What is a large intrusive rock called?
A body of intrusive igneous rock which crystallizes from magma cooling underneath the surface of the Earth is called a pluton. If the pluton is large, it may be called a batholith or a stock depending on the area exposed at the surface.
What are the characteristics of intrusive igneous rocks?
Some intrusive rocks solidified in fissures as dikes and intrusive sills at shallow depth and are called subvolcanic or hypabyssal. They show structures intermediate between those of extrusive and plutonic rocks. They are very commonly porphyritic, vitreous, and sometimes even vesicular.
Which igneous rocks are mafic in composition?
The diagram here is a cross-section through part of the crust showing a variety of intrusive igneous rocks. Except for the granite (a), all of these rocks are mafic in composition.
What is the largest igneous intrusive body?
LopolithsLopoliths. Lopoliths are the largest known intrusions of dense magma and form a thick saucer shape within the surrounding country rocks.
What is the name of the largest intrusive body?
Batholiths are large bodies of intrusive igneous rock . Formed when magma cools and crystallizes beneath Earth's surface, batholiths are the largest type of pluton . By definition, a batholith must cover at least 39 mi2 (100 km2), although most are even larger.
What is a large intrusive igneous rock?
A body of intrusive igneous rock which crystallizes from magma cooling underneath the surface of the Earth is called a pluton. If the pluton is large, it may be called a batholith or a stock depending on the area exposed at the surface.
What are intrusive rock bodies called?
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth.
What is an intrusive batholith?
A batholith (from Ancient Greek bathos 'depth', and lithos 'rock') is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than 100 km2 (40 sq mi) in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust.
What does batholith mean?
Definition: Despite sounding like something out of Harry Potter, a batholith is a type of igneous rock that forms when magma rises into the earth's crust, but does not erupt onto the surface.
Which of the following is largest intrusive volcanic landforms?
Batholiths: These are huge mass of igneous rocks, usually of granite. These rock masses formed due to cooling down