Rigid bacteria with a helical cell shape are called vibrios. spirilla. spirochetes. coccobacilli.
What is the shape of bacteria?
Due to the presence of a rigid cell wall, bacteria maintain a definite shape, though they vary as shape, size and structure. When viewed under light microscope, most bacteria appear in variations of three major shapes: the rod (bacillus), the sphere (coccus) and the spiral type (vibrio).
What are spiral shaped bacteria called?
Spiral shape is one of the three primary shapes of bacteria. Spiral bacteria are twisted and commonly occur in two forms: spirillum (spirilla plural) and spirochetes. These cells resemble long, twisted coils. Spirochetes . Spirochetes (also spelled spirochaete) bacteria are long, tightly coiled, spiral-shaped cells.
What are cylindrical or rod-shaped bacteria called?
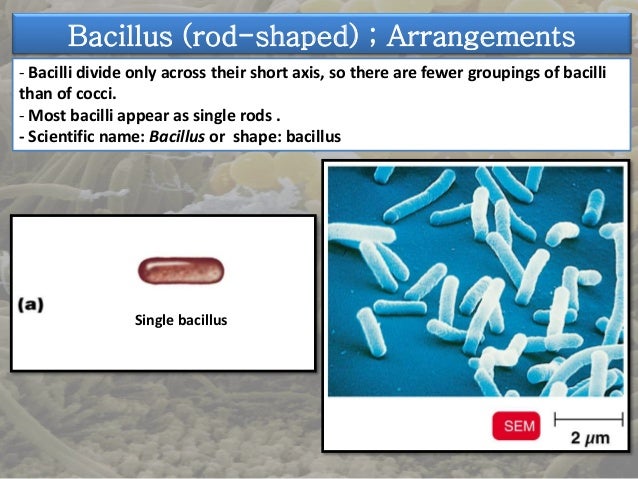
The cylindrical or rod-shaped bacteria are called ‘bacillus’ (plural: bacilli). 1. Diplobacilli Most bacilli appear as single rods. Diplobacilli appear in pairs after division.
What is an example of a star shaped bacteria?
The star-shaped bacteria is an unusually shaped bacteria that resembles a flat, six-pronged star. An example of this species is Stella which is found in freshwater, soil, and sewage. Examples include Stella humosa and Stella vacuolata. These are found in the soil when decomposition is underway.
Can bacteria be helical?
Helical and rod-shaped bacteria swim in helical trajectories with little additional propulsion from helical shape - PMC. The .
What are the 3 types of spiral bacteria?
The spiral shape can appear in several forms: vibrio, spirillum, and spirochete. The metric unit micrometer (1/1,000,000 or 10-6 of a meter) is used to measure bacterial size.
What is the scientific name of bacteria that are shaped as spirals?
Spirillum, genus of spiral-shaped bacteria of the family Spirillaceae, aquatic except for one species (S. minus) that causes a type of rat-bite fever in man. The term spirillum is used generally for any of the corkscrew-like species.
What is the shape of spirilla bacteria?
spiral-shaped bacteriaBacteria are classified according to their shape, or morphology. Spherical bacteria are known as cocci, rod-shaped bacteria are bacilli, and spiral-shaped bacteria are spirilla.
Which of the following bacteria are thick rigid and spiral?
SpirillumSpirillum (plural, spirilla). A bacterium with rigid spiral (helical) structure (not easily band, not flexible), thick, long, and move with flagella, 6–15 μm long and spiral in shape is called spirillum.
What are Palisades bacteria?
Palisade Bacteria: This particular arrangement is formed during the process of cell division when the bacteria or bacilli bend at the area of the division leading to the formation of a palisade-like arrangement. This bacteria resembles a picket fence or Chinese letters.
What is a spiral or corkscrew shaped bacteria?
Spirilla – are spiral or corkscrew shaped bacteria.
What is the name for corkscrew shaped bacteria quizlet?
Spirillum: (1) a helical or corkscrew-shaped bacterium.
What is an example of spiral bacteria?
Spirillum volutansHelicobacter pyloriSpirillum minusBorrelia recurrentisTreponema pallidumLeptospira interrogansSpiral bacteria/Representative species
What is the shape of cocci?
coccus, plural Cocci, in microbiology, a spherical-shaped bacterium.
How do you name bacteria shapes?
