oral-aboral axis of the embryo DEFINITON: Axis that runs from the oral pole and to the aboral pole of the spherical embryo (Stage 3 through early Stage 6). The oral pole is centered around the embryonic pharynx; the aboral pole is located opposite the embryonic pharynx.
How is the oral aboral axis established?
Beside this, how is oral Aboral axis established? In embryos of indirectly developing echinoids, the secondary (oral–aboral) larval axis is established after fertilization by an as yet undiscovered process. Effective entrainment of the oral–aboral axis requires that the embryos remain immobilized in rosettes until the hatching blastula stage.
What is the aboral direction?
What is Aboral direction? , aboral (ab-ō'rad, -răl), In a direction away from the mouth; opposite of orad. Click to see full answer.
What is the difference between the oral and aboral pole?
The oral pole is centered around the embryonic pharynx; the aboral pole is located opposite the embryonic pharynx. Click on the '-' and '+' to collapse and expand term 'is a' and 'part of' relationships. Dynamically explore this term by selecting additional relationships to display (checkboxes on the right).
Where is the oral axis of the embryo located?
oral-aboral axis of the embryo DEFINITON: Axis that runs from the oral pole and to the aboral pole of the spherical embryo (Stage 3 through early Stage 6). The oral pole is centered around the embryonic pharynx; the aboral pole is located opposite the embryonic pharynx.
How is the oral-Aboral axis defined in cnidaria?
We have investigated how the oral-aboral axis is established in the hydrozoan jellyfish Podocoryne carnea. Vital labeling experiments showed that the oral end of the blastula derives from the animal pole region of the egg as has been demonstrated for other cnidarian species.
What is the Aboral side?
: situated opposite to or away from the mouth.
How do you tell the difference between the Aboral and oral surfaces?
The body is divided into a central disk from which radiate five arms. The principal body axis, and the axis of symmetry, is the short oral-aboral axis, which passes vertically through the center of the disk. The animal's pale lower side is the oral surface and the dark upper side is the aboral surface.
What controls the oral-Aboral axis formation in sea urchins?
In the sea urchin embryo, the oral-aboral axis is specified after fertilization by mechanisms that are largely unknown. We report that early sea urchin embryos express Nodal and Antivin in the presumptive oral ectoderm and demonstrate that these genes control formation of the oral-aboral axis.
What is oral side and Aboral side?
Explanation: Sea stars have two surfaces: the oral and the aboral. The oral is the side with the sea star's mouth and most people would think of it as the "bottom." The aboral is the opposite side, and this is where the madreporite lies. The madreporite is the opening to the water vascular system.
What is Aboral direction?
ab·o·rad. , aboral (ab-ō'rad, -răl), In a direction away from the mouth; opposite of orad.
What is Aboral surface?
In biology, aboral surfaces are surfaces away from or opposite the mouth. The term is a compound of the Latin preposition ā, a, abs, meaning from or away from and the noun ōs, ōris n., meaning mouth. It is also the opposite of oral which is the end containing the mouth of a radially symmetrical animal.
How would you distinguish the oral and Aboral sides of a sea star?
Questions: Answer: The aboral side of a sea star contains the madreporite while the oral side of a sea star contains the star's mouth and is located on the “bottom” of the sea star. Answer: The madreporite filters water into the sea star's vascular system.
What does Aboral mean in zoology?
away from or opposite the mouthaboral. / (æbˈɔːrəl) / adjective. zoology away from or opposite the mouth.
What is the axis specification of an embryo?
Axis specification is the symmetry breaking process that initiates pattern formation in a developing embryo. Axial polarities can be specified either cell-autonomously, by spatial localization and subsequent segregation of molecular determinants among dividing cells (‘preformation’), or conditionally, by way of self-organizing processes that depend on stochastic anisotropies and intercellular signaling (‘epigenesis’). Although axis specification in animals involves varying combinations of preformation and epigenesis, many deuterostome embryos are spectacularly regulative, a hallmark of conditional epigenetic specification. A protein that plays a recurring role in deuterostome axis specification is Nodal, a member of the TGFβ family of extracellular signaling ligands. Nodal locally activates both its own expression as well as that of its more diffusible extracellular antagonist Lefty, thus embodying an epigenetic system of short-range activation and long-range inhibition (Juan and Hamada, 2001; Chen and Schier, 2002; Solnica-Krezel, 2003; Duboc et al., 2008). Such systems provide for the self-organization of defined spatial patterns from subtle anisotropies that are present or which arise stochastically within relatively homogeneous precursors (Turing, 1952; Gierer and Meinhardt, 1972).
What are the two axis of differentiation in sea urchins?
