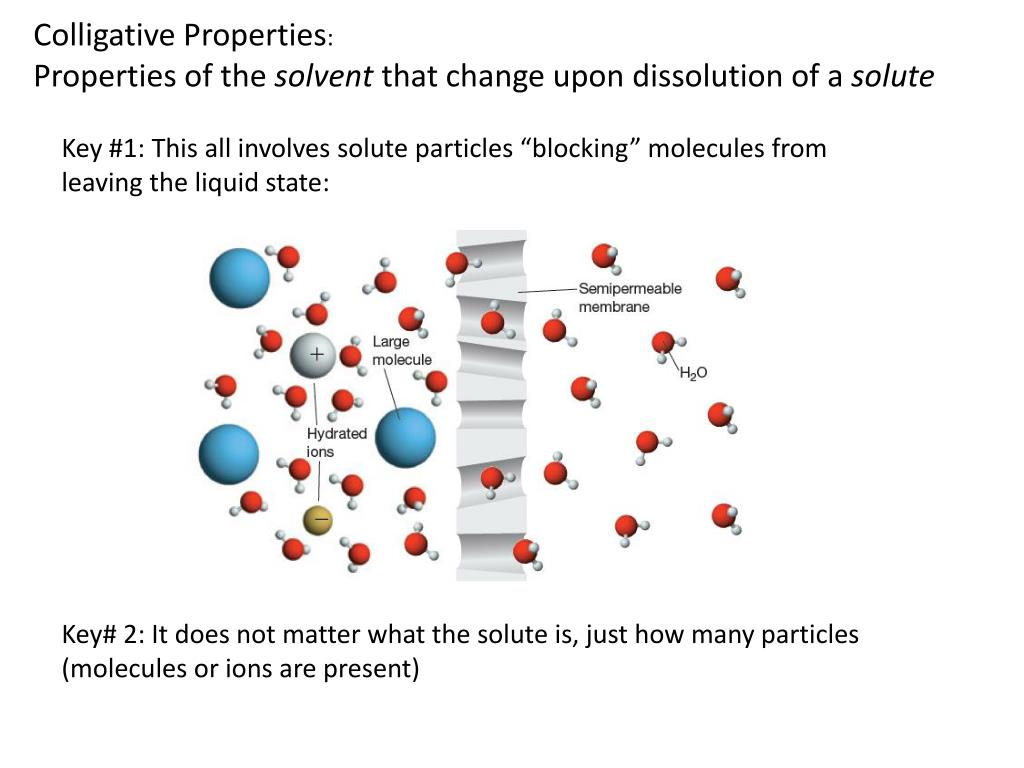
What is Van t Hoff factor for KCl in aqueous solution? Theoretically one mol of KCl gives one mol of potassium ion and one mol of chloride ion, the total is 2. In actual nothing is 100% and so the actual Van't hoff factor for KCl is close to 2.
What is the van\'t Hoff factor of KCl?
The van\'t Hoff factor of a 0.005 M aqueous solution of KCl is 1.95. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
What is the van t Hoff factor of a real solution?
However, the van’t Hoff factor of a real solution may be lower than the calculated value for a real solution at high concentration values or when the solute ions associate with one another. The van’t Hoff factor is a positive number, but it isn’t always an integer value.
What is the van t Hoff factor of a strong electrolyte?
For strong electrolytes, the ideal van’t Hoff factor is greater than 1 and equal to the number of ions formed in aqueous solution. Strong acids, strong bases, and salts are strong electrolytes. For example:
What are the observed values of molar mass and van t Hoff factor?
The observed value of molar mass is lesser than the normal value. The value of the Van’t Hoff factor is less than one. The value of i is greater than one. The values of the colligative properties are lower than expected. Example: reduced boiling point and freezing point. Higher values of colligative properties are observed.
What is the Vant Hoff factor for a KCl solution?
Substancesvan't Hoff factor (i)KCI2NaCl2K2SO43
What is the i value for KCl in chemistry?
question. Explanations:- Van't hoff factor"i" for KCl is close to 2 since it's ionic compound and ionic compounds ionization is high. KCl breaks to give potassium and chloride ions as: Theoretically one mol of KCl gives one mol of potassium ion and one mol of chloride ion, the total is 2.
What is the Vant Hoff factor for NaCl in an aqueous solution?
Based on the above method we will calculate Van't Hoff factor for NaCl. Sodium chloride consists of two ions i.e. the sodium ion and the chlorine ion. So, the Van't Hoff factor for NaCl considering complete dissociation is 2.
Is NaCl Vant Hoff factor?
The ideal van't Hoff factor is equal to the number of ions that form when an ionic compound dissolves....Learning Objective.CompoundiNaCl2KBr2LiNO 32CaCl 233 more rows
Is KCl aqueous?
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt-like taste....Potassium chloride.NamesRelated compoundsPotassium chlorate Potassium perchlorate56 more rows
What is KCl solution?