Bacteria are classified into five groups according to their basic shapes: spherical (cocci), rod (bacilli), spiral (spirilla), comma (vibrios) or corkscrew (spirochaetes).
What are the 4 types of bacteria?
Bacteria can be classified based on their shape into bacillus, coccus, vibrio and spirillum.
Which type of bacteria divides in multiple planes?
Sarcinae: cells remain in groups of eight and divide in three planes. Staphylo: cells remain in clusters and divide in multiple planes. Though these are the most common shapes and arrangements for bacteria, some bacteria have unusual and much less common forms. These bacteria have varying shapes and are said to be pleomorphic —they have different ...
What is the shape of spirilla bacteria?
Spirilla Bacteria. SCIEPRO/Science Photo Library/Getty Images. Spiral shape is one of the three primary shapes of bacteria. Spiral bacteria are twisted and commonly occur in two forms: spirillum (spirilla plural) and spirochetes.
What are the different types of bacteria?
Bacillus is one of the three primary shapes of bacteria. Bacillus (bacilli plural) bacteria have rod-shaped cells. These cells can exist in several different arrangements that include: 1 Monobacillus: remains single rod-shaped cell after dividing. 2 Diplobacilli: cells remain in pairs after dividing. 3 Streptobacilli: cells remain in chains after dividing. 4 Palisades: cells in a chain are arranged side-by-side instead of end-to-end and are partially attached. 5 Coccobacillus: cells are short with a slight oval shape, resembling both coccus and bacillus bacteria.
What is the spiral shape of a spirochete?
This spirochete bacterium (Treponema pallidum) is spirally twisted in form, elongated and appearing thread-like (yellow). It causes syphilis in humans. Spiral shape is one of the three primary shapes of bacteria. Spiral bacteria are twisted and commonly occur in two forms: spirillum (spirilla plural) and spirochetes.
What is vibrio bacteria?
A number of species of vibrio bacteria are pathogens and are associated with food poisoning. These bacteria can infect open wounds and cause blood poisoning. An example of a Vibrio species that causes gastrointestinal distress is Vibrio cholerae which is responsible for cholera. Cite this Article.
What is a spirillum minus?
These cells may also have flagella, which are long protrusion used for movement, at each end of the cell. An example of a spirillum bacterium is Spirillum minus, which causes rat-bite fever.
What are some examples of bacillus bacteria?
More examples of bacillus bacteria include Bacillus anthracis, which cause anthrax and Bacillus cereus, which commonly cause food poisoning .
What is the first odd shape bacteria?
The first odd shape bacteria is a rectangular-shaped bacteria, which is also known as an arcula. Bacterial species of this genus include Haloarcula vallismortis or Haloarcula marismortui. They are extremely halophilic and grow at temperatures between 40 Celsius and 45 Celsius . They are not pathogenic and are not known to cause any diseases.
What determines the shape of a bacterium?
The rigidity of its cell wall determines the shape of a bacterium. It also endows the bacterium with flexibility and other added advantages. Bacteria are grouped into 2 major groups namely Gram +ve or Gram -ve based on the response to Gram’s stain.
What are the two types of bacteria that are usually found in pairs?
They can be found in different arrangements, namely, diplococci (in pairs), tetrads (arrangement of groups of four), streptococci (in pairs), and staphylococci (in clusters). Diplococci Bacteria: These bacteria are usually found in pairs as two joined cells.
What is the name of the genus of streptobacilli?
The name streptobacilli originates from the word “ strepto ” meaning chain and “ bacilli ” meaning “ rod-shaped “. Species from this genus of bacteria are known to be pathogenic. An example of streptobacilli bacteria includes Streptobacillus moniliformis that is the causative agent of rat-bite fever.
What are some examples of diplobacilli?
An example of diplobacilli bacteria is Coxiella burnetii which is an intracellular gram-negative pathogen and causes a disease known as Q fever. Another example is that of Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis that causes chronic nasal infection in humans.
What are the strains of Vibrio?
Other strains of Vibrio bacteria are non-cholera strains and cause other types of illnesses. Spirilla Bacteria: This type of bacteria is a genus of spiral-shaped bacteria that are gram-negative and flagellated. Spirillum minus is an example of spirilla bacteria that are implicated in rat-bite fever.
What is a filamentous bacteria?
The Filamentous bacteria are long thin filament-like bacteria that can branch and form networks called mycelium. An example is Candidatus savagella that is found in the gut of animals like rodents, fish, etc. and can be important to immune development.
