How many neutrons can be found in oxygen?
Stable oxygen atoms may contain 8, 9, or 10 neutrons—by far (over 99.7 %) the most common is with 8 neutrons, next (about 0.2 %) is 10 neutrons. The frequency of occurrence of these isotopes varies somewhat depending on sample.
What is the number of protons and electrons in oxygen?
Oxygen is the 8th element in the periodic table. This means that oxygen has 8 protons and 8 electrons. In order to get the number of neutrons you take the atomic weight in this case 15.9999~16 and you subtract it by the number of protons (16-8). To get the number of valence electrons just look at the numbers above the oxygen on the periodic table.
How many nucleons are in oxygen?
The key properties of an atom (like oxygen) are described by the Atomic Number (which is 8 for Oxygen) and the total number of nucleons (which is 16 for Oxygen). The atomic number gives the number of protons in the atom. The number of nucleons gives the total number of protons plus neutrons in the atom.
How many neurons protons and electrons does oxygen have?
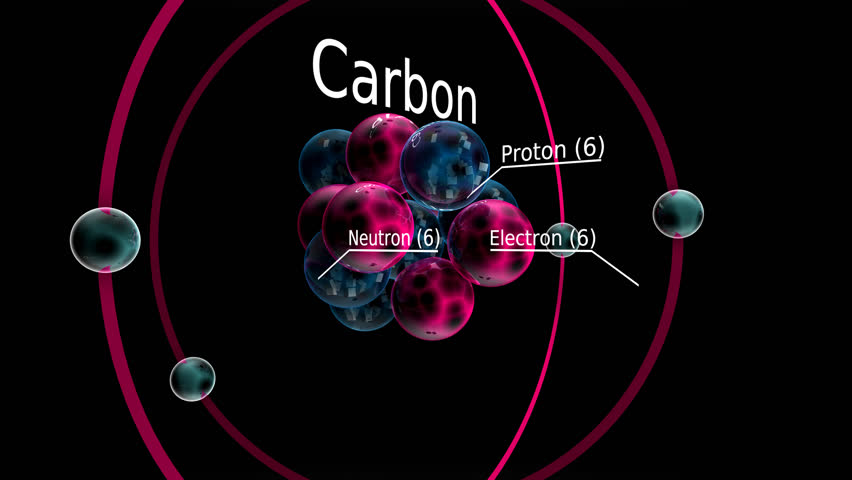
Oxygen has eight protons, eight neutrons, and eight electrons. Oxygen is different from carbon because it has more particles. Each kind of atom has a different number of the three particles. Protons and neutrons are in the center, or nucleus, of the atom.
See more
What is the neutron number of oxygen?
8 neutronsConsider oxygen, which has an atomic number (Z) of 8. This means that oxygen atoms have 8 protons. Most atoms of oxygen also have 8 neutrons.
Is oxygen 10 or 8 neutrons?
Like all elements, oxygen is made up of a nucleus of protons and neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of electrons. All oxygen atoms have 8 protons, but the nucleus might contain 8, 9, or 10 neutrons.
Does oxygen have 7 neutrons?
Most oxygen atoms also have 8 neutrons, but it is possible for an oxygen atom to have 9 or 10 neutrons.
Does oxygen have 0 neutrons?
0:404:05How to find the Number of Protons, Electrons, Neutrons for Oxygen (O)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we're going to have eight electrons for each of these isotopes of oxygen we'll talk more aboutMoreSo we're going to have eight electrons for each of these isotopes of oxygen we'll talk more about isotopes in a minute we're left with finding the neutrons.
How do u find neutrons?
For all atoms with no charge, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. The mass number, 40, is the sum of the protons and the neutrons. To find the number of neutrons, subtract the number of protons from the mass number. number of neutrons=40−19=21.
What has 8 protons and 10 neutrons?
oxygen 18Therefore, oxygen 16 has 8 protons and 8 neutrons, oxygen 17 has 8 protons and 9 neutrons, and oxygen 18 has 8 protons and 10 neutrons.
How many neutrons does oxygen 14 have?
List of isotopesNuclideZNExcitation energy14 O8615 O8716 O8823 more rows
Why is o2 neutral?
