make up a nitrogenous base pair because their available hydrogen bond donors and hydrogen bond acceptors pair with each other in space. Guanine and cytosine are said to be complementary to each other.
Does cytosine pair with guanine?
Guanine pairs with cytosine, and adenine pairs with thymine in DNA. Interstrand hydrogen bonds are responsible for this pairing.
How many hydrogen bonds does adenine have?
Adenine has only two hydrogen bonding sites whereas Cytosine has three hydrogen bonds. Therefore an Adenine-Cytosine paring is not energetically favorable. It can only bond with a base with two hydrogen sites. This is the second factor.
Which base pairs with thymine?
The only base that Adenine pairs with is Thymine which is a pyrimidine and has only two hydrogen bonding sites. Thus AT and GC paring rule comes into existence.
What are the two bases that make up DNA?
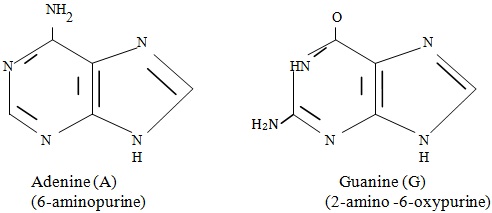
Adenine and guanine are two bases involved in the structure of DNA that are referred to as purine bases. The other two bases involved in the construction and composition of DNA are thymine and cytosine; these two are referred to as pyrimidine bases. That would be the first factor, that a purine must bond to a pyrimidine in the construction of a "rung" of the DNA double-helix ladder. Adenine correctly bonds to thymine, while guanine correctly bonds to cytosine. This pairing is referred to as "complementary base pairing". The other factor that preserves the correct pairing of the complementary base pairs is the use of the existing DNA strand as a template to build new strands of DNA. The original strand unwinds and breaks its bonds right down the middle, each side having a base sequence to serve as a template. New bases are assembled according to the specified order of the existing DNA strand, using complementary base pairing. When complete, there are now two strands of DNA, where there was originally only one.
Does adenine pair with guanine?
Under normal circumstances, adenine does not pair up with guanine or cytosine; any other mismatches cannot occur. What 2 factors prevent a mismatch? - eNotes.com
Is guanine a purine?
Adenine and Guanine are bothe purines. Purine-purine pairings are energetically unfavorable, since moelcules are too close to each othet. (This is the other way round for pyrimidines, they are too apart for stable bonding). Therefore because of this reason Adenine can't bond with Guanine. This is the first factor.
Answer
3) The structural problem which prevents adenine from pairing with guanine is that the bases are both long. 4) Rosalind Franklin contributed to the understanding of DNA by producing images of DNA by producing images of DNA molecules using X-rays.
Answer
3) The structural problem which prevents adenine from pairing with guanine is that the bases are both long.
New questions in Biology
How can the peak of Mount Kilimanjaro be glacial when it is located so close to the equator?
What is the relationship between adenine and thymine?
The pairing between adenine and thymine, and between guanine and cytosine, results in a complementary relationship between the sequence of bases on the two intertwined chains and gives DNA its self-encoding character . For example, if we have the sequence 5'-ATCTC-3' on one chain, the opposite chain must have the complementary sequence 3'-TACAC-5\
What happens when strands of polynucleotide are separated?
However, when polynucleotide strands are separate, water molecules are lined up on the bases. When strands come together in the double helix, the water molecules are displaced from the bases. This creates disorder and increases entropy, thereby stabilizing the double helix.
How many hydrogen bonds are there in a G:C base pair?
A G:C base pair has three hydrogen bonds, because the exocyclic NH, at C2 on guanine lies opposite to, and can hydrogen bond with, a carbonyl at C2 on cytosine. Likewise, a hydrogen bond can form between N't of guanine and N3 of cytosine and between the carbonyl at C6 of guanine and the exocyclic NR, at C4 of cytosine.
What are the edges of the A:T base pair?
The edge of an A:T base pair displays the following chemical groups in the following order in the major groove: a hydrogen bond acceptor (the N7 of adenine), a hydrogen bond donor (the exocyclic amino group on C6 of adenine), a hydrogen bond acceptor (the carbunyl group on C4 of
Why is the double helix important?
An important feature of the double helix is that the two base pairs have exactly the same geometry; having an A:T base pair or a G;C base pair between the two sugars does not perturb the arrangement of the sugars because the d¡stance between the sugar attachment points are the same for both base pairs. Neither does T:A or C:G. In other words,
How to tell if a polynucleotide is right handed?
In your mind's eye, hold your right hand up to the DNA molecule in Figure 6-9 with your thumb pointing up and along the long axis of the helix and your fingers following the grooves in the helix. Trace along one strand of the helix in the direction in which your thumb is pointing. Notice that yuu go around the helix in the same direction as your fingers are pointing. This does not work if yuu use your left hand. Try it!
What forces stabilize the double helix?
Hydrogen bonds are not the only force that stabilizes the double helix. A second important contribution comes from stacking interactions between the bases. The bases are flat, relatively water-insoluble molecules, and they tend to stack above each other roughly perpendicular to the direction of the helical axis.