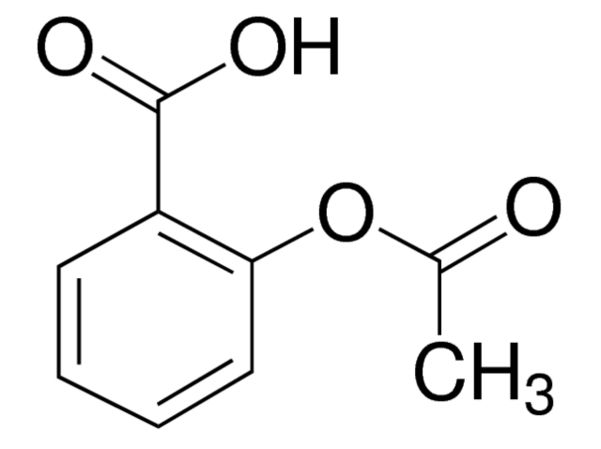
Identification of Aspirin Chemical Compound
| Chemical Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.15742 g/mol |
| IUPAC Name | 2- (acetyloxy)benzoic acid |
| SMILES String | CC (=O)Oc1ccccc1C (O)=O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C9H8O4/c1-6 (10)13-8-5-3-2-4-7 ... |
What is the formula for aspirin C9H8O4?
4 rows · Molar mass of C9H8O4 = 180.15742 g/mol. This compound is also known as Aspirin. Convert grams ...
What is the molar mass of aspirin?
Aspirin | HC9H7O4 or C9H8O4 | CID 2244 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities ...
What is the molar mass of C9H8O4?
3 rows · Jan 18, 2020 · Answer and Explanation: The molar mass of aspirin with a chemical formula of C9 H8 O4 is ...
What is molecular weight?
6 rows · Molecular Weight Description. The aspirin molecule consists of 8 Hydrogen atom (s), 9 Carbon ...
What is the molecular mass of aspirin C9H8O4 )?
What is the moles of aspirin? So, aspirin, C9H8O4 , has a molar mass of 180.157 g mol−1 .Nov 27, 2021
What is the molar mass of aspirin C9H8O4 quizlet?
A 360. mg sample of aspirin, C9H8O4, (molar mass 180.
What is the name of C9H8O4?
AspirinAspirin is a medicine that is very common. The molecular formula for Aspirin is C9H8O4.
How many total atoms are in C9H8O4?
type of element. For example, in a molecule of aspirin, C9H8O4, there are 9 carbon atoms, 8 hydrogen atoms and 4 oxygen atoms. compound. For example, one mole of aspirin contains 9 moles of carbon atoms, 8 moles of hydrogen atoms and 4 moles of oxygen atoms.
How many carbon atoms are present in 0.325 grams of aspirin C9H8O4?
Of the correct answer is 9.77 times 10 to the 21st carbon atoms. Thanks so much for watching.
What is the molecular formula of aspirin?
C₉H₈O₄Aspirin / Formula
Is aspirin C9H8O4 an element or compound?
The chemical compound chosen was 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. This compound is most commonly known as Aspirin(C9H8O4).
What is aspirin molecular structure?
Chemical formula = C9H8O4 or CH3COOC6H4COOH or HC9H7O4. Aspirin is prepared by chemical synthesis from salicylic acid, through acetylation with acetic anhydride. The molecular weight of aspirin is 180.16g/mol. It is odourless, colourless to white crystals or crystalline powder.
How much aspirin is lethal?
The lethal dose of aspirin for an adult is probably in the region of 25 to 30 g but recovery has been achieved by appropriate treatment after the ingestion of twice or thrice this amount.
How many aspirin tablets should be stored?
Chewable aspirin tablets containing 81 mg of the drug should be stored in child-resistant containers holding not more than 36 tablets each in order to limit the potential toxicity associated with accidental ingestion in children. Aspirin suppositories should be stored at 2-15 °C.
How is acetylsalicylic acid prepared?
Acetylsalicylic acid is prepared by reacting acetic anhydride with salicylic acid at a temperature of <90 °C either in a solvent (e.g., acetic acid or aromatic, acyclic, or chlorinated hydrocarbons) or by the addition of catalysts such as acids or tertiary amines.
What is the most commonly used analgesic and antipyretic medication?
Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid is perhaps the most commonly used analgesic and antipyretic medication worldwide, having been in clinical use for over 100 years.
What is acetylsalicylic acid?