Explanation: For oxygen, Z , the atomic number =8 . There are 8 protons in its nucleus (and protons are positively charged particles). To balance this charge (the atom is electrically neutral after all), the oxygen nucleus is surrounded by 8 negatively charged electrons.
How many neutrons does oxygen 20 have?
8 neutronsThe oxygen atom has therefore 8 neutrons, 8 protons and 8 electrons.
How many electrons does 02 have?
2, 6Oxygen / Electrons per shell
What element has 9 protons and 10 neutrons?
fluorine atomsConsider fluorine atoms with 9 protons and 10 neutrons.
What is the mass number of o2?
15.999 uOxygen / Atomic mass
How many electrons are in an oxygen atom?
Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Oxygen is 8. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
How many protons are in oxygen?
Oxygen is a chemical element with atomic number 8 which means there are 8 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
What is electron configuration?
The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed ...
Why is 16O so abundant?
The relative and absolute abundance of 16O is high because it is a principal product of stellar evolution. Oxygen-17 is composed of 8 protons, 9 neutrons, and 8 electrons. Both 17O and 18O are secondary isotopes, meaning that their nucleosynthesis requires seed nuclei. Oxygen-18 is composed of 8 protons, 10 neutrons, and 8 electrons.
Why do neutrons stabilize the nucleus?
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, because they attract each other and protons , which helps offset the electrical repulsion between protons. As a result, as the number of protons increases, an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form a stable nucleus.
What happens when there are too many neutrons in a nucleus?
If there are too many or too few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is not stable and it undergoes radioactive decay . Unstable isotopes decay through various radioactive decay pathways, most commonly alpha decay, beta decay, or electron capture.
What is the total electrical charge of the nucleus?
The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze , where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A.
Who discovered oxygen?
Oxygen was isolated by Michael Sendivogius before 1604, but it is commonly believed that the element was discovered independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, in Uppsala, in 1773 or earlier, and Joseph Priestley in Wiltshire, in 1774. Priority is often given for Priestley because his work was published first.
How is oxygen gas produced?
Oxygen gas can also be produced through electrolysis of water into molecular oxygen and hydrogen. DC electricity must be used: if AC is used, the gases in each limb consist of hydrogen and oxygen in the explosive ratio 2:1. A similar method is the electrocatalytic O. 2 evolution from oxides and oxoacids.
What are the uses of oxygen?
Common uses of oxygen include production of steel, plastics and textiles, brazing, welding and cutting of steels and other metals, rocket propellant, oxygen therapy, and life support systems in aircraft, submarines, spaceflight and diving .
How do paleoclimatologists measure oxygen 18?
Paleoclimatologists measure the ratio of oxygen-18 and oxygen-16 in the shells and skeletons of marine organisms to determine the climate millions of years ago (see oxygen isotope ratio cycle ). Seawater molecules that contain the lighter isotope, oxygen-16, evaporate at a slightly faster rate than water molecules containing the 12% heavier oxygen-18, and this disparity increases at lower temperatures. During periods of lower global temperatures, snow and rain from that evaporated water tends to be higher in oxygen-16, and the seawater left behind tends to be higher in oxygen-18. Marine organisms then incorporate more oxygen-18 into their skeletons and shells than they would in a warmer climate. Paleoclimatologists also directly measure this ratio in the water molecules of ice core samples as old as hundreds of thousands of years.
How does photosynthesis release oxygen?
Photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere, while respiration, decay, and combustion remove it from the atmosphere. In the present equilibrium, production and consumption occur at the same rate. Free oxygen also occurs in solution in the world's water bodies. The increased solubility of O.
What is the energy that is released in combustion?
Dioxygen provides the energy released in combustion and aerobic cellular respiration, and many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as do the major constituent inorganic compounds of animal shells, teeth, and bone.
How much oxygen is in freshwater?
At 25 °C and 1 standard atmosphere (101.3 kPa) of air, freshwater contains about 6.04 milliliters (mL) of oxygen per liter, and seawater contains about 4.95 mL per liter. At 5 °C the solubility increases to 9.0 mL (50% more than at 25 °C) per liter for water and 7.2 mL (45% more) per liter for sea water.
How many protons and electrons are in oxygen?
So for your question, the Periodic Table tells us that oxygen has an Atomic Number of 8, so there are 8 protons and 8 electrons.
