What does linear motion stand for?
Linear motion meaning the change of position of an object with respect to time interval. We live in a universe that is in continuous motion. The fundamental particle of a matter i.e. atom is also in constant motion. Every physical process happening in the universe is composed of some sort of motion. The motion can either be fast or slow, but ...
What are some linear motion examples?
Which are given as:
- Translatory motion
- Rotatory motion
- Vibratory motion
What is linear motion example?
This multi-axis linear motor XY Stage is compact ... the first of its kind high performance sample positioning stage where the motion... Tenorshare, the highly professional team with more than ten years of experience, has announced a giveaway for the ...
What is the importance of linear motion?
- Linear actuators feature absolutely accurate movement and positioning precision;
- They are safe and can be made from top-grade materials that enable the application for medical purposes;
- Electric actuators don’t require maintenance. It reduces the costs associated with it;
- Electric actuators are built in a variety of sizes, including really tiny ones.
What is linear motion give two examples?
The two examples of the Linear motion are: Rolling of ball on ground. Moving of bicycler on road.
What is linear motion and non linear motion?
Linear motion does not require a net force but nonlinear motion requires a net force. • A net force acting parallel to the movement will cause a linear motion; a net force applied in a direction not parallel to the movement will cause nonlinear motion.Oct 7, 2011
What is the example of simple linear motion?
Some examples of linear motion are a parade of soldiers, a train moving along a straight line, and many more.
What is linear motion and its types?
Linear motion can be defined as the movement of a body on a straight line without any deviation. Important examples of linear motion are: An athlete running on a straight track of a park, a bullet shot from a pistol always moves in a straight line, etc.Jan 17, 2022
What is linear motion class 11?
-Uniform Linear motion: The type of motion in which the object travels in a straight line with constant velocity in equal intervals of time. The acceleration of the object is zero in this motion.
What is linear motion class 9?
Linear Motion In linear motion, the particles move from one point to another in either a straight line or a curved path. The linear motion depending on the path of motion is further divided as follows. Rectilinear Motion – The path of the motion is a straight line. Curvilinear Motion – The path of the motion is curved.
What are the 3 examples of linear motion?
give 5 examples of linear motion falling of a stone from a height. soldiers marching in a parade. moving of a car on a straight road. walking on a straight road. sun rays falling to the earth.Nov 16, 2012
What is linear motion give five examples?
An example of Linear motion is: Falling of stone from a certain height, an athlete running 200 m on a straight track, train running in a straight track, car moving at a constant speed.
Which are the two types of linear motion?
What are the two types of linear motion ? Explain along with examples Rectilinear Motion – The path of the motion is a straight line. Curvilinear Motion – The path of the motion is curved. ... hope u mark the brainliest.Thanks.Thanks.Jan 19, 2021
How do you draw a linear motion?
25:1631:12Graphical analysis of Linear Motion - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if we have constant acceleration then the velocity is going to change at a constant rate thatMoreSo if we have constant acceleration then the velocity is going to change at a constant rate that means the slope will be straight it will be a straight line on a V versus T graph.
What is the other name of linear motion?
rectilinear motionlinear motion, also called uniform motion or rectilinear motion, motion in one spatial dimension.
What is linear motion in biomechanics?
Linear motion is movement in a straight line. Our body produces forces that cause angular motion of our joints that are then combined to cause linear motion of our bodies. This is known as general motion.May 25, 2017
1.What causes linear motion?
Linear motion is a movement in a straight line. The angular motion of the joints that our body produces by applying force are then combined to form...
2. Is linear and non-linear motion the same?
In linear motion net force is not required whereas non-linear motion requires net force. A net force that is acting parallel to the movement of a b...
3. What is accelerating uniformly?
When the speed of an object is increasing at a constant rate then it is said to be accelerating uniformly. The rate of acceleration is always const...
4. How is linear and rotatory motion created?
When the line of force passes through the center of mass of a body then direct force is applied resulting in linear motion and rotatory motion is c...
5. What are the two types of linear motion?
On thIs site of Vedantu we have discussed in detail about the meaning and types of linear motion. To get a detailed Insight on this topic kindly re...
6. Linear Motion Definition and How is It different from Circular Motion?
Linear motion physics is also known as rectilinear motion. It is a motion on a straight line in one dimension. When an object travels in a straight...
7. Define Linear Motion With Example.
Linear motion is a type of motion on a straight line in one dimension. When an object travels in a straight line it changes its position along with...
8. What is the Difference Between Linear Motion and Rectilinear Motion?
An object is in a linear motion if the object moves in a straight line, on the other hand, An object is in a rectilinear motion if two objects are...
What is linear motion?
Linear motion. Linear motion is movement in a straight line. Our body produces forces that cause angular motion of our joints that are then combined to cause linear motion of our bodies. This is known as general motion.
What are some examples of linear motion?
Some examples of linear motion are a parade of soldiers, a train moving along a straight line and many more.
What is it called when an object moves in a straight line?
