Does Reynolds number have units?
Unit of Reynolds Number = units of ρ x unit of u x unit of D / unit of μ Unit of Reynolds Number = (kg/m 3) x (m/s) x m / (kg/m.s) Unit of Reynolds Number = kg x m x m x m.s/ (m 3 x s x kg) Hence, we can say that the Reynolds number is a unitless property.
What is the SI unit of the Reynolds number?
- Re is the Reynolds number,
- u is the velocity of a fluid (with respect to the object),
- L is the characteristic linear dimension,
- ρ is the fluid density (you might want to estimate the density of air at given temperature, just check our air density calculator ),
- μ is the dynamic viscosity of a fluid,
- ν is the kinematic viscosity of a fluid ( ν = μ / ρ ).
What does the Reynolds number tell us?
Strouhal Number
- Multiphysics Modelling of Fluid Flow Systems. ...
- High-Frequency versus Low-Frequency Vibration Calculations. ...
- Introduction of Tidal Energy. ...
- Physiological and toxicological considerations. ...
- A one-dimensional performance model for turbocharger turbine under pulsating inlet condition
What is Reynolds number and its importance?
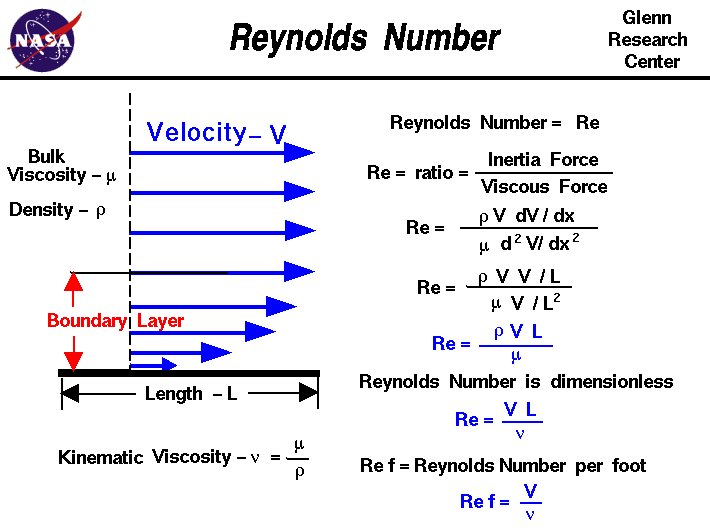
Reynolds Number is a very important quantity for studying fluid flow patterns. It is a dimensionless parameter and widely used in fluid mechanics. Reynolds Number of a flowing fluid is defined as the ratio of inertia force to the viscous force of that fluid and it quantifies the relative importance of these two types of forces for given flow ...
Why Reynolds number is Unitless?
The Reynolds number (Re) is the ratio of inertial resistance to viscous resistance for a flowing fluid. The Reynolds number is a non-dimensional (unitless) factor governing resistance due to viscosity (among other things).
What is the SI unit and dimensions of Reynolds number?
Therefore, the Reynolds Number is dimensionally represented as M0 L0 T0.
What are the units of Reynolds number in pipe flow?
The Reynolds number for pipe flow is defined as Re = DVρ/μ, where D is the pipe diameter, V is the average flow velocity in the pipe, ρ is the density of the flowing fluid and μ is the dynamic viscosity of the flowing fluid. Re is a dimensionless number.
What units is viscosity in for Reynolds number?
The Reynolds number formula depends on a viscosity. We generally distinguish two types of viscosity: Dynamic viscosity μ is a quantity that measures the force needed to overcome internal friction in a fluid. The units of dynamic viscosity are: Pa / s , N / (m² * s) or kg / (m * s) .
What is Renault unit?
ρ is the density of the fluid (SI units: kg/m3) u is the flow speed (m/s) L is a characteristic linear dimension (m) (see the below sections of this article for examples) μ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa·s or N·s/m2 or kg/(m·s)) ν is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid (m2/s).
