- Calculate the mean (simple average of the numbers).
- For each number: Subtract the mean. Square the result.
- Calculate the mean of those squared differences. This is the variance.
- Take the square root of that to obtain the population standard deviation.
How do you calculate point of estimate?
Use the point estimate formulas:
- MLE = S / T = 92 / 100 = 0.92.
- Laplace = (S + 1) / (T + 2) = 93 / 102 = 0.9118.
- Jeffrey = (S + 0.5) / (T + 1) = 92.5 / 101 = 0.9158.
- Wilson = (S + z²/2) / (T + z²) = (92 + (-1.6447)²/2) / (100 + (-1.6447)²) = 0.9089.
What is the formula for calculating standard deviation?
Formulas for Standard Deviation. Population Standard Deviation Formula. σ = √ ∑(X−μ)2 n σ = ∑ ( X − μ) 2 n. Sample Standard Deviation Formula. s =√ ∑(X−¯X)2 n−1 s = ∑ ( X − X ¯) 2 n − 1.
What is the difference between population and standard deviation?
• Population standard deviation is the exact parameter value used to measure the dispersion from the center, whereas the sample standard deviation is an unbiased estimator for it. • Population standard deviation is calculated when all the data regarding each individual of the population is known. Else, the sample standard deviation is calculated.
How do you calculate standard deviation on a calculator?
- Sx shows the standard deviation for a sample, while σx shows the standard deviation for a population. ...
- A lower standard deviation value means that the values in your list don't vary much from the mean, while a higher value means your data is more spread out.
- x̄ represents the mean, or average, of the values.
- Σx represents the sum of all values.
How do you find the point estimate of a population standard deviation?
Population standard deviationStep 1: Calculate the mean of the data—this is μ in the formula.Step 2: Subtract the mean from each data point. ... Step 3: Square each deviation to make it positive.Step 4: Add the squared deviations together.Step 5: Divide the sum by the number of data points in the population.More items...
What is the estimated population standard deviation?
The population standard deviation a measures the spread of a vector in ℝn. It is defined to be the square root of the population variance of the vector. The sample standard deviation s is defined to the square root of the sample variance of the vector.
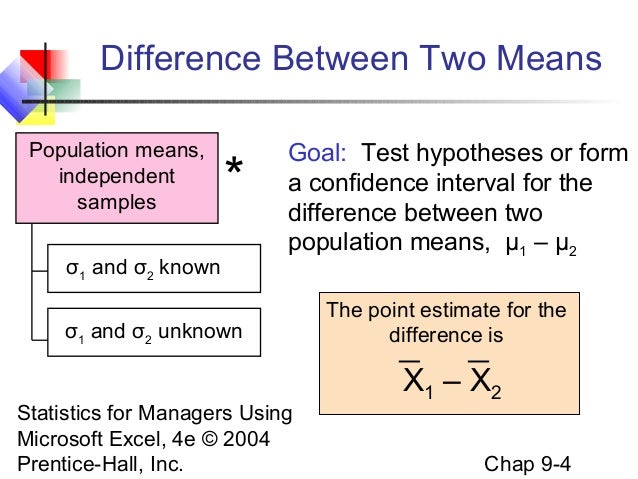
What is the point estimate of the population mean?
A point estimate of the mean of a population is determined by calculating the mean of a sample drawn from the population. The calculation of the mean is the sum of all sample values divided by the number of values.
What is the best point estimate for the population standard deviation?
So the best point estimate for the population standard deviation is a sample standard deviation. In this problem, we are told the sample variance is 1.5.
What is the purpose of standard deviation?
Standard deviation tells you how spread out the data is. It is a measure of how far each observed value is from the mean.Sep 26, 2018
How do you find the point estimate with the mean and standard deviation?
0:203:04Point Estimate Definition & Example - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet me show you a few examples the sample standard deviation s is a point estimate for theMoreLet me show you a few examples the sample standard deviation s is a point estimate for the population standard deviation sigma the sample mean x bar is a point estimate for the population mean mu.
How do you find the point estimate?
How to find the point estimate?Determine the total number of coin tosses - this will be the number of trials T. Let's assume T = 100.Count the number of times that you got heads. ... Decide on your confidence interval. ... The point estimate calculator will find the z-score for you. ... Use the point estimate formulas:
What is a point estimate in stats example?