Lesson Summary. When an object moves in a straight line, this is known as linear motion. Sometimes, objects move in a circle around a fixed axis, also known as rotary motion. Moving up and down, side to side, or back and forth is known as oscillatory motion.
Is linear motion one dimension?
Linear motion (also called rectilinear motion) is a one-dimensional motion along a straight line, and can therefore be described mathematically using only one spatial dimension.
Who created the laws of motion?
Newton’s laws of motion, three statements describing the relations between the forces acting on a body and the motion of the body, first formulated by English physicist and mathematician Isaac Newton, which are the foundation of classical mechanics.….
What is wave motion?
In sound, for instance, a single sine wave produces a pure tone, and the distinctive timbre of different musical instruments playing the same note results from the admixture of sine waves of different frequencies.
What is uniform motion?
According to Newton’s first law (also known as the principle of inertia), a body with no net force acting on it will either remain at rest... A body in motion may be said to have momentum equal to the product of its mass and its velocity.
Is there a difference between uniform motion and rest motion?
In fact, in classical Newtonian mechanics, there is no important distinction between rest and uniform motion in a straight line; they may be regarded as the same state of motion seen by different observers, one moving at the same velocity as the particle, the other moving at constant velocity with respect to the particle. ...
What is linear motion?
Linear motion, also called rectilinear motion, is one-dimensional motion along a straight line, and can therefore be described mathematically using only one spatial dimension. The linear motion can be of two types: uniform linear motion with constant velocity or zero acceleration; and non-uniform linear motion with variable velocity ...
What are the two types of linear motion?
Linear motion can be in 2 types 1) Rectilinear motion 2) Curvilinear motion. Linear motion is the most basic of all motion. According to Newton's first law of motion, objects that do not experience any net force will continue to move in a straight line with a constant velocity until they are subjected to a net force. Under everyday circumstances, external forces such as gravity and friction can cause an object to change the direction of its motion, so that its motion cannot be described as linear.
What is acceleration in math?
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Acceleration is the second derivative of displacement i.e. acceleration can be found by differentiating position with respect to time twice or differentiating velocity with respect to time once. The SI unit of acceleration is#N#m s − 2 {displaystyle mathrm {ms^ {-2}} }#N#or metre per second squared.
How to compare linear motion to general motion?
One may compare linear motion to general motion. In general motion, a particle's position and velocity are described by vectors, which have a magnitude and direction. In linear motion, the directions of all the vectors describing the system are equal and constant which means the objects move along the same axis and do not change direction. The analysis of such systems may therefore be simplified by neglecting the direction components of the vectors involved and dealing only with the magnitude.
How are acceleration, velocity, time and displacement related?
In case of constant acceleration, the four physical quantities acceleration, velocity, time and displacement can be related by using the Equations of motion
What does the gradient of a line on a displacement time graph represent?
These relationships can be demonstrated graphically. The gradient of a line on a displacement time graph represents the velocity. The gradient of the velocity time graph gives the acceleration while the area under the velocity time graph gives the displacement. The area under an acceleration time graph gives the change in velocity.
Are we missing a good definition for linear motion? Don't keep it to yourself..
The ASL fingerspelling provided here is most commonly used for proper names of people and places; it is also used in some languages for concepts for which no sign is available at that moment.
Definitions & Translations
Get instant definitions for any word that hits you anywhere on the web!
What is linear motor?
It’s as if the stator and rotor were cut along a radial plane and then unrolled so that they could provide linear thrust. When the stationary part of the motor is energized, it causes motion in the moving part that contains some kind of conductive material.
What type of actuator produces linear motion?
Common linear actuators include mechanical, electro-mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic and piezoelectric. A rotary source linear actuator typically uses an electric motor to provide its input energy.
What is rotary source linear actuator?
A rotary source linear actuator typically uses an electric motor to provide its input energy. This actuator can use a lead screw to turn the motor’s rotational motion into straight-line motion. The best fit for the application depends on factors such as required output, size and power requirements.
What is the primary source of motion?
Sometimes the primary source of motion is non-linear or rotary, such as a motor. In this case, some other mechanical means such as belts, pulleys, chains or other mechanical components convert the rotary motion to linear motion. Other types of linear actuators produce linear motion on their own, such as through fluid (hydraulic or air) pressure.
What are the factors that determine the best linear motor?
Choosing the best linear motor for an application involves a number of factors including force and thermal considerations, loads on bearings, and space and clearance considerations.
What are the benefits of a linear motor?
Linear motor benefits include high speeds and fast response times, high precision and stiffness, and because there are no mechanical transmission components the elimination of backlash.
Do you need preloading for a linear guide?
Pre-loading may also be required depending on the application requirements. Lubrication is another important consideration, as is any method to minimize contamination of the linear guide system from environmental factors such as dust and other contaminants using bellows or special seals.
What is linear motion?
n. 1. a. The act or process of translating, especially from one language into another. b. The state of being translated. 2. A translated version of a text....
What is the definition of a transformation in which the origin of a coordinate system is moved to another position?
