Major Events in Mitosis
| Stage | Major Features |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes align on the metaphase plate |
| Anaphase | Sister chromatids separate, becoming ind ... |
| Telophase | Chromosomes arrive at spindle poles, the ... |
| Cytokinesis | Cytoplasm divides; cell wall forms in pl ... |
What are the 7 stages of mitosis in order?
What are the 7 stages of mitosis in order?
- Interphase. Cell performs normal functions, Cell growth (G1 and g2), Synthesizes new molecules and organelles.
- Prophase.
- Prometaphase.
- Metaphase.
- Anaphase.
- Telophase.
- Cytokinesis.
What happens to the cell during anaphase?
What are vestigial organs give examples?
- Sinuses. Human cheekbones hold the maxillary sinuses.
- Appendix. It is one of the most commonly known vestigial organs.
- Coccyx.
- Wisdom Tooth.
- External Ear.
- Nictitating Membrane.
- Tonsils.
- More to Explore:
What happens during the interphase stage of mitosis?
What are the main events that occur during interphase?
- Prophase. Chromosomes become visible, or in other words they condense.
- Metaphase.
- Anaphase.
- Telophase.
What phase of mitosis is before and after mitosis?
Mitosis occurs immediately after cytokinesis c. Mitosis occurs after G2 and before cytokinesis d. Mitosis occurs in between G1 and G2. Click to see full answer. Then, where is mitosis in the cell cycle? Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. This is when the cell grows and copies its DNA before moving into mitosis.
What happens when cells cross over in mitosis?
So that the cells of an organism may be of high genetic variability and may lead to loss of function, harmony and even the individuality at the level of species. Mitosis leads to the production of two cells which are genetically identical ...
Why is mitosis important?
Why mitosis? Mitosis is the cell division responsible for growth and repair. An adult human being is made up of billions of cells and all cells have the same genetic component. This genetic stability is achieved by mitosis. If crossing over and recombination is common in mitosis, then there will be variation in each cell division.
How does zygote divide?
Zygote divides by mitosis to form genetically identical daughter cells. 2) Repair: In the case of wound healing; that should be replaced with the same type of cells with the same genetic quality. This is achieved by mitosis. 3) Replacement: Take blood cells as example. RBC has a life span of 120 days.
What is the name of the process where two cells are genetically identical to each other?
Mitosis leads to the production of two cells which are genetically identical to that of the parent cell (that is chromosome number remains the same). Prophase: condensation of chromosomes begins. Metaphase: arrangement of chromosomes at the centre often called metaphase plate or equatorial plate.
How do cells grow?
1) Growth of the organism: An adult human being is made up of billions of cells and all cells have the same genetic component. This genetic stability is achieved by mitosis. All these cells are formed from the first cell zygote by mitosis. Zygote divides by mitosis to form genetically identical daughter cells.
What is Anaphase
The cell cycle refers to the process of cellular growth and division that is experienced by cells in the human body. During mitosis, two new diploid somatic cells are produced. By contrast, meiosis results in the production of four haploid gametes.
Characteristics of Anaphase
What are the characteristics of anaphase? During both mitosis and meiosis, some basic characteristics are associated with anaphase. This step has been described as perhaps the most essential phase during cell division, due to the dramatic separation of the sister chromatids.
What Happens in Anaphase of Mitosis
What happens to the chromosomes during anaphase? During anaphase of mitosis, two distinct mechanisms occur resulting in the separation of the sister chromatids. At the beginning of anaphase, the chromosomes are clearly visible, with sister chromatids joined at the centromere via a protein called cohesin.
How many phases does mitosis occur in?
In order to accomplish this goal, mitosis occurs in four discrete, consistently consecutive phases: 1) prophase, 2) metaphase, 3) anaphase, and 4) telophase . We have an overview of mitosis here, which is more of an intro to what mitosis is and how it works. If you're a little shaky on mitosis still, that's definitely where you should start.
What are the stages of mitosis?
The four stages of mitosis are known as prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Additionally, we’ll mention three other intermediary stages (interphase, prometaphase, and cytokinesis) that play a role in mitosis. During the four phases of mitosis, nuclear division occurs in order for one cell to split into two.
What happens after prometaphase?
It’s kind of like catching a fish with a fishing pole—eventually, the chromatids are going to be separated and drawn to opposite ends of the cell. And that’s the end of prometaphase. After prometaphase ends, metaphase—the second official phase of mitosis—begins.
What is the third phase of mitosis?
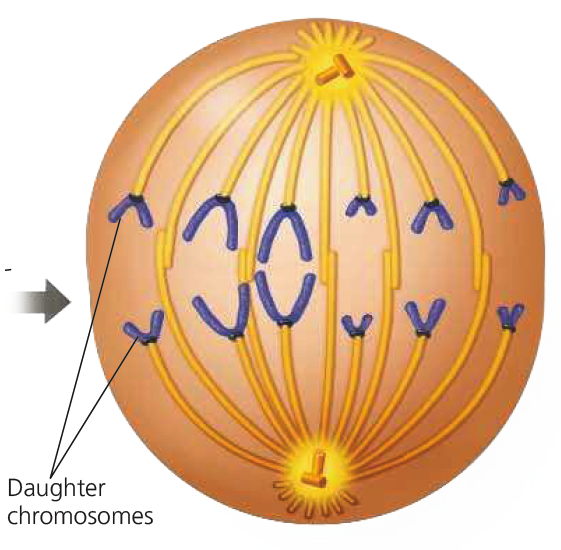
The third phase of mitosis, following metaphase and preceding telophase, is anaphase. Since the sister chromatids began attaching to centrosomes on opposite ends of the cell in metaphase, they’re prepped and ready to start separating and forming genetically-identical daughter chromosomes during anaphase.
How does mitosis occur?
Mitosis results in two new nuclei—which contain DNA—that eventually become two identical cells during cytokinesis . Mitosis occurs in eukaryotic (animal) cells.
What is interphase in biology?
We can think of interphase as a transitional phase. Interphase is when the parent cell prepares itself for mitosis. This phase isn’t considered part of mitosis, but understanding what happens during interphase can help the steps of mitosis make a little more sense.
What is the role of mitosis in the cell cycle?
The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two new cells, known as “daughter cells.”. In order to pass its genetic material to the two new daughter cells, ...