What are the three basic shapes of bacteria?
The three basic bacterial shapes are coccus (spherical), bacillus (rod-shaped), and spiral (twisted), however pleomorphic bacteria can assume several shapes. Cocci (or coccus for a single cell) are round cells, sometimes slightly flattened when they are adjacent to one another.
Why do bacteria have a definite shape?
The cell structure is simpler than that of other organisms as there is no nucleus or membrane bound organelles. Due to the presence of a rigid cell wall, bacteria maintain a definite shape, though they vary as shape, size and structure. When viewed under light microscope, most bacteria appear in variations of three major shapes: the rod (bacillus), ...
How are cocci formed?
The cocci are arranged in a cuboidal manner, as the cells are formed by regular cell divisions in three planes. Cocci that divide in three planes and remain in groups cube like groups of eight. Examples: Sarcina ventriculi, Sarcina ureae, etc. 5. Staphylococci.
What is a spiral bacterial cell?
Arrangement of Spiral Bacteria. Spirilla (or spirillum for a single cell) are curved bacteria which can range from a gently curved shape to a corkscrew-like spiral. Many spirilla are rigid and capable of movement. A special group of spirilla known as spirochetes are long, slender, and flexible. 1.
What are some examples of cocci?
3. Tetrads. The cocci are arranged in packets of four cells, as the cells divide in two plains. Examples: Aerococcus, Pediococcus and Tetragenococcus.
What is the shape of a spirochete?
Spirochetes have a helical shape and flexible bodies. Spirochetes move by means of axial filaments, which look like flagella contained beneath a flexible external sheath but lack typical bacterial flagella.
How big is an oscillatoria?
Oscillatoria is about 7 µm in diameter. The bacterium, Epulosiscium fishelsoni , can be seen with the naked eye (600 µm long by 80 µm in diameter). One group of bacteria, called the Mycoplasmas, have individuals with size much smaller than these dimensions.
What is the name of the microscopic organism that is not visible to the naked eye?
Bacteria are the ubiquitous microscopic organisms that are not visible with the naked eye. Bacterial morphology (size, shape and arrangement of bacterial cells) is one of the mostly used feature for the differentiation of various bacterial species.
Which cocci divide in multiple planes and remain in groups cube like groups of eight?
Sarcinae : Cocci that divide in three planes and remain in groups cube like groups of eight. Staphylococci : Cocci that divide in multiple planes and form grape like clusters or sheets.
Which cocci remain in pairs after dividing?
Diplococci : Cocci that remain in pairs after dividing. Streptococci : Cocci that remain in chains, like beads on a string. Tetrads : The cocci that are arranged in packets of four cells, as the cells divide in two plains. Sarcinae : Cocci that divide in three planes and remain in groups cube like groups of eight.
Abstract
It has frequently been hypothesized that the helical body shapes of flagellated bacteria may yield some advantage in swimming ability. In particular, the helical-shaped pathogen Helicobacter pylori is often claimed to swim like a corkscrew through its harsh gastric habitat, but there has been no direct confirmation or quantification of such claims.
INTRODUCTION
Bacteria come in a wide variety of shapes, and bacterial morphology affects selective adaptation ( 1 ). One important mechanism by which morphology could affect biological function is through motility ( 2 ); for example, cell length has been shown to affect the tumbling ( 3) and, hence, chemotactic ability in Escherichia coli.
RESULTS
The swimming of bacteria can be easily visualized by time-resolved optical microscopy, and their trajectories can be obtained from frame-by-frame digital processing of movies to follow individual bacteria as they swim ( 30, 32 ).
DISCUSSION
Our overall conclusion is that helical shape adds only a small advantage in motility. The results reported here and the earlier studies of Liu et al.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
All experiments reported in this paper were done on the LSH100 strain of H. pylori, a derivative of the human clinical isolate G27 ( 38, 57) and its isogenic mutant with a straight rod shape, LSH100 Δ csd6 ( 26, 28 ). The culture procedure was identical to that used by Martinez et al. ( 28) and is described briefly here.
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Hardcastle for helpful discussions regarding his work on H. pylori motility and for training M.A.C. in the early stages of this work; B. Turner for very helpful discussions regarding mucin and providing purified PGM; N. Salama for providing the parent culture of LSH100 and its rod-shaped mutant Δ csd6, as well as for discussions on H.