What is meant by more substituted alkene?
Stability is simply a measure of energy. Lower energy molecules are more stable than higher energy molecules. More substituted alkenes are more stable than less substituted ones due to hyperconjugation. They have a lower heat of hydrogenation.
Which alkene is most stable?
Which alkene is the most stable? methylpent-2-ene Why highly alkylated alkenes are more stable? The overlap of these orbitals helps the atoms share electrons and makes the molecule more stable. This is why alkenes with more substituent groups are more stable than those with fewer. Additional substituents can increase hyperconjugation and thus molecule stability. Why ]
Why more substituted alkenes are more stable?
The amount of energy released during a hydrogenation reaction, known as the heat of hydrogenation, is inversely related to the stability of the starting alkene: the more stable the alkene, the lower its heat of hydrogenation. Examining the heats of hydrogenation for various alkenes reveals that stability increases with the amount of substitution.
Which alkene is capable of stereoisomerism?
Stereoisomerism occurs when substances have the same molecular formula, but a different arrangement of their atoms in space. E-Z isomerism is one type of this isomerism. It applies to: alkenes and other organic compounds that contain C=C bonds. cyclic alkanes.
Is the most substituted alkene the most stable?
Alkenes have substituents, hydrogen atoms attached to the carbons in the double bonds. The more substituents the alkenes have, the more stable they are. Thus, a tetra substituted alkene is more stable than a tri-substituted alkene, which is more stable than a di-substituted alkene or an unsubstituted one.
How do you know which product is more substituted?
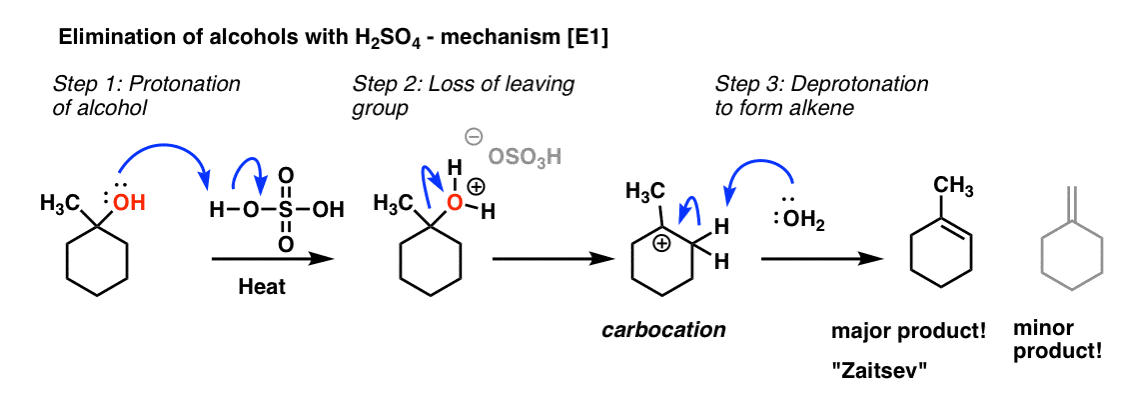
1. In Elimination Reactions, The “More Substituted” Alkene Tends To Be The Major Product. For example, if you heat the alcohol below with a strong acid (like sulfuric acid, H2SO4) you obtain one major product (an alkene) and a minor product (also an alkene).
What is less and more substituted alkene?
A less substituted carbon atom accommodates the negative charge better than a more substituted carbon atom, so a less substituted alkene is more stable in this case. For other reactions such as alcohol dehydration, the more substituted alkene is formed because the intermediate has a carbocation character.
What is substitution in alkenes?
In a substitution reaction, one atom is swapped with another atom. These are very useful reactions in the chemical industry because they allow chemists to change one compound into something more useful, building up designer molecules like drugs.
Which alkene will be the major product?
3-methylcyclohex-1-ene is formed as the major product in the E2 reaction of the given compound.
How do you know which carbon is the most substituted?
the “most substituted” carbon is the carbon of the alkene that is attached to the most carbons (or “fewer number of hydrogens”, if you prefer). the “less substituted” carbon is the carbon of the alkene that is attached to the fewest carbons (or “greater number of hydrogens”)
What is the least substituted alkene?
Silver oxide (Ag2O) is often used. Heating with strong base results in an elimination reaction: NR3 is lost and and a new alkene is formed. The interesting observation here is that the alkene product from this process tends to be the least substituted alkene (“Hofmann product”) not the Zaitsev product.
How do you determine which alkene is most stable?
The relative stability of alkenes can be determined by comparing their heats of hydrogenation. The lower heat of hydrogenation indicates the more stable alkene.
Are more substituted alkenes more reactive?
Relative stability of alkenes can be measured by using heats of hydrogenation upon reduction to the related alkane. More substituted alkenes are more stable than less substituted. Alkenes with the largest groups trans are more stable than cis.
What is a substituted alkane?