Point estimate. A point estimate of a population parameter is a single value of a statistic. For example, the sample mean x is a point estimate of the population mean μ. Similarly, the sample proportion p is a point estimate of the population proportion P.
What is the point estimate for this 95 confidence interval?
The point estimate for the population proportion is the sample proportion, and the margin of error is the product of the Z value for the desired confidence level (e.g., Z=1.96 for 95% confidence) and the standard error of the point estimate.
What is point estimation and interval estimation?
A point estimate is a single value estimate of a parameter. For instance, a sample mean is a point estimate of a population mean. An interval estimate gives you a range of values where the parameter is expected to lie. A confidence interval is the most common type of interval estimate.
What is a point estimate quizlet?
Point Estimate. The value of a sample statistic that is used to estimate a population parameter is called a point estimate.
How do you find the point estimate of a population on a TI 84?
2:216:53How to Find the Point Estimate for the Mean TI 84 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo anytime that it tells you to find a point estimate for the mean all that's telling you to do isMoreSo anytime that it tells you to find a point estimate for the mean all that's telling you to do is find x-bar.
How to find the true value of a population?
To estimate the true value for a population, we take samples from the population and use the statistics obtained from the samples to estimate the parameter. Here are a few examples of point estimates and when you might use each one: 1 Sample means are used to find the center of continuous data. 2 Sample proportions are used to find the mean part or share per whole. 3 Sample standard errors describe the spread of data for means and proportions.
What is bias in statistics?
Bias - skewing of a statistical results due to a limited sample; causes the researcher to over or underestimate the center of the data. Variability - lack of consistency of sample; ex. repeated samples that do not give similar results but differ widely among themselves.
What are the factors that affect the accuracy of an arrow?
Just as wind and direction are important factors to your arrow's accuracy, so are bias and variability important factors to the accuracy of a researcher's point estimate. High bias throws off the estimate causing the researcher to over or underestimate the center of the data.
How to find the point estimate?
This point estimate calculator is very useful, especially in finding point estimate statistics. The best thing about this online tool is that it’s very easy to use. If you need to find the most accurate point estimates, follow these steps: 1 First of all, enter the value for the Number of Successes. 2 Then enter the value for the Number of Trials. 3 Finally, enter the value for the Confidence Interval which is a percentage value. 4 These are the only values needed by this calculator to give you the point estimate statistics. After entering all of the required values, the calculator will generate a number of results including the Best Point Estimation, the Maximum Likelihood Estimation, the Laplace Estimation, Jeffrey’s Estimation, and the Wilson Estimation.
Is a statistic a point estimate?
Using the simplest definition, any statistic can also be a point estimate. This is because a statistic serves as an estimator of a given parameter in a population. Consider these examples: A sample standard deviation “s” is the point estimate of a population standard deviation “σ.”.
Can you use a point estimate calculator to calculate a biased coin?
After you have tossed your biased coin for a certain number of times and you’ve collected enough data pertaining to the “behavior” of the coin, you can use that data when using the point estimate calculator. Of course, you can also perform the calculations manually then check the results with the calculator.
How to calculate population standard deviation?
Population standard deviation. Step 1: Calculate the mean of the data—this is in the formula. Step 2: Subtract the mean from each data point. These differences are called deviations. Data points below the mean will have negative deviations, and data points above the mean will have positive deviations.
How to find the mean of a data point?
Step 1: Calculate the mean of the data—this is in the formula. Step 2: Subtract the mean from each data point. These differences are called deviations. Data points below the mean will have negative deviations, and data points above the mean will have positive deviations.
The Importance of Representative Samples
When we collect a sample from a population, we ideally want the sample to be like a “mini version” of our population.
Point Estimates & Confidence Intervals
Although a point estimate represents our best possible estimate of some true population parameter, it’s unlikely that it will exactly match the population parameter.
What is an interval estimate?
An interval estimate is a type of estimation that uses a range (or interval) of values, based on sampling information, to “capture” or “cover” the true population parameter being inferred / estimated.
What is inferential statistics?
Ok, so we’ve discussed the fact that inferential statistics is a collection of methods that allow us to make inferences about a population based on information obtained from a sample of data.