Sucrose is common table sugar. It is a disaccharide, a molecule composed of two monosaccharides: glucose and fructose. Sucrose is produced naturally in plants, from which table sugar is refined.
What are the disadvantages of sucrose?
The Side Effects of Sucrose
- Sugar Crash. When you consume too much sucrose in one meal, you may experience a “sugar crash” within a few hours.
- Tooth Decay. Sugar is a large contributor to tooth decay. ...
- Weight Gain and Insulin Resistance. Because sugar is high in calories, eating large amounts of sugary foods can lead to weight gain. ...
- Cholesterol Changes. ...
What are facts about sucrose?
- CANCER MYTH: Sucralose has been linked to cancer. ...
- SAFETY MYTH: Sucralose was approved following very little testing. ...
- DIABETES MYTH: Sucralose affects blood sugar control in people with diabetes. ...
- WEIGHT GAIN MYTH: No-calorie sweeteners actually cause weight gain by increasing sugar cravings. ...
- CHILDREN MYTH: Sucralose is not safe for children. ...
What are two sugars combine to make sucrose?
How can I lose my hips and thighs in 7 days?
- Lie on an exercise mat on your right side.
- Slowly raise up your top leg (left leg) as high as you can go. Keep your toes pointed forward.
- Pause at the top, then lower your leg to the starting position. Make sure to keep your pelvis steady and your core engaged.
- Repeat 10 times on each side.
Is sucrose and sugar the same thing?
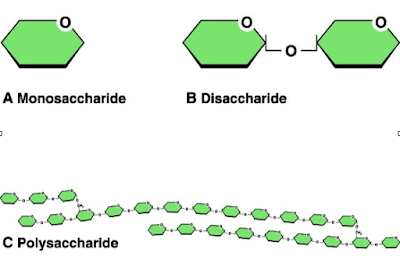
Sugar or table sugar is also known as sucrose. In fact, there are many different types of sugar: glucose, galactose, fructose, and lactose are all types of sugar, along with sucrose. Sucrose consists of one glucose molecule and one fructose molecule bonded together.
See more
What is the monosaccharide of sucrose?
Monosaccharides such as glucose can be linked together in condensation reactions. For example, sucrose (table sugar) is formed from one molecule of glucose and one of fructose, as shown below. Molecules composed of two monosaccharides are called disaccharides.
What is the composition of the sucrose?
Sucrose is a disaccharide, or double sugar, being composed of one molecule of glucose linked to one molecule of fructose. Because one molecule of water (H2O) is lost in the condensation reaction linking glucose to fructose, sucrose is represented by the formula C12H22O11 (following the general formula Cn[H2O]n − 1).
What is the monosaccharide composition?
Simple monosaccharides have a linear and unbranched carbon skeleton with one carbonyl (C=O) functional group, and one hydroxyl (OH) group on each of the remaining carbon atoms.
What is the percent composition of sucrose?
Percentage Composition from Formulas A more complex example is sucrose (table sugar), which is 42.11% carbon, 6.48% hydrogen, and 51.41% oxygen by mass. This means that 100.00 g of sucrose always contains 42.11 g of carbon, 6.48 g of hydrogen, and 51.41 g of oxygen.
Is sucrose a disaccharide or monosaccharide?
DisaccharidesDisaccharideCommon nameMonosaccharidesSucroseTable sugarGlucose-fructoseLactoseMilk sugarGalactose-glucoseMaltoseMalt sugarGlucose-glucoseIsomaltoseGlucose-glucose
Is monosaccharide a sugar?
Monosaccharides include glucose, galactose and fructose - all commonly found in food. Monosaccharides are single sugar molecules that are the building blocks for all other sugars and carbohydrates. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of these.
How many monosaccharides are there?
3 monosaccharidesFood carbohydrates have to be broken down to monosaccharides before they can be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, and they also circulate in blood in monosaccharide form. There are 3 monosaccharides: Glucose. Fructose.
What are 5 examples of monosaccharides?
Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose, galactose, xylose and ribose.
What is the name of the sugar that is formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic?
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar or bivose) is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides (simple sugars) are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
What is the acetal bond between glucose and fructose?
In sucrose, the components glucose and fructose are linked via an acetal bond between C1 on the glucosyl subunit and C2 on the fructosyl unit. The bond is called a glycosidic linkage. Glucose exists predominantly as two isomeric "pyranoses" (α and β), but only one of these forms links to the fructose.
Is maltose a disaccharide?