A substituted cycloalkane is a cycloalkane in whose molecule not all carbon atoms are members of a ring.
What is substitution alkane?
The atoms attached to carbon are replaced by the other atoms or compounds to make a new product. e.g. methane reacts with Chloride in the presence of light to replace H-atom by Cl to make chloromethane.
Why are conjugated alkenes more stable?
Since having more electron density delocalized makes the molecule more stable conjugated dienes are more stable than non conjugated and cummulated dienes.
What is highly substituted alkene?
Highly substituted alkene means the alkene which has greater number of alkyl group attached with the double bonded carbon atom. Subsitution of alkene refers to how many other carbons the alkene is attached to. For instance if the alkene is trisubstituted, it would be attached to 3 carbons and 1 hydrogen. More subsituted alkenes are more stable ...
What is the subsitution of an alkene?
Subsitution of alkene refers to how many other carbons the alkene is attached to. For instance if the alkene is trisubstituted, it would be attached to 3 carbons and 1 hydrogen. More subsituted alkenes are more stable which is why they are usually favored.
Why is alkene less stable than alkane?
Alkene are less stable than alkane due to presence of pi bond. Energy of pi bond is higher than sigma bond so in alkane no. of sigma bond are high so its stability, highly substituted and conjugated alkene are relatively stable due to single bolnd charectar in alkene.
What is the major product of 2-iodobutane?
For example, when 2-iodobutane is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH), 2-butene is the major product and 1-butene is the minor product. More generally, Zaitsev's rule predicts that in an elimination reaction, the most substituted product will be the most stable, and therefore the most favored.
How to name an alkene?
For straight-chain alkenes with 4 or more carbon atoms, that name does not completely identify the compound. For those cases, and for branched acyclic alkenes, the following rules apply: 1 Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule. If that chain does not contain the double bond, name the compound according to the alkane naming rules. Otherwise: 2 Number the carbons in that chain starting from the end that is closest to the double bond. 3 Define the location k of the double bond as being the number of its first carbon. 4 Name the side groups (other than hydrogen) according to the appropriate rules. 5 Define the position of each side group as the number of the chain carbon it is attached to. 6 Write the position and name of each side group. 7 Write the names of the alkane with the same chain, replacing the "-ane" suffix by " k -ene".
What is an alkene compound?
Chemical compound. A 3D model of ethylene, the simplest alkene. In chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon that contains a carbon –carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal.
What is terminal alkene?
Terminal alkenes are precursors to polymers via processes termed polymerization. Some polymerizations are of great economic significance, as they generate as the plastics polyethylene and polypropylene. Polymers from alkene are usually referred to as polyolefins although they contain no olefins. Polymerization can proceed via diverse mechanisms. conjugated dienes such as buta-1,3-diene and isoprene (2-methylbuta-1,3-diene) also produce polymers, one example being natural rubber.
How do alkenes react with addition?
Alkenes react in many addition reactions, which occur by opening up the double-bond. Most of these addition reactions follow the mechanism of electrophilic addition. Examples are hydrohalogenation, halogenation, halohydrin formation, oxymercuration, hydroboration, dichlorocarbene addition, Simmons–Smith reaction, catalytic hydrogenation, epoxidation, radical polymerization and hydroxylation .
What is reduction of alkynes?
Reduction of alkynes is a useful method for the stereoselective synthesis of disubstituted alkenes . If the cis -alkene is desired, hydrogenation in the presence of Lindlar's catalyst (a heterogeneous catalyst that consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate and treated with various forms of lead) is commonly used, though hydroboration followed by hydrolysis provides an alternative approach. Reduction of the alkyne by sodium metal in liquid ammonia gives the trans -alkene.
What is the method of synthesis of alkene?
Another important method for alkene synthesis involves construction of a new carbon–carbon double bond by coupling of a carbonyl compound (such as an aldehyde or ketone) to a carbanion equivalent. Such reactions are sometimes called olefinations. The most well-known of these methods is the Wittig reaction, but other related methods are known, including the Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction .
What is the reaction used to determine the position of a double bond in an unknown alkene?
This reaction and the ozonolysis can be used to determine the position of a double bond in an unknown alkene. The oxidation can be stopped at the vicinal diol rather than full cleavage of the alkene by using osmium tetroxide or other oxidants: R'CH=CR 2 + 1/2 O 2 + H 2 O → R'CH (OH)-C (OH)R 2.
Which is more stable, a less substituted alkene or a more substituted alkene?
A less substituted carbon atom accommodates the negative charge better than a more substituted carbon atom, so a less substituted alkene is more stable in this case. For other reactions such as alcohol dehydration, the more substituted alkene is formed because the intermediate has a carbocation character. The more stable intermediate is the more ...
Is tetrasubstitution better than disubstitution?
Tetrasubstitution is better than trisubstitution which is better than disubstitution. Clearly, monosubstitution is the least desirable case.
Is the methyl group equatorial or spontaneous?
