Which organs have no lymphatic supply?
Anatomy
- Lymph nodes are kidney-shaped, encapsulated lymphoid organs: Afferent lymphatics enter on the convex surface. Through the concave depression (hilum): The efferent lymphatic leaves. ...
- 2–20 mm in diameter
- 500–600 lymph nodes in the body
- Seen along lymphatic vessels, occur as chains or groups (neck, groin, axillae, mesenteries, abdomen)
What are the small organs found on lymphatic vessels?
The primary functions of the lymphatic vessels and system include:
- Aiding absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive tract
- Providing defense against invading microorganisms and disease
- Returning excess tissue fluid to the blood circulation
What is the largest lymphatic gland in the body?
- spleen. blood reservoir; largest lymphatic organ; removes aged and defective red blood cells.
- lymph nodes. filter lymph; monitor composition of lymph.
- thymus.
- Peyer's patches.
- Peyer's patches and tonsils.
Which organ is without lymphatic drainage?
tissues and organs without lymphatic drainage. CNS (brain and spinal cord) bone marrow inner ear eye cartilage. connective tissue framework--reticular fibers--reticular cells = fibroblasts which produce reticular fibers (type III collagen) lamina propria--non-encapsulated lymphatic tissue
What are the organs of the lymphatic system?
Organs Of The Lymphatic System. The Lymphatic System is made of capillaries, vessels, nodes, lymph and various organs. Here we will talk about the organs. On the page The Lymphatic System you will find details on lymph, capillaries, vessels etc. as well as general information on the Introduction To Lymph Page.
Where is the thymus gland located?
The Thymus Gland is a small gland under our breast bone just above the area of our hearts. It sits between our lungs. It is here that white blood cells are produced. It is mostly active when we are young and shrinks as we age.
What are the glands in the mouth?
Referred to as glands also, both the Tonsils and Adenoids are in our mouth and are our first line of defense of substances entering our body. They serve as protectors to the digestive system and lungs from infections, germs, bacteria and viruses.
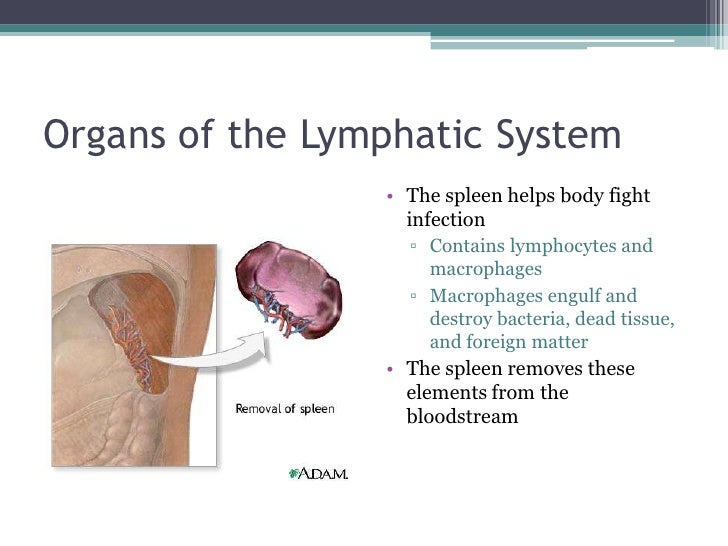
Where is the spleen located?
It is found on the left side of the body just under the rib cage approximate to the transverse/descending portion of our colon. It actually has very similar characteristics of the nodes except the spleen is filled with blood.
What is the spleen?
It is in the spleen that the blood is filtered and replenished. The spleen consists of two types of tissues, red pulp and white pup. The red pulp filters out the worn out and damaged red blood cells and destroys them and replaces them with fresh red blood cells made in the bone marrow.
What is the largest lymphatic organ?
Spleen: This largest lymphatic organ is located on your left side under your ribs and above your stomach. The spleen filters and stores blood and produces white blood cells that fight infection or disease.
What are the major lymphoid organs?
Primary lymphoid organs: These organs include the bone marrow and the thymus. …
What is the largest secondary lymphoid organ?
The spleen is the largest secondary lymphoid organ in the body. It contains two morphologically and functionally distinct compartments: Red pulp – filters the blood of foreign material and old or damaged red blood cells. White pulp – site of immune reactions to blood-borne antigens.
What is the smallest lymphatic organ?
Lymph Nodes. One of the Lymphoid Organs, its the smallest organ found along, there thousands of them. Thymus. One of the Lymphiod Organs, site of T-cell maturation, and secretes thymosins. Spleen.
What are the 6 lymphatic trunks?
Bronchomediastinal lymph trunks. Lumbar lymph trunks. Intercostal lymph trunks. Intestinal lymph trunk—unpaired.
What is lymph filtered by?
The lymph drains into lymphatic capillaries. The lymphatic capillaries conduct the fluid into larger lymphatic vessels, which carry it toward lymph nodes and lymphoid organs. The nodes and organs filter the lymph and eliminate harmful substances.
Are memory cells mature monocytes?
Memory cells are mature monocytes. Memory cells respond to antigens more rapidly than naive T cells. Upon reexposure to a pathogen, memory cells engage in the T cell recall response, destroying the pathogen quickly. … Memory cells respond to antigens more rapidly than naive T cells.