**Pain, fever, and inflammation** Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), in the regular tablet form (immediate-release), is indicated to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation associated with many conditions, including the flu, the common cold, neck and back pain, dysmenorrhea, headache, tooth pain, sprains, fractures, myositis, neuralgia, synovitis, arthritis, bursitis, burns, and various injuries. It is also used for symptomatic pain relief after surgical and dental procedures [FDA label]. The _extra strength_ formulation of acetylsalicylic acid is also indicated for the management migraine pain with photophobia (sensitivity to light) and phonophobia (sensitivity to sound) [FDA label]. **Other indications** ASA is also indicated for various other purposes, due to its ability to inhibit platelet aggregation. These include: Reducing the risk of cardiovascular death in suspected cases of myocardial infarction (MI) [FDA label]. Reducing the risk of a first non-fatal myocardial infarction in patients, and for reducing the risk of morbidity and mortality in cases of unstable angina and in those who have had a prior myocardial infarction [FDA label]. For reducing the risk of transient ischemic attacks (TIA) and to prevent atherothrombotic cerebral infarction (in conjunction with other treatments) [FDA label]. For the prevention of thromboembolism after hip replacement surgery [FDA label]. For decreasing platelet to platelet adhesion following carotid endarterectomy, aiding in the prevention of transient ischemic attacks (TIA) [FDA label]. Used for patients undergoing hemodialysis with a silicone rubber arteriovenous cannula inserted to prevent thrombosis at the insertion site [FDA Label]. **Important note regarding use of the extended-release formulation [F4405]** In the setting of acute myocardial infarction, or before percutaneous interventions, the extended-release form of acetylsalicylic acid should not be used. Use immediate-release formulations in scenarios requiring rapid onset of action [Label, F4405]. The extended-release form is taken to decrease the incidence of mortality and myocardial infarction (MI) for individuals diagnosed with chronic coronary artery disease (CAD), including patients with previous myocardial infarction (MI) or unstable angina or with chronic stable angina. Additionally, the extended-release form is used to decrease the risk of death and recurrent episodes of stroke in patients with a history of stroke or TIA [F4405].
What is ASA in a blood test?
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) blocks prostaglandin synthesis. It is non-selective for COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes [A177241, A10989, A32682]. Inhibition of COX-1 results in the inhibition of platelet aggregation for about 7-10 days (average platelet lifespan). The acetyl group of acetylsalicylic acid binds with a serine residue of the cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) enzyme, leading to irreversible inhibition. This prevents the production of pain-causing prostaglandins. This process also stops the conversion of arachidonic acid to thromboxane A2 ( TXA2 ), which is a potent inducer of platelet aggregation [FDA label]. Platelet aggregation can result in clots and harmful venous and arterial thromboembolism, leading to conditions such as pulmonary embolism and stroke. It is important to note that there is 60% homology between the protein structures of COX-1 and COX-2. ASA binds to serine 516 residue on the active site of COX-2 in the same fashion as its binding to the serine 530 residue located on the active site of COX-1. The active site of COX-2 is, however, slightly larger than the active site of COX-1, so that arachidonic acid (which later becomes prostaglandins) manages to bypass the aspirin molecule inactivating COX-2 [A32682, A177256]. ASA, therefore, exerts more action on the COX-1 receptor rather than on the COX-2 receptor [A177268]. A higher dose of acetylsalicylic acid is required for COX-2 inhibition [A177325].
What are salicylates used for?
Salicylates are indicated to relieve myalgia, musculoskeletal pain, and other symptoms of nonrheumatic inflammatory conditions such as athletic injuries, bursitis, capsulitis, tendinitis, and nonspecific acute tenosynovitis. /Included in US product labeling/
What is the molecular structure of aspirin?
The molecular structure image of aspirin is available in chemical structure page of aspirin, which provides the molecular geometry information, i.e., the spatial arrangement of atoms in aspirin and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together.
How many atoms are in an aspirin molecule?
The aspirin molecule consists of 8 Hydrogen atom (s), 9 Carbon atom (s) and 4 Oxygen atom (s) - a total of 21 atom (s). The molecular weight of aspirin is determined by the sum of the atomic weights of each constituent element multiplied by the number of atoms, which is calculated to be:
What is the SDF file for aspirin?
The structure data file (SDF/MOL File) of aspirin is available for download in the SDF page of aspirin, which provides the information on atoms, bonds, connectivity and coordinates of aspirin. The aspirin structure data file can be imported to most of the chemistry-related software, providing three-dimensional visualization and further analysis.