Full Answer
Is there a medical definition for'profuse bleeding'?
Whilst there is no specific medical definition for 'profuse bleeding', the term can be broken into two parts and still make sense.
What is blood perfusion?
Blood perfusion. A physiological term that refers to the process of nutritive delivery of arterial blood to a capillary bed in the biological tissue.
What are the causes of profuse bleeding?
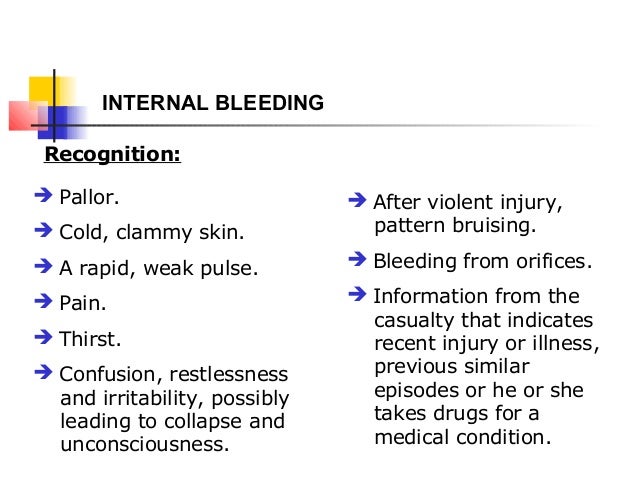
Aside from skin damage, there are a number of internal malfunctions that can lead to profuse bleeding, which will manifest itself as the appearance of blood in a person's excrement or urine, or as a leak of blood from some orifices.
What is arterial bleeding?
Arterial bleeding is the most severe and urgent type of bleeding. It can result from a penetrating injury, blunt trauma, or damage to organs or blood vessels. Because the blood comes from the arteries, it is distinctive from the other types of bleeding.
What is perfused bleeding?
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue.
What does perfused mean in medical terms?
Listen to pronunciation. (per-FYOO-zhun) Bathing an organ or tissue with a fluid. In regional perfusion, a specific area of the body (usually an arm or a leg) receives high doses of anticancer drugs through a blood vessel.
How would you define perfusion?
Perfusion is defined as the passage of fluid through the lymphatic system or blood vessels to an organ or a tissue.
Does perfusion mean blood flow?
Perfusion is the volume of blood flowing through certain mass (or volume) of tissue per unit time. Blood flow is usually given in units mL/(100 g * min) or mL/(mL * min).
What is another word for perfusion?
•Other relevant words: (noun) insertion, intromission, introduction.
What does perfusion mean in nursing?
Perfusion is defined as the passage of fluid through the lymphatic system or blood vessels to an organ or a tissue.
What is the difference between perfusion and hypoperfusion?
Hypoperfusion refers to the condition wherein there is a decreased perfusion (blood flow) in an organ or tissue. Hyperperfusion, in contrast, is one in which there is an increased perfusion. Related term(s): lung perfusion agents.
What are the two types of perfusion?
Definition of Perfusion Peripheral perfusion is passage (flow) of blood to the extremities of the body. Central perfusion is passage (flow) of blood to major body organs, including the heart and lungs.
What is an example of perfusion?
Perfusion definition The injection of fluid into a blood vessel in order to reach an organ or tissues, usually to supply nutrients and oxygen. The injection of fluid into a blood vessel in order to reach an organ or tissues, usually to supply nutrients and oxygen. The act of perfusing.
What causes perfusion?
Tissue perfusion is dependent on blood flow. The three major factors affecting blood flow are the circulating volume, cardiac pump function, and the vasomotor tone or peripheral vascular resistance. The interplay of these three factors can be seen in the formula for cardiac output (CO):
What is local perfusion?
Local/Tissue perfusion: the volume of blood that flows through arteries and capillaries to the target tissues.
What is impaired perfusion?
Causes of Impaired Tissue Perfusion Any condition that limits blood flow can cause reduced perfusion to vital organs and distal extremities. This reduced blood flow can result in tissue death, leading to organ damage, loss of limb, or even patient death.
What does "perifuse" mean?
To force blood or other fluid to flow from the artery through the vascular bed of a tissue or to flow through the lumen of a hollow structure (for example, an isolated renal tubule). Compare: perifuse, superfuse.
What is the purpose of a vascular bed?
To force blood or other fluid to flow from an artery through the vascular bed of a tissue or to flow through the lumen of a hollow structure (e.g., an isolated renal tubule).
Intracranial bleeding
This occurs when a blood vessel inside the cranium, or skull, ruptures and bleeds around or into the brain. It usually is due to long-term high blood pressure, which causes weakening of the arterial walls.
Pleural cavity bleeding
The pleural cavity is the space surrounding the lungs. When bleeding occurs here, it interferes with normal lung expansion, which can affect the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the blood.
Abdominal bleeding
This refers to bleeding in the large cavity of the torso, which contains organs such as the stomach, liver, and kidneys.
Bleeding from bone fractures
Bones feature an extensive network of blood vessels. This means that sustaining a bone fracture can result in life threatening bleeding — particularly if the fracture occurs in a long bone, such as the humerus, radius, ulna, femur, fibula, or pelvis.
Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract
Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract has many possible causes, such as a tumor or inflammation of the colon, stomach, or esophagus.