3. (Mathematics ) maths a transformation in which the origin of a coordinate system is moved to another position so that each axis retains the same direction or, equivalently, a figure or curve is moved so that it retains the same orientation to the axes
What is the definition of mathsa transformation?
3. (Mathematics) mathsa transformation in which the origin of a coordinate system is moved to another position so that each axis retains the same direction or , equivalently, a figure or curve is moved so that it retains the same orientation to the axes
What does "translation" mean?
a. The act or process of translating, especially from one language into another.
Which process specifies the sequence of amino acids that line up on a ribosome for protein synthesis?
6. Genetics.the process by which messenger RNA specifies the sequence of amino acids that line up on a ribosome for protein synthesis.
What is the act of changing the unity or wholeness of something?
change of integrity- the act of changing the unity or wholeness of something
What is linear motion?
In linear motion, the particles move from one point to another in either a straight line or a curved path. The linear motion depending on the path of motion is further divided as follows
What is rotatory motion?
Rotatory motion is the motion that occurs when a body rotates on its own axis. A few examples of the rotatory motion are as follows: The motion of the earth about its own axis around the sun is an example of rotary motion.
What are some examples of oscillatory motion?
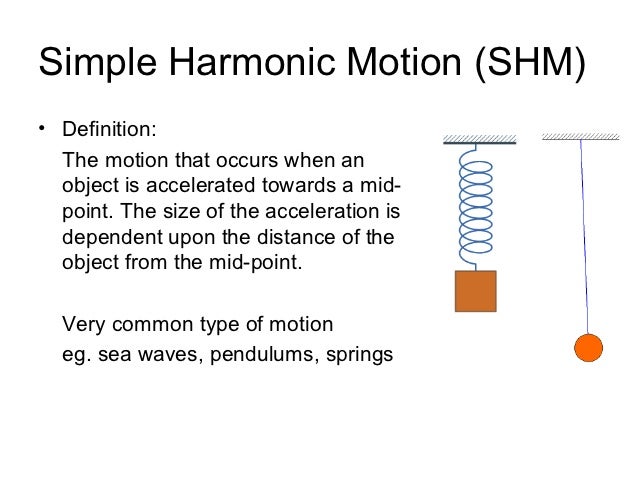
A few examples of oscillatory motion are. When a child on a swing is pushed, the swing moves to and fro about its mean position. The pendulum of a clock exhibits oscillatory motion as it moves to and fro about its mean position. The string of the guitar when strummed moves to and fro by its mean position resulting in an oscillatory motion.
What is displacement in math?
On the other hand, displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final position. It requires both magnitude and direction for complete representation. Motion Definition Types Of Motion Examples Of Motion.
What are the three types of motion?
According to the nature of the movement, motion is classified into three types as follows: Linear Motion. Rotary Motion. Oscillatory Motion.
What is the motion of an automobile?
The automobiles that carry passengers from the place of pick up to the destination possess motion. In this case, the position of passengers is changed from one place to another.
Why is it important to study motion?
It is important that we give due attention to the study of motion because of its importance in the physical world. Motion is mainly described in terms of the following terms:
Overview
Linear motion, also called rectilinear motion, is one-dimensional motion along a straight line, and can therefore be described mathematically using only one spatial dimension. The linear motion can be of two types: uniform linear motion with constant velocity or zero acceleration; and non-uniform linear motion with variable velocity or non-zero acceleration. The motion of a particle (a point-like object) along a line can be described by its position , which varies with (time). An exampl…
Displacement
The motion in which all the particles of a body move through the same distance in the same time is called translatory motion. There are two types of translatory motions: rectilinear motion; curvilinear motion. Since linear motion is a motion in a single dimension, the distance traveled by an object in particular direction is the same as displacement. The SI unit of displacement is the metre. If is the initial position of an object and is the final position, then mathematically the displa…
Velocity
Velocity refers to a displacement in one direction with respect to an interval of time. It is defined as the rate of change of displacement over change in time. Velocity is a vectorial quantity, representing a direction and a magnitude of movement. The magnitude of a velocity is called speed. The SI unit of speed is that is metre per second.
The average velocity of a moving body is its total displacement divided by the total time needed …
Jerk
The rate of change of acceleration, the third derivative of displacement is known as jerk. The SI unit of jerk is . In the UK jerk is also known as jolt.
Jounce
The rate of change of jerk, the fourth derivative of displacement is known as jounce. The SI unit of jounce is which can be pronounced as metres per quartic second.
See also
• Angular motion
• Centripetal force
• Inertial frame of reference
• Linear actuator
• Linear bearing
Further reading
• Resnick, Robert and Halliday, David (1966), Physics, Chapter 3 (Vol I and II, Combined edition), Wiley International Edition, Library of Congress Catalog Card No. 66-11527
• Tipler P.A., Mosca G., "Physics for Scientists and Engineers", Chapter 2 (5th edition), W. H. Freeman and company: New York and Basing stoke, 2003.
External links
Media related to Linear movement at Wikimedia Commons