Which is more important fluid intake or fluid output?
The person is said to be in negative fluid balance if his output is greater than his intake. Conversely, a positive fluid balance occurs when intake is greater than output. If the difference is alarming, consult your doctor. Keep the chart to show to the doctor, and start a fresh one for the next 24-hours.
What is strict intake and output?
Write out the ‘Screening/Measurements’ order, Strict I/O, without abbreviations. What does this order mean? Strict intake and output. This order means that are observing everything the patient is consuming and measuring the bodily waste. 16. The medication order benztropine mesylate 1 mg/mL (Cogentin) is ordered to give 1 mg.
Should urine output be the same as fluid intake?
Typically, fluid intake is about equal to the urine output. The fluid intake that is double the urine output indicates fluid retention. The fluid intake that is half the urine output indicates dehydration.
What is daily fluid intake?
For example, water:
- Gets rid of wastes through urination, perspiration and bowel movements
- Keeps your temperature normal
- Lubricates and cushions joints
- Protects sensitive tissues
What is the typical fluid intake and output per day?
In the normal resting state, input of water through ingested fluids is approximately 1200 ml/day, from ingested foods 1000 ml/day and from aerobic respiration 300 ml/day, totaling 2500 ml/day.
What is normal fluid volume intake?
So how much fluid does the average, healthy adult living in a temperate climate need? The U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine determined that an adequate daily fluid intake is: About 15.5 cups (3.7 liters) of fluids a day for men. About 11.5 cups (2.7 liters) of fluids a day for women.
What is the ratio of fluid intake to urine output?
Median daily water intake was 1.4 L (IQR 0.67–1.94). Median 24-hour urine volume was 2.01 L (IQR 1.20–2.73). A 1 L increase in daily water intake was associated with a 710 mL increase in 24-hour urine output (95% CI 0.55–0.87).Jan 28, 2020
How do you monitor fluid intake and output?
Measure drainage in a calibrated container. Observe it at eye level and take the reading at the bottom of the meniscus. Evaluate patterns and values outside the normal range, keeping in mind the typical 24-hour intake and output. (See Fluid Gains and Losses.)
Is 500 ml of water a day enough?
Intake of more than 500 ml of fluids per day will result in the excretion of solute-free water. The recommended total daily fluid intake of 3,000 ml for men and of 2,200 ml for women is more than adequate.
How do you measure fluid intake?
0:255:17Measuring Fluid Intake - CNA State Board Exam Skill - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFor fluid intake all we're measuring is what is gone out of the container. So if this container wasMoreFor fluid intake all we're measuring is what is gone out of the container. So if this container was full at the beginning this is how much that your resident drank and that's what we care about.
Is 30 mL per hour normal urine output?
Urine output of less than 30 mL/hr (roughly 0.5 mL / kg / hour for a 70-kilogram patient) should be considered cause for concern.Aug 4, 2012
What is considered low urine output?
What is oliguria? Oliguria is a medical term for low urine output (how much you pee). In the case of an adult, this means less than 400 milliliters (mL) to 500 mL (around two cups) of urine per 24 hours. The numbers depend on weight in terms of children and infants.Dec 28, 2021
What is normal urine output per hour?
Normal urine output is defined as 1.5 to 2 mL/kg per hour …
What is intake output chart?
The intake and output chart is a tool used for the purpose of documenting and sharing information regarding the following: Whatever is taken by the patient especially fluids either via the gastrointestinal tract (entrally) or through the intravenous route (parenterally) Whatever is excreted or removed from the patient.
What is a positive fluid balance?
Positive fluid balance is a state of fluid overload resulting from fluid administration during resuscitation and subsequent therapies. Fluid overload is defined by “a cut off value of 10% of fluid accumulation as this is associated with worse outcomes” (Malbrain et al, 2014)
What are early signs of dehydration?
Symptoms of dehydration in adults and children include:feeling thirsty.dark yellow and strong-smelling pee.feeling dizzy or lightheaded.feeling tired.a dry mouth, lips and eyes.peeing little, and fewer than 4 times a day.
Introduction
Normally, the amount of total body water should be balanced through the ingestion and elimination of water: ins and outs. To ensure this balance, as a nurse, you may need to track and record all fluid intake and output on an intake and output sheet, commonly known as an I&O sheet.
Procedure
Add all fluid volumes served to that client. For example, during your shift, the client could have been served with 200 mL of water, 360 mL of soda, and 140 mL of milk. All together, these equal 700 mL ( Fig. 3a ).
Procedure
Provide these clients with urine receptacles specifically labeled with their name and bed location.
Why is the intake output chart so named?
The Intake-Output chart is so named because on one side is the Intake and the other the Output. Measurements of volume are in ml. The chart is for a 24 hour period but, for practical reasons, it does not follow the calendar day (i.e. is not from 12 Midnight to 12 Midnight of the next day).
When providing and monitoring fluid intake and output, clinical care providers use two types of forms/charts, one for
When providing and monitoring fluid intake and output, clinical care providers use two types of forms/charts, one for purposes of planning and the other for recording findings . Each type consists of different components as shown below:
What is IV fluid order?
A proper IV fluid order would indicate the type of fluid to be given, the starting time, the period it is to be administered. When properly written it also acts as the plan. It is important that the doctor prescribes the type of fluid to be given, the amount of each type, the total amount for period and the route / site planned. It would mean that the order and plan is written on the same form. The nurse needs only to calculate the rate. This arrangement is subject to policies of the hospital concerned.
How much water does a 50-90 kg person need?
The water intake of a 50-90 kg adult person is about 2500 to 3000 ml per day or 2 ml/kg/hour. Normally, this is accomplished by:
How much urine does an adult have?