Maltose, a Disaccharide. Two molecules of glucose are linked by an α-1,4-glycosidic bond to form the disaccharide maltose.
What is the structure of monosaccharides?
All monosaccharides have the same general formula of (CH 2 O) n, which designates a central carbon molecule bonded to two hydrogens and one oxygen. The oxygen will also bond to a hydrogen, creating a hydroxyl group. Because carbon can form 4 bonds, several of these carbon molecules can bond together.
How many carbons are in a monosaccharide?
This simple monosaccharide is composed of 6 carbons, each labeled in the image. The first carbon is the carbonyl group. Because it is at the end of the molecule, glucose is in the aldose family. Typically, monosaccharides with more than 5 carbons exist as rings in solutions of water.
What is the monosaccharide that is produced in mammals?
Galactose. Galactose is a monosaccharide produced in many organisms, especially mammals. Mammals use galactose in milk, to give energy to their offspring. Galactose is combined with glucose to form the disaccharide lactose .
What is the most basic form of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharide Definition. A monosaccharide is the most basic form of carbohydrates. Monosac charides can by combined through glycosidic bonds to form larger carbohydrates, known as oligosaccharides or polysaccharides. An oligosaccharide with only two monosaccharides is known as a disaccharide. When more than 20 monosaccharides are combined ...
Why is glucose important for plants?
Glucose is an important monosaccharide in that it provides both energy and structure to many organism. Glucose molecules can be broken down in glycolysis, providing energy and precursors for cellular respiration. If a cell does not need any more energy at the moment, glucose can be stored by combining it with other monosaccharides. Plants store these long chains as starch, which can be disassembled and used as energy later. Animals store chains of glucose in the polysaccharide glyocogen, which can store a lot of energy.
Why are monosaccharides monomers?
However, a monosaccharide is a monomer because it can form polysaccharide polymers when connected in series with other monosaccharides. 3. As mentioned, monosaccharides consisting of more than 5 carbons often tend to form rings in nature.
How do monosaccharides work?
Monosaccharides have many functions within cells. First and foremost, monosaccharides are used to produce and store energy. Most organisms create energy by breaking down the monosaccharide glucose, and harvesting the energy released from the bonds. Other monosaccharides are used to form long fibers, which can be used as a form of cellular structure.
What are monosacharides?
The only monosacharides are glucose and fructose. Everything else is a different degree of polysacharides.
What is the secret sugar in sugar cane?
Marauders kept stealing the glucose from the plants so they tried to hide it in disaccharides. SUCROSE (table sugar) is the hidden sugar of Sugar Cane. You have to have a KEY [enzyme] to unlock the usable parts, glucose and fructose. Bacteria soon figured it out and began their marauding ways again, taking the sucrose from them for themselves … but not all bacteria .. many lack the enzyme “Lactase” and cannot break down sucrose. The three most important disaccharides are Maltose, Lactose and sucrose.
Why is fructose considered a ketone?
Fructose is considered a ketone because of the presence of ketone atomic groups.
What is the difference between sweet and non-sweet glucose?
The difference between the sweet and non-sweet forms of glucose relates to the type of chemical bond connecting the glucose molecules.
What is the product of the sun and carbon dioxide in the green part of plants?
Glucose is the product of the sun and carbon dioxide in the green part of plants. The process is called photosynthesis.
Why are polysaccharides needed?
Polysaccharides are just a good way to store up glucose in tight columns for use as demands require. Keys are needed to break it down so the being that made it can keep it all to itself and not share with the rest of the world. Unfortunately, keys always are found and the plants must overproduce to have any for themselves … but that's not so bad … man toils in the fields cultivating and growing the plants, keeping weeds at bay.
Is glucose an aldose sugar?
Because of the presence of aldehyde atomic groups in its molecular structure, glucose is an aldose sugar.
What is sucrose made of?
Chemical compound. Sucrose is made up of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose joined together. It is a disaccharide, a molecule composed of two monosaccharides: glucose and fructose. Sucrose is produced naturally in plants, from which table sugar is refined. It has the molecular formula C 12 H 22 O 11 .
How is sucrose formed?
The energy for the reaction is gained by the cleavage of uridine diphosphate (UDP). Sucrose is formed by plants, algae and cyanobacteria but not by other organisms. Sucrose is the end product of photosynthesis and is found naturally in many food plants along with the monosaccharide fructose. In many fruits, such as pineapple and apricot, sucrose is the main sugar. In others, such as grapes and pears, fructose is the main sugar.
What is the linkage between sucrose and glucose?