How is Reynolds number calculated?
The Reynolds number (Re) of a flowing fluid is calculated by multiplying the fluid velocity by the internal pipe diameter (to obtain the inertia force of the fluid) and then dividing the result by the kinematic viscosity (viscous force per unit length).
What is the unit of discharge?
The discharge is the volume of water that is transported each second, and the volumes are expressed in litres (l) or in cubic metres (m3) [1 m3 = 1000 l], and the letter Q is commonly used as the symbol for the discharge.
Is Reynolds number linear?
An increasing Reynolds number indicates increasing turbulence of flow. where: V is the flow velocity, D is a characteristic linear dimension, (travelled length of the fluid; hydraulic diameter etc.)
How do you calculate Reynolds number in English units?
The Reynolds Number formula is: “Re = VDρ/μ” or “Re = VD/v” where “V” is the fluid velocity, “D” is the characteristic distance, “ρ” is the fluid density, “ν” is the kinematic viscosity, and “μ” is the dynamic viscosity both of which can be acquired from data tables.
What is the Reynolds number?
The Reynolds number represents the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces and is a convenient parameter for predicting if a flow condition will...
How is the Reynolds number calculated?
Determine the type of flow (internal, external, steady-state etc.). Choose or calculate the characteristic linear dimension From tables, determine...
At what Reynolds number is turbulent flow?
For external flow, if the Reynolds number is greater than 3500, the flow is turbulent.
What is the critical Reynolds number?
The critical Reynolds number is associated with the laminar-turbulent transition, in which a laminar flow becomes turbulent. This is an extraordina...
What are applications of the Reynolds number?
Reynolds number plays an important part in calculations in fluid dynamics and heat transfer problems. It is essential for calculation of the fricti...
What is the Reynolds number of a fish?
For most fish, the Reynolds number is in the range of 1 × 10 5, for a human it is in the range of 1 × 10 6. At higher Reynolds numbers, an object is able to force its way through a flow field even across the streamlines.
What is the Reynolds number of a small organism?
As an example, for very small organism, e.g., bacteria, the Reynolds number is very small, typically in the range of 1 × 10 −6. Given the small dimensions, these objects do not have a significant inertia and are thus mainly driven by the viscous forces of the fluid.
What happens to fluid flow at high Reynolds numbers?
The flow slowly oozes around objects. At high Reynolds numbers, there are lots of accelerations and instabilities. The flow can be very chaotic and turbulent. But, interestingly, in thin layers of fluid near walls, viscosity remains important and can have a huge influence on the gross flow by triggering separation.
What is the CGS unit of viscosity?
The cgs unit of viscosity is poise (P) and this name has been used in honour of a French physiologist Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille. It is also commonly used particularly in ASTM standards, as centipoise (cP). The cgs unit for kinematic viscosity is stok.
What is the SI unit of mass?
If you mean its SI unit of mass then it is the kilogram. Its abbreviation is kg. If you mean its volume, then its SI unit is the cubic meter or m^3. If you mean its density, then the SI unit is kilogram per cubic meter or kg/m^3. If you mean the amount of the substance, then its SI unit is the mole.
Is Reynolds number important in industrial flow?
However, for industrial situations involving external flow, Reynolds number is a very important index. Say you are testing flow over a wing of an Aircraft, and you would like to measure the flow charasitics past the aerofoil for various Reynolds numbers.
Do you get the same answer if you work in SI, or American, or Imperial units?
Making sure you get the same answer is a great way to confirm that you understand how to work with units properly. Usually values called numbers or ratios are unitless or what we call dimensionless. Like Avogadro’s number.
Is Reynolds number based on thickness?
One way to think about this is that the length scale in the boundary layer is very small, so a Reynolds number based on the boundary layer thickness (instead of the gross size of the object) is low , indicating that viscosity is still important.