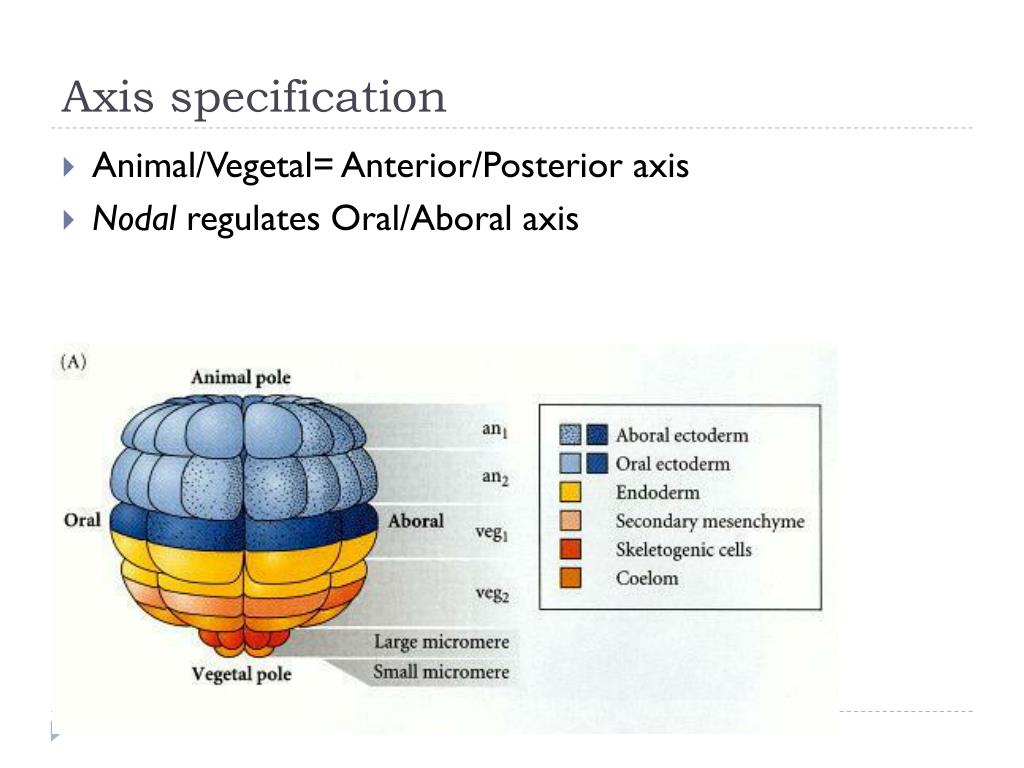
In the bilaterally symmetric sea urchin embryo, cell differentiation occurs along two orthogonal axes: the maternally determined animal-vegetal axis, along which respectively differentiate ectoderm , endoderm, and mesoderm; and the conditionally specified oral-aboral (OA) axis, along which differentiate oral ecto derm, ciliated band ectoderm, and aboral ectoderm, as well as various mesodermal cell types. Specification of oral ectoderm is initiated by the zygotic activation of nodal(Duboc et al., 2004). Following its initial activation, nodalexpression is amplified by way of a positive feedback ‘community effect’ involving Nodal signaling, which also activates lefty, whose expression is required to confine nodalactivity to prospective oral ectoderm in the early to mid-blastula stage embryo (Duboc et al., 2004; Nam et al., 2007; Range et al., 2007). Although the spatial information underlying the initial anisotropy in nodalexpression has not been fully elucidated, a strong candidate is an asymmetric distribution of mitochondria that prefigures the prospective OA axis, which could regulate the activities of maternal transcription factors required for nodalactivity (Coffman and Davidson, 2001; Coffman et al., 2004). This regulation likely involves p38, a stress-activated protein kinase that responds to reactive oxygen species (Torres and Forman, 2003), and whose inhibition has been shown to suppress nodalexpression and hence development of oral ectoderm (Bradham and McClay, 2006).
What is the C-terminal sequence of OMP-25?
The C-terminal sequence of OMP-25 targets GFP to mitochondria. (A) Wide-field images comparing appearance of blastula-stage embryos expressing unmodified GFP and GFP fused to the C-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence of OMP25, translated from injected mRNA. (B) Overlapping subcellular localization of GFP-OMP25 (green) and MitoTracker (red). Arrows show colocalization of the two signals on globular and filamentous structures. Bar = 10 μM. The dashed line shows the profile that is quantified in (C). (C) Pixel intensities of GFP (green) and MitoTracker (red) signals plotted along the horizontal line shown in the merged image in (B), using Zeiss software.
Does nodal 5P-GFP have a spatial correlation?
It is possible that the relative weakness of the spatial correlation between nodal-5P-GFPexpression and mitochondrial density results from irregularities associated with microinjection and/or expression of the exogenous transgene reporter. In addition, nodalappears ab initioto be expressed broadly in a gradient (Duboc et al., 2004; Flowers et al., 2004; Range et al., 2007), and given the long half-life of GFP, this would tend to randomize the mosaic expression pattern of the reporter at early blastula stage. In light of these possibilities we used phospho-Smad2/3 immunofluorescence staining (Yaguchi et al., 2007) to further examine the correlation between nodalactivity and mitochondrial distribution. As shown previously (Yaguchi et al., 2007), phospho-Smad2/3 signal was found to be confined to nuclei on one side of early blastula stage (13 hr) embryos (Fig. 1D). In a significant majority of embryos (74/102; P=5×10−6) the side containing nuclear phospho-Smad2/3 displayed a higher than average MitoTracker intensity compared to the embryo as a whole (Fig. 1D, E). These data further indicate that mitochondrial density and nodalactivity are positively correlated in the early embryo.
What is the aboral surface?
Freebase. Aboral. In biology, aboral surfaces are surfaces away from or opposite the mouth. The term is a compound of the Latin preposition ā, a, abs, meaning from or away from and the noun ōs, ōris n., meaning mouth. It is also the opposite of oral which is the end containing the mouth of a radially symmetrical animal
What is the ambulacral?
: of, relating to, or being any of the radial areas of echinoderms along which run the principal nerves, blood vessels, and elements of the water-vascular system ambulacral grooves.