What is the number of electrons in an atom that is not oxygen?
For example, if an atom has 9 protons, it will no longer be oxygen, but will instead be Fluorine. Any atom that doesn’t have 8 protons is not oxygen. The amount of electrons must be the same as the number of protons in the atom for it to be neutrally charged. So the number of electrons should also be 8.
What is the atomic number of an atom?
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus and the number of electrons in a neutral atom. For the number of neutrons you have to know which ISOTOPE you are talking about. Each isotope of an element has a different number of neutrons, and therefore, a different mass number (nucleon number).
How to find neutrons in an atom?
An easy way to find the number of neutrons in an atom would be to look at the atomic mass and subtract the number of protons from it. For example, if your atom has an atomic mass of 14, and you know that there are 8 protons in your atom, you can subtract 8 from 14 which gives you 6.
What number of electrons do atoms need to have to balance out the charge?
The most simple explanation is that atoms really want their total number of electrons to be one of a sequence of magic numbers: 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, 86, 118.
Is oxygen the same as neutrons?
They are NOT the same thing. For oxygen Z=8, which means that there are eight protons in the nucleus, and eight electrons outside the nucleus. Oxygen has an average atomic mass of 15.999, but that is NOT the number of neutrons, nor is it rounded to that. Instead, we need to know the isotope of oxygen.
Overview
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At st…
History of study
One of the first known experiments on the relationship between combustion and air was conducted by the 2nd century BCE Greek writer on mechanics, Philo of Byzantium. In his work Pneumatica, Philo observed that inverting a vessel over a burning candle and surrounding the vessel's neck with water resulted in some water rising into the neck. Philo incorrectly surmised that parts of the air in the vessel were converted into the classical element fire and thus were abl…
Characteristics
At standard temperature and pressure, oxygen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas with the molecular formula O 2, referred to as dioxygen.
As dioxygen, two oxygen atoms are chemically bound to each other. The bond can be variously described based on level of theory, but is reasonably and simply described as a covalent double bond that results from the filling of molecular orbitals formed from the atomic orbitals of the indivi…
Biological production and role of O2
In nature, free oxygen is produced by the light-driven splitting of water during oxygenic photosynthesis. According to some estimates, green algae and cyanobacteria in marine environments provide about 70% of the free oxygen produced on Earth, and the rest is produced by terrestrial plants. Other estimates of the oceanic contribution to atmospheric oxygen are higher, while some estimates are lower, suggesting oceans produce ~45% of Earth's atmospheri…
Industrial production
One hundred million tonnes of O 2 are extracted from air for industrial uses annually by two primary methods. The most common method is fractional distillation of liquefied air, with N 2 distilling as a vapor while O 2 is left as a liquid.
The other primary method of producing O 2 is passing a stream of clean, dry air through one bed of a pair of identical zeolite molecular sieves, which absorbs the nitrogen and delivers a gas strea…
Storage
Oxygen storage methods include high-pressure oxygen tanks, cryogenics and chemical compounds. For reasons of economy, oxygen is often transported in bulk as a liquid in specially insulated tankers, since one liter of liquefied oxygen is equivalent to 840 liters of gaseous oxygen at atmospheric pressure and 20 °C (68 °F). Such tankers are used to refill bulk liquid-oxygen storage containers, which stand outside hospitals and other institutions that need large volume…
Applications
Uptake of O 2 from the air is the essential purpose of respiration, so oxygen supplementation is used in medicine. Treatment not only increases oxygen levels in the patient's blood, but has the secondary effect of decreasing resistance to blood flow in many types of diseased lungs, easing work load on the heart. Oxygen therapy is used to treat emphysema, pneumonia, some heart disorders (congestive heart failure), some disorders that cause increased pulmonary artery pres…
Compounds
The oxidation state of oxygen is −2 in almost all known compounds of oxygen. The oxidation state −1 is found in a few compounds such as peroxides. Compounds containing oxygen in other oxidation states are very uncommon: −1/2 (superoxides), −1/3 (ozonides), 0 (elemental, hypofluorous acid), +1/2 (dioxygenyl), +1 (dioxygen difluoride), and +2 (oxygen difluoride).
Water (H 2O) is an oxide of hydrogen and the most familiar oxygen compound. Hydrogen atoms are covalently …