Article Summary & FAQs
The Reynolds number represents the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces and is a convenient parameter for predicting if a flow condition will be laminar or turbulent. It is defined as a characteristic length multiplied by a characteristic velocity and divided by the kinematic viscosity.
Reynolds Number
The Reynolds number represents the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces and is a convenient parameter for predicting if a flow condition will be laminar or turbulent. It is defined as a characteristic length multiplied by a characteristic velocity and divided by the kinematic viscosity.
History of Reynolds Number
The concept was introduced by George Stokes in 1851, but Arnold Sommerfeld named the Reynolds number in 1908 after Osborne Reynolds (1842–1912), who performed exhaustive experiments in the 1880s. Osborn Reynolds discovered that the flow regime depends mainly on the ratio of the inertia forces to viscous forces in the fluid.
Critical Reynolds Number
The Reynolds number at which the flow becomes turbulent is called the critical Reynolds number. The value of the critical Reynolds number is different for different geometries.
Reynolds Number Regimes
Laminar flow. For practical purposes, if the Reynolds number is less than 2000, the flow is laminar. The accepted transition Reynolds number for flow in a circular pipe is Red,crit = 2300.
Reynolds Number and Internal Flow
The configuration of the internal flow (e.g., flow in a pipe) is a convenient geometry for heating and cooling fluids used in energy conversion technologies such as nuclear power plants.
Hydraulic Diameter
Since the characteristic dimension of a circular pipe is an ordinary diameter D and especially reactors contain non-circular channels, the characteristic dimension must be generalized.
What is Reynolds Number? Definition
The dimensionless Reynolds number is important in predicting trends in fluid behavior. The Reynolds number, abbreviated as Re, determines whether the fluid flow is laminar or turbulent.
Equation or Formula of Reynolds Number & Units
Reynolds number determines whether a fluid flow will be laminar or turbulent by taking into account numerous parameters such as velocity, length, viscosity, and flow type. It is defined as the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces and may be stated in terms of units and parameters, as shown below:
Reynolds Number Fluid Flow in Pipe (Closed Channel)
When fluid is flowing through a pipe there is a difference in the pattern of fluid flow, it can be smooth that is laminar or filled with eddies that are turbulent this can be defined in Reynolds number format as follows:
Reynolds Number for Laminar and Turbulent Flow
Depending on the velocity and viscosity of the fluid, laminar flow or turbulent flow may occur when a fluid flows through a pipe or in between two flat plates or simply we can say within a closed channel.
Reynolds Number for an Open Channel
Fluid flow having a free surface open to the atmosphere is referred to as open channel flow. Streams, rivers, and conduits are just a few examples. Open channel flow presumes that the pressure at the surface is constant and that the hydraulic grade line is located at the fluid’s surface.
Reynolds Number for a Flying Object
Just like fluid flows in a pipe or an open channel, we have air as a fluid flowing abundantly with varied pressure in the atmosphere. This air obstructs the path of a flying object such that the object needs to shear through the fluid to fly smoothly.
Reynolds Number for an Object Immersed in a Fluid
In a viscous fluid, a moving item is comparable to a stationary item in a flowing fluid stream. The flow of a static fluid around a moving object might be laminar, turbulent, or a mixture of the two.
What is Reynolds number?
We know that Reynolds Number (Re)=inertia force/viscous force. When viscous force dominates over the inertia force, the flow is smooth and at low velocities; the Reynolds Number value is comparatively less and flow is known as laminar flow. On the other hand, when inertia force is dominant, the value of Reynolds number is comparatively higher ...
Who invented Reynolds number?
The concept of Reynold’s number was introduced by George Stokes in 1851. However, the name “Reynolds Number” was given with the name of the British physicist Osborne Reynolds, who popularized its use in 1883. The Reynolds number depends on the relative internal movement due to different fluid velocities.
What does Reynolds number 2100 mean?
“2100<Reynolds Number (Re)<4000” indicates flow transition from laminar to turbulent and the flow consists of a mixed behavior. However, note that the value of Reynolds number (Re) at which turbulent flow begins is dependent on the geometry of the fluid flow, which is different for pipe flow and external flow.