In sucrose, the monomers glucose and fructose are linked via an ether bond between C1 on the glucosyl subunit and C2 on the fructosyl unit. The bond is called a glycosidic linkage. Glucose exists predominantly as a mixture of α and β "pyranose" anomers, but sucrose has only the α form. Fructose exists as a mixture of five tautomers but sucrose has only the β- D -fructofuranose form. Unlike most disaccharides, the glycosidic bond in sucrose is formed between the reducing ends of both glucose and fructose, and not between the reducing end of one and the non-reducing end of the other. This linkage inhibits further bonding to other saccharide units, and prevents sucrose from spontaneously reacting with cellular and circulatory macromolecules in the manner that glucose and other reducing sugars do. Since sucrose contains no anomeric hydroxyl groups, it is classified as a non- reducing sugar .
How to measure the purity of sucrose?
The purity of sucrose is measured by polarimetry, through the rotation of plane-polarized light by a sugar solution. The specific rotation at 20 °C using yellow "sodium-D" light (589 nm) is +66.47°. Commercial samples of sugar are assayed using this parameter. Sucrose does not deteriorate at ambient conditions.
Where is sucrose extracted?
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from either sugarcane or sugar beet. Sugar mills – typically located in tropical regions near where sugarcane is grown – crush the cane and produce raw sugar which is shipped to other factories for refining into pure sucrose. Sugar beet factories are located in temperate climates where the beet is grown, and process the beets directly into refined sugar. The sugar refining process involves washing the raw sugar crystals before dissolving them into a sugar syrup which is filtered and then passed over carbon to remove any residual colour. The sugar syrup is then concentrated by boiling under a vacuum and crystallized as the final purification process to produce crystals of pure sucrose that are clear, odorless, and sweet.
When was sucrose invented?
The word sucrose was coined in 1857, by the English chemist William Miller from the French sucre ("sugar") and the generic chemical suffix for sugars -ose. The abbreviated term Suc is often used for sucrose in scientific literature.
How is sugar extracted from cane sugar?
Since the 6th century BC, cane sugar producers have crushed the harvested vegetable material from sugarcane in order to collect and filter the juice. They then treat the liquid (often with lime (calcium oxide)) to remove impurities and then neutralize it. Boiling the juice then allows the sediment to settle to the bottom for dredging out, while the scum rises to the surface for skimming off. In cooling, the liquid crystallizes, usually in the process of stirring, to produce sugar crystals. Centrifuges usually remove the uncrystallized syrup. The producers can then either sell the sugar product for use as is, or process it further to produce lighter grades. The later processing may take place in another factory in another country.
Who are the authors of the paper "Process for the enzymatic preparation from sucrose of a?
Francois B. Paul, Pierre F. Monsan, Magali M. C. Remaud, Vincent P. Pelenc, "Process for the enzymatic preparation from sucrose of a mixture of sugars having a high content of isomaltose, and products obtained." U.S. Patent US4861381, issued April, 1956.
What was the first substance to be synthesized?
Sucrose was first synthesized enzymatically in the laboratory from potassium D-glucosyl-1-phosphate and D-fructose. The first chemical synthesis was accomplished by reaction of 3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-1,2-anhydro-alpha-D-glucopyranose with 1,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-D-fructofuranose.
What is a sweetener?
Sweetener in foods and soft drinks, manufacture of syrups, source of invert sugar, confectionary, preserves and jams, demulcent, pharmaceutical products, caramel, chemical intermediate for detergents, emulsifying agents, and other sucrose derivatives. Lewis, R.J., Sr (Ed.).
What is the starting material in fermentative prodn?
Starting material in fermentative prodn of ethanol, butanol, glycerol, citric and levulinic acids. Used in pharmaceuticals as a flavor, as a preservative, as antioxidant (in form of invert sugar), as demulcent, as substitute for glycerol, as granulation agent and excipient for tablets, as coating for tablets.
Is sucrose a solid?
Sucrose appears as white odorless crystalline or powdery solid. Denser than water. CAMEO Chemicals. Sucrose is a glycosyl glycoside formed by glucose and fructose units joined by an acetal oxygen bridge from hemiacetal of glucose to the hemiketal of the fructose.
Is sucrose a reducing agent?
SUCROSE is a reducing agent . Can react explosively with oxidizing agents such as chlorates and perchlorates. Is hydrolyzed by dilute acids and by invertase (a yeast enzyme) (NTP, 1992). Chars rapidly and exothermically when mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid.
Is A4 a human carcinogen?
A4: Not classifiable as a human carcinogen.