In the trisubstituted isomer, the methyl group adopts an axial position to avoid an A 1,3 interaction if the methyl group were equatorial. 1) International Institute of Standards and Technology, Dept. of Commerce, USA.
Which atoms are less electronegative?
Carbon atoms are less electronegative (more willing to donate electrons) than most atoms. Yet, they are pretty electron rich--compare to H, which is technically less electronegative but doesn't have any electrons. So, alkyl groups have a +I effect (likely to donate some electron density to their neighbors).
Why do sp2 carbons want electrons more?
more. sp2 carbons want electrons more because the sp2 orbitals have more s character . In turn, that means the electrons are closer to the nucleus compared with sp3 orbitals and thus lower in energy. Steric hinderance causes bonds to be pushed away from each other, which causes them to move closer to the other orbitals.
Which two scientists believed that the least substituted alkene would be favored?
Markovnikov, who published in 1870 what is now known as Markovnikov 's rule, and Zaitsev held conflicting views regarding elimination reactions: the former believed that the least substituted alkene would be favored, whereas the latter felt the most substituted alkene would be the major product.
What is the major product of 2-iodobutane?
For example, when 2-iodobutane is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH), 2-butene is the major product and 1-butene is the minor product. More generally, Zaitsev's rule predicts that in an elimination reaction, the most substituted product will be the most stable, and therefore the most favored.
How do alkyl groups contribute to the electron density?
Alkyl groups are electron donating by inductive effect, and increase the electron density on the sigma bond of the alkene. Also, alkyl groups are sterically large, and are most stable when they are far away from each other. In an alkane, the maximum separation is that of the tetrahedral bond angle, 109.5°.
Who published an empirical rule similar to Zaitsev's?
Aleksandr Nikolaevich Popov published an empirical rule similar to Zaitsev's in 1872, and presented his findings at the University of Kazan in 1873. Zaitsev had cited Popov's 1872 paper in previous work and worked at the University of Kazan, and was thus probably aware of Popov's proposed rule. In spite of this, Zaitsev's 1875 Liebigs Annalen paper ...
Which carbon is more atom or group attached to the central carbon than propane?
The highlighted carbon is currently being considered the "central" carbon. Simply put... Since isobutane (1) has one more atom or group attached to the central carbon than propane (2), it is more substituted. Since propane (2) has one more atom or group attached to the central carbon than ethane (3), it is more substituted.
What does "substituted" mean?
What does substituted mean? It just means that there are a different number of non-hydrogen groups on a particular atom. Below, (1) is a tertiary (3∘), (2) is a secondary (2∘), and (3) is a primary (1∘) central carbon. The highlighted carbon is currently being considered the "central" carbon.
Overview
Synthesis
Alkenes are produced by hydrocarbon cracking. Raw materials are mostly natural gas condensate components (principally ethane and propane) in the US and Mideast and naphtha in Europe and Asia. Alkanes are broken apart at high temperatures, often in the presence of a zeolite catalyst, to produce a mixture of primarily aliphatic alkenes and lower molecular weight alkanes. The mixture is …
Structural isomerism
Alkenes having four or more carbon atoms can form diverse structural isomers. Most alkenes are also isomers of cycloalkanes. Acyclic alkene structural isomers with only one double bond follow:
• C2H4: ethylene only
• C3H6: propylene only
• C4H8: 3 isomers: 1-butene, 2-butene, and isobutylene
Structure and bonding
A carbon–carbon double bond consists of a sigma bond and a pi bond. This double bond is stronger than a single covalent bond (611 kJ/mol for C=C vs. 347 kJ/mol for C–C), but not twice as strong. Double bonds are shorter than single bonds with an average bond length of 1.33 Å (133 pm) vs 1.53 Å for a typical C-C single bond.
Physical properties
Many of the physical properties of alkenes and alkanes are similar: they are colorless, nonpolar, and combustible. The physical state depends on molecular mass: like the corresponding saturated hydrocarbons, the simplest alkenes (ethylene, propylene, and butene) are gases at room temperature. Linear alkenes of approximately five to sixteen carbon atoms are liquids, and higher alkenes are waxy solids. The melting point of the solids also increases with increase in molecul…
Reactions
Alkenes are relatively stable compounds, but are more reactive than alkanes. Most reactions of alkenes involve additions to this pi bond, forming new single bonds. Alkenes serve as a feedstock for the petrochemical industry because they can participate in a wide variety of reactions, prominently polymerization and alkylation.
IUPAC Nomenclature
Although the nomenclature is not followed widely, according to IUPAC, an alkene is an acyclic hydrocarbon with just one double bond between carbon atoms. Olefins comprise a larger collection of cyclic and acyclic alkenes as well as dienes and polyenes.
To form the root of the IUPAC names for straight-chain alkenes, change the -an …
See also
• Alpha-olefin
• Annulene
• Aromatic hydrocarbon ("Arene")
• Cycloalkene
• Dendralene