What is the Reynolds number associated with the laminar-turbulent transition?
The Reynolds number associated with the laminar-turbulent transition is known as the Critical Reynolds Number . This laminar to turbulent transition is a highly complicated process, which is not yet fully understood.
Is Reynolds number dimensionless?
As the Reynolds Number is the ratio of two forces, there is no unit of Reynolds Number. So, Reynold’s Number is dimensionless.
History
Osborne Reynolds (1842-1912), Irish-British physicists and engineer, published a famous paper in 1883, "An experimental investigation of the circumstances which determine whether the motion of water shall be direct or sinuous, and the law of resistance in parallel channels" in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.
Reynolds Number Units
The Reynolds number is unitless and dimensionless. That it is unitless means that it has no direct standard of measurement, the Reynolds number is determined by the properties of fluid flow.
Turbulent Flow and Laminar Flow
The Reynolds number describes the dynamics of a fluid flow as either laminar or turbulent. Lower Reynolds numbers correspond to laminar flows; higher Reynolds numbers correspond to turbulent flows. Between these two regimes is a critical Reynold number, which is described in the next section.
Experimental Set-up
In this experiment, the dependency of laminar and turbulent flow on the velocity of water in a pipe is tested.
What is Reynolds number?
The Reynolds number is the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces exerted on a fluid which is in relative motion to a surface. On one hand, inertial forces generate fluid friction which is a factor in developing turbulent flow. On the other hand, viscous forces counteract this effect and progressively inhibit turbulence.
Is Reynolds number a non-dimensional factor?
Although the Reynolds number can be defined in several different ways, it remains a non-dimensional factor.
Overview
Derivation
The Reynolds number can be obtained when one uses the nondimensional form of the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations for a newtonian fluid expressed in terms of the Lagrangian derivative:
Each term in the above equation has the units of a "body force" (force per unit volume) with the same dimensions of a density times an acceleration. Each te…
Definition
The Reynolds number is the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces within a fluid which is subjected to relative internal movement due to different fluid velocities. A region where these forces change behavior is known as a boundary layer, such as the bounding surface in the interior of a pipe. A similar effect is created by the introduction of a stream of high-velocity fluid into a low-velocity fluid, such …
History
Osborne Reynolds famously studied the conditions in which the flow of fluid in pipes transitioned from laminar flow to turbulent flow. In his 1883 paper Reynolds described the transition from laminar to turbulent flow in a classic experiment in which he examined the behaviour of water flow under different flow velocities using a small stream of dyed water introduced into the centre of clear water fl…
Flow in a pipe
For flow in a pipe or tube, the Reynolds number is generally defined as
where
• DH is the hydraulic diameter of the pipe (the inside diameter if the pipe is circular) (m),
• Q is the volumetric flow rate (m /s),
Laminar–turbulent transition
In boundary layer flow over a flat plate, experiments confirm that, after a certain length of flow, a laminar boundary layer will become unstable and turbulent. This instability occurs across different scales and with different fluids, usually when Rex ≈ 5×10 , where x is the distance from the leading edge of the flat plate, and the flow velocity is the freestream velocity of the fluid outside the boundary layer.
Flow in a wide duct
For a fluid moving between two plane parallel surfaces—where the width is much greater than the space between the plates—then the characteristic dimension is equal to the distance between the plates. This is consistent with the annular duct and rectangular duct cases above taken to a limiting aspect ratio.
Flow in an open channel
For flow of liquid with a free surface, the hydraulic radius must be determined. This is the cross-sectional area of the channel divided by the wetted perimeter. For a semi-circular channel, it is quarter the diameter (in case of full pipe flow). For a rectangular channel, the hydraulic radius is the cross-sectional area divided by the wetted perimeter. Some texts then use a characteristic dimension that is four times the hydraulic radius, chosen because it gives the same value of Re f…