Urine output in an adult is between 1000 to 1500 ml per day. Another normal means of output of water is through evaporation of water from the skin and mucous membranes (mouth, throat, respiratory tract) and also through sweating.
What happens to urine output when there is more loss?
If there is more loss, due to either higher temperature of the environment or the person’s body, then the amount of urine output is expected to be less.
Why is it important to keep IV drips in a ward?
It is very convenient for IV drip solutions to be kept as part of the ward stock, because large amounts are used especially in acute care wards. However, issues arise when additions like electrolyte such as Potassium or drugs such as inotropes (dopamine, dobutamine), heparin and antibiotics need to be added.
Why do we drink fluids?
We generally consume fluids not to quench our thirst, but as components of everyday foods (e.g. soup, milk), as beverages used as mild stimulants (tea, coffee) and for pure pleasure. As common example is alcohol consumption which can increase individual pleasure and stimulate social interaction.
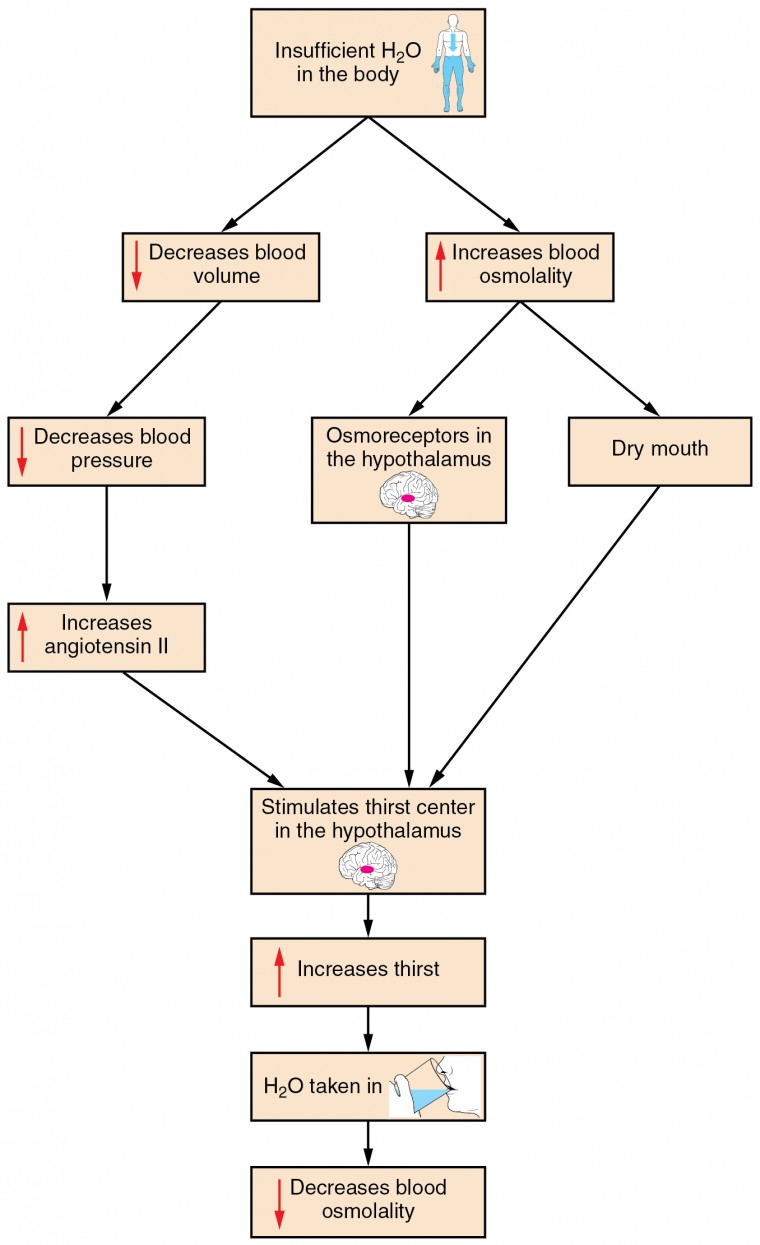
What is the main fluid regulatory process?
Apart from urinary excretion, the other main fluid regulatory process is drinking, mediated through the sensation of thirst. There are two distinct mechanisms of physiological thirst: the intracellular and the extracellular mechanisms. When water alone is lost, ionic concentration increases.
Why is hydration important?
Hydration status is critical to the body’s process of temperature control. Body water loss through sweat is an important cooling mechanism in hot climates and in physical activity. Sweat production is dependent upon environmental temperature and humidity, activity levels, and type of clothing worn.
What is the role of water in health?
In this section, the role of water in health is generally characterized in terms of deviations from an ideal hydrated state, generally in comparison to dehydration. The concept of dehydration encompasses both the process of losing body water and also the state of dehydration.
What are the effects of water consumption on energy?
B. The effects of water consumption on overall energy intake. There is an extensive literature that focuses on the impact of sugar-sweetened beverages on weight and risk of obesity, diabetes and heart disease; however the perspective of providing more water and its impact on health has not been examined.
How is fluid balance controlled?
Most of the components of fluid balance are controlled by homeostatic mechanisms responding to the state of body water. These mechanisms are sensitive and precise, and are activated with deficits or excesses of water amounting to only a few hundred milliliters.
How long can a human live without water?
Without water, humans can survive only for days. Water comprises from 75% body weight in infants to 55% in elderly and is essential for cellular homeostasis and life.1Nevertheless there are many unanswered questions about this most essential component of our body and our diet. This review attempts to provide some sense of our current knowledge ...