KCl, or Potassium Chloride, is a storage and hydration solution for pH pens and probes. Our Bluelab pH Probe KCl Storage Solution is a storage solution designed specifically for use with Bluelab pH Pens or pH Probes.
What is the N factor of NaCl?
N = 1 because in case of ionic solid (NaCl) the n factor is equl to charge on cation.
How to calculate van't Hoff factor?
The most common equation is:#N#i = moles of particles in solution / moles dissolved solute
What is the van't Hoff factor?
The van’t Hoff factor applies to colligative properties and appears in the formulas for osmotic pressure, vapor pressure, freezing point depression, and boiling point elevation. The factor is named for Dutch chemist Jacobus Henricus van’t Hoff, a founder of the field of physical chemistry and the first winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Do weak electrolytes dissociate in water?
Weak electrolytes do not fully dissociate in water, so the van’t Hoff factor won’t be the same as the number of ions formed. You’ll need to set up an ICE table (Initial, Change, Equilibrium) to determine the concentration of reactants and products and use the formula to calculate the van’t Hoff factor.
Is the van't Hoff factor a property of the solute?
The deviation is greatest for solutes with multiple charges. Ideally, the van’t Hoff factor is a property of the solute, but the measured value may depend on the solvent.
Does solubility affect van't Hoff factor?
Take care, however, because solubility affects measured van’t Hoff factor values. For example strontium hydroxide [Sr (OH) 2] is a strong base that fully dissociates into its ions, but is has a low solubility in water. You might predict the van’t Hoff factor to be 3 (Sr 2+, OH –, OH – ), but the experimental value will be lower. Also, the van’t Hoff factor for concentrated solutions in always slightly lower than the value for an ideal solution.
Does van't Hoff factor depend on concentration?
It is a property of the solute and does not depend on concentration for an ideal solution. However, the van’t Hoff factor of a real solution may be lower than the calculated value for a real solution at high concentration values or when the solute ions associate with one another.
Who wrote the law of the perfect solution?
Lewis, Gilbert Newton (1908). “The Osmotic Pressure of Concentrated Solutions and the Laws of the Perfect Solution”. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 30 (5): 668–683. doi: 10.1021/ja01947a002
class 5
The Fish Tale Across the Wall Tenths and HundredthsParts and Whole Can you see the Pattern?
class 9
Circles Coordinate Geometry What is Democracy? Why Democracy?Nazism and the Rise of Hitler Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
What is the Van't Hoff factor?
The extent to which a substance associates or dissociates in a solution is described by the Van’t Hoff factor. For example, when a non-electrolytic substance is dissolved in water, the value of i is generally 1. However, when an ionic compound forms a solution in water, the value of i is equal to the total number of ions present in one formula unit of the substance.
Who is Van't Hoff?
This factor is named after the Dutch physical chemist Jacobus Henricus Van’t Hoff, who won the first Nobel Prize in chemistry. It is important to note that the measured value of the Van’t Hoff factor for electrolytic solutions is generally lower than the predicted value (due to the pairing of ions). The greater the charge on the ions, the greater ...
Why is the molar mass of a solute lower than expected?
Since the molar mass is inversely proportional to the colligative properties, its value tends to be lower than expected. When solute particles associate with each other, the total number of particles in the solution decreases, leading to a decrease in the colligative properties.
What ions does NaCl dissociate into?
For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) dissociates into Na + and Cl – ions when dissolved in water.
How many mol of NaCl are in a solution?
But while calculating the molar mass using the colligative properties, we consider only 1 mol of NaCl to be present in the solution. Some of the substances tend to associate in aqueous state and for such molecules, the number of ions/molecules present in the solution is less than the actual number of molecules.
What happens when a solute dissolves in a solvent?
Van’t Hoff explained that when solutes are dissolved in a solvent they dissociate into ions. Since colligative properties depend only on the number of solute particles, the dissociation of solute molecules into ions results in an increase in the number of particles and hence affects the colligative properties.
How many moles of NaCl are there before dissociation?
So before dissociation there is 1 mole of NaCl and after dissociation there is 2 moles of ion one is of Na and other is of Cl
How much sodium chloride can be dissolved in water?
Notice, however, that it does not increase significantly. In fact, you can expect to be able to dissolve no more than 40 g of sodium chloride per 100 g of water at 80∘C.So, at 80∘C, you will ahve an unsaturated solution if you dissolve less than 40 g of sodium chloride, and a saturated solution if you dissolve about 40 g of sodium chloride.
What does the solubility graph tell you?
A substance's solubility graph tells you how its solubility changes, let's say starting from room temperature, when temperature is either decreased or increased.
Is NaCl dissolved in water?
At room temperature and concentrations up to solid saturation, NaCl dissolved in water is effectively completely dissociated. The deviation in the van’t Hoff factor is a matter of increasing non-ideality of the solution with increasing concentration rather than a change in the relative quantities of NaCl (0) vs Na (+) and Cl (-).