What is the use of UniProt?
UniProt is the central resource for storing and interconnecting information from large and disparate sources, and the most comprehensive catalog of protein sequence and functional annotation.
What is the UniProt database?
The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt) is a comprehensive resource for protein sequence and annotation data. The UniProt databases are the UniProt Knowledgebase (UniProtKB), the UniProt Reference Clusters (UniRef), and the UniProt Archive (UniParc).02-Feb-2021
What is UniProt annotation?
UniProt uses InterPro to classify sequences at superfamily, family and subfamily levels and to predict the occurrence of functional domains and important sites. InterPro integrates predictive models of protein function, so-called 'signatures', from a number of member databases.16-Jul-2020
Is UniProt and Swiss-Prot same?
UniProtKB/TrEMBL is a computer-annotated (unreviewed) supplement to Swiss-Prot, which strives to gather all protein sequences that are not yet represented in Swiss-Prot.
How reliable is UniProt?
UniProtKB encompasses several individual protein sequence resources that are depicted on this page. If you are talking about a sequence that is from SwissProt (manually reviewed/curated sequences) or UniRef100 clusters then that sequence is likely perfectly accurate.26-Oct-2018
Is UniProt a primary database?
Uniprot was originally formulated as a primary database for protein sequences and functional annotation based on experimental evidence. Nowadays it combines a network of sister databases centralising all levels of annotation produced for protein sequences.
What are the important features of UniProt?
UniProt is a freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from the research literature.
What is a Psi Blast?
PSI-BLAST (Position-Specific Iterative Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) derives a position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM) or profile from the multiple sequence alignment of sequences detected above a given score threshold using protein–protein BLAST.
What is an annotated protein?
Last modified August 13, 2020. Sequence annotations describe regions or sites of interest in the protein sequence, such as post-translational modifications, binding sites, enzyme active sites, local secondary structure or other characteristics reported in the cited references.13-Aug-2020
What is annotated sequence?
Definition. Sequence annotation is the process of marking specific features in a DNA, RNA or protein sequence with descriptive information about structure or function.
What is a UniProt number?
An accession number (AC) is assigned to each sequence upon inclusion into UniProtKB. Accession numbers are stable from release to release. If several UniProtKB entries are merged into one, for reasons of minimizing redundancy, the accession numbers of all relevant entries are kept.10-Apr-2018
How large is UniProt?
The UniProt knowledgebase is a large resource of protein sequences and associated detailed annotation. The database contains over 60 million sequences, of which over half a million sequences have been curated by experts who critically review experimental and predicted data for each protein.28-Nov-2016
How often is UniProt released?
every 8 weeksUniProt releases are published every 8 weeks (4 weeks until the last 2019 release, 2019_11), with possible exceptions in January and summer due to reduced staff during holidays.26-Jan-2021
What is UniProt database?
UniProt is a freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from the research literature.
Who is Uniprot funded by?
UniProt is funded by grants from the National Human Genome Research Institute, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the European Commission, the Swiss Federal Government through the Federal Office of Education and Science, NCI-caBIG, and the US Department of Defense.
What is a UniProt reference cluster?
The UniProt Reference Clusters (UniRef) consist of three databases of clustered sets of protein sequences from UniProtKB and selected UniParc records. The UniRef100 database combines identical sequences and sequence fragments (from any organism) into a single UniRef entry. The sequence of a representative protein, the accession numbers of all the merged entries and links to the corresponding UniProtKB and UniParc records are displayed. UniRef100 sequences are clustered using the CD-HIT algorithm to build UniRef90 and UniRef50. Each cluster is composed of sequences that have at least 90% or 50% sequence identity, respectively, to the longest sequence. Clustering sequences significantly reduces database size, enabling faster sequence searches.
What is UniProt consortium?
The UniProt consortium comprises the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB), and the Protein Information Resource (PIR). EBI, located at the Wellcome Trust Genome Campus in Hinxton, UK, hosts a large resource of bioinformatics databases and services.
Why does Uniparc only store one sequence?
In order to avoid redundancy, UniParc stores each unique sequence only once. Identical sequences are merged, regardless of whether they are from the same or different species. Each sequence is given a stable and unique identifier (UPI), making it possible to identify the same protein from different source databases.
When was Swiss Prot created?
Swiss-Prot was created in 1986 by Amos Bairoch during his PhD and developed by the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and subsequently developed by Rolf Apweiler at the European Bioinformatics Institute.
What is Swiss Prot?
UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot is a manually annotated, non-redundant protein sequence database. It combines information extracted from scientific literature and biocurator -evaluated computational analysis. The aim of UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot is to provide all known relevant information about a particular protein. Annotation is regularly reviewed to keep up with current scientific findings. The manual annotation of an entry involves detailed analysis of the protein sequence and of the scientific literature.
What is Uniprot in science?
UniProt provides an up-to-date, comprehensive body of protein information.
Who makes UniProt?
Who produces UniProt? UniProt is produced by the UniProt Consortium (Figure 1), a collaboration between the European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the Protein Information Resource (PIR).
UniProt
UniProt is a comprehensive, high-quality and freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from the research literature.
Some articles on uniprot
Funding For UniProt ... UniProt is funded by grants from the National Human Genome Research Institute, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the European Commission, the Swiss Federal Government through the Federal Office of ...
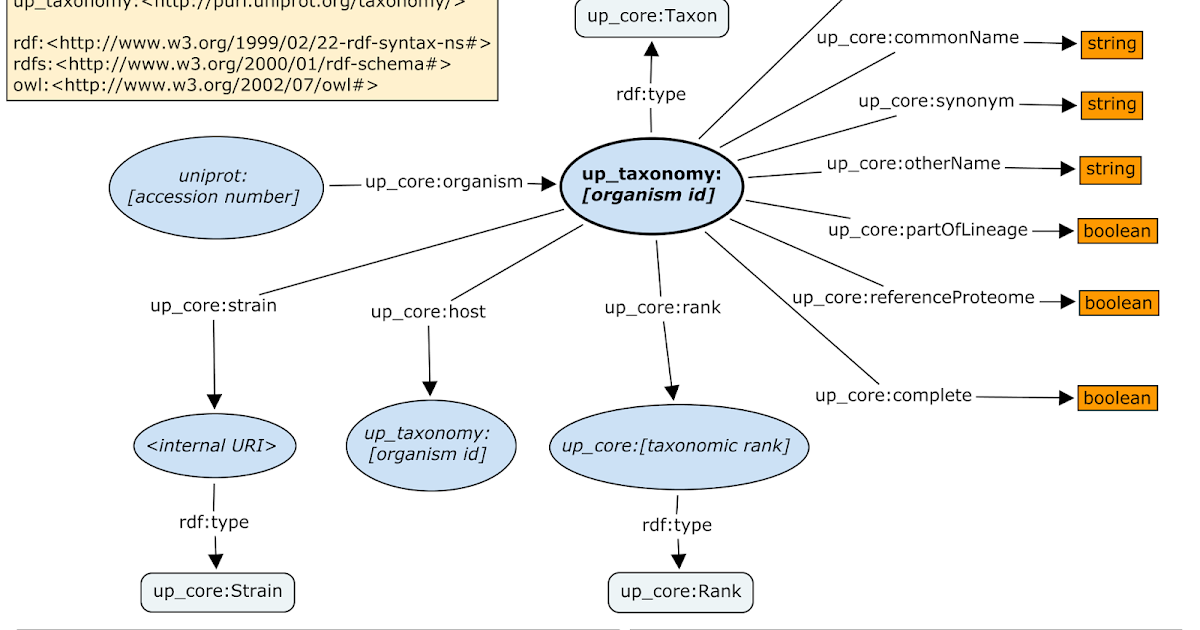
Overview
- UniProt has been supported by the NIH grants U01HG02712 (2002-2010) and U41HG006104 (2010-2014). UniProt activities at EMBL-EBI have benefited from the FP7 SLING project (2009-2012, contract number 226073), British Heart Foundation grants SP/07/007/23671 and RG/13/5/…
The UniProt consortium
The roots of UniProt databases
Organization of UniProt databases
UniProt is a freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from the research literature. It is maintained by the UniProt consortium, which consists of several European bioinformatics organisations and a foundat…
Funding
The UniProt consortium comprises the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB), and the Protein Information Resource (PIR). EBI, located at the Wellcome Trust Genome Campus in Hinxton, UK, hosts a large resource of bioinformatics databases and services. SIB, located in Geneva, Switzerland, maintains the ExPASy (Expert Protein Analysis System) servers that are a central resource for proteomics tools and databases. PIR, hosted by t…
External links
Each consortium member is heavily involved in protein database maintenance and annotation. Until recently, EBI and SIB together produced the Swiss-Prot and TrEMBL databases, while PIR produced the Protein Sequence Database (PIR-PSD). These databases coexisted with differing protein sequence coverage and annotation priorities.
Swiss-Prot was created in 1986 by Amos Bairoch during his PhD and developed by the Swiss Insti…