How do you write the standard enthalpy of formation equation?
What are the types of enthalpy?
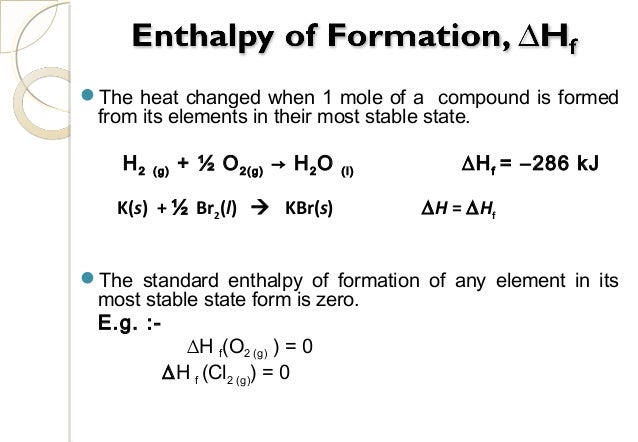
- Heat of formation. The enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of compound is formed from its elements.
- Heat of combustion. The enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of compound is completely burnt in excess of air or oxygen.
- Heat of neutralization.
- Heat of solution.
How to calculate standard enthalpy?
Solution:
- Let us assume that the carbon is in its standard state of graphite (as opposed to diamond or buckminsterfullerene). ...
- We must look up the standard enthalpy of formation for the other two substances: ΔH f, Fe 2 O 3 o = −825.50 kJ/mol ( source ) ΔH f, ...
- Hess' Law: ΔH rxn o = Σ ΔH f, products o − Σ ΔH f, reactants o
- Sustitute values into equation:
What is the standard energy of formation?
• The standard Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔG° f ) is the free energy change for a reaction producing one mole of a substance from the elements, with all components in standard state. • As temperature changes, ΔG also changes.
What is the standard heat of formation?
The standard heat of formation is defined as the amount of heat absorbed or evolved at 25° C (77° F ) and at one atmosphere pressure when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements, each substance being in its normal physical state (gas,…
What is the standard enthalpy of formation of an element?
zeroThe standard enthalpy of formation of a substance is the enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mole of the substance is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states. A pure element in its standard state has a standard enthalpy of formation of zero.
How does enthalpy of formation relate to stability?
Enthalpy of formation (heat of formation; ΔHfo): The hypothetical enthalpy change (ΔH) when a substance is synthesized from the corresponding elements in their standard states. A more negative (or less positive) enthalpy of formation indicates a more stable isomer.
Why is the standard enthalpy of formation of an element 0?
The enthalpy of formation for an element in its elemental state will always be 0 because it takes no energy to form a naturally-occurring compound.
Does lower enthalpy of formation mean more stable?
Higher enthalpy means heat had to be absorbed to form the substance, which makes the substance a higher-energy compound. High energy compounds tend to be more reactive, therefore less stable.
Which heat formation is more stable?
The sum of the heats of formation and combustion in this example are the same. If you have a more negative heat of formation, i.e., more stable, you have a smaller heat of combustion.
Does higher heat of formation mean more stable?
The heats of formation therefore permit precise comparison of the stability of isomeric compounds. The more negative the heat of formation, the greater is the stability.
Which of the following standard enthalpy of formation is zero?
We calculate standard enthalpies of carbon compounds with reference to graphite. So, standard enthalpy is zero for graphite.
Which substance has a standard enthalpy of formation of zero?
Which substance has an enthalpy of formation of zero? N2(g) (The enthalpy of formation of an element in its standard state is zero.
When enthalpy of formation is considered the stable form of carbon is assumed?
Graphite is thermodynamically the most stable form of carbon. Its standard enthalpy of formation is thus taken as zero.
Which of the energy from is more stable?
The lower the potential energy of the system, the more stable it is. Chemical processes usually occur because they are thermodynamically favourable. "Thermodynamically favourable" means from high energy to low energy, or, put another way, from less stable to more stable.
Does more exothermic mean more stable?
In the case of an exothermic reaction, the reactants are at a higher energy level as compared to the products, as shown below in the energy diagram. In other words, the products are more stable than the reactants.
Why is lower energy more stable?
Answer: From chemical point of view, a molecule will be stable if there are more attractive forces and less repulsive forces. Repulsive forces increases the potential energy of the molecule. Hence molecules with lower energy are more stable.
Standard Enthalpy of Formation
A standard enthalpy of formation ΔH ∘ f Δ H f ° is an enthalpy change for a reaction in which exactly 1 mole of a pure substance is formed from free elements in their most stable states under standard state conditions.
Example: Evaluating an Enthalpy of Formation
Ozone, O 3 ( g ), forms from oxygen, O 2 ( g ), by an endothermic process. Ultraviolet radiation is the source of the energy that drives this reaction in the upper atmosphere.
Solution
ΔH ∘ f Δ H f ° is the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a substance in its standard state from the elements in their standard states. Thus, ΔH ∘ f Δ H f ° for O 3 ( g) is the enthalpy change for the reaction:
What is the standard enthalpy of formation for an element in its standard state?
The standard enthalpy of formation for an element in its standard state is zero.
What is the enthalpy of a standard state?
The standard enthalpy of formation for an element in its standard state is ZERO!!!! Elements in their standard state are not formed, they just are. So, ΔHfofor C (s, graphite) is zero, but the ΔHfofor C (s, diamond) is 2 kJ/mol. That is because graphite is the standard state for carbon, not diamond.
What is the enthalpy of Br2in?
An example: the enthalpy of formation for Br2in its standard state is zero. The enthalpy of formation for Br (monoatomic gas) is 111.881 kJ/mol. This is because Br (monoatomic gas) is not bromine in its standard state. Only Br2(diatomic liquid) is. (2) There is never a compound on the reactant side, only elements.
What does the symbol ° mean in chemistry?
The subscripted "f" is taken to mean formation when used in the thermochemistry area. (There are other uses of a subscripted "f," however the differences in context will be obvious.) The symbol "°" is taken to mean "standard conditions." (Yes, I know that symbol is also used for degrees Celsius. Context is all important!!!!)
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?
Exothermic chemical reactions will have a negative ΔH and endothermic reactions have a positive ΔH. The reason for the sign convention has to do with chemistry's viewpoint of the system and the surroundings.
What is a formation reaction?
Once again, a formation reaction involves making a substance from its elements and ONLY the elements.
Is the standard enthalpy still being determined?
By the way, standard enthalpies of various substance s are still being determined. Hereis an example from 2007. Values of this type remain in the professional literature and are incorporated into future editions of standard reference sources.
What is the standard enthalpy of formation?
The standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its constituent elements, with all substances in their standard states. For an element: the form in which the element is most stable under 1 bar of pressure.
What is enthalpy in physics?
It is the sum of the internal energy added to the product of the pressure and volume of the system. It reflects the capacity to do non-mechanical work and the capacity to release heat. Enthalpy is denoted as H; specific enthalpy denoted as h.
What is the enthalpy of combustion?
Standard enthalpy of combustion is defined as the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is completely burnt in oxygen gas at 298K and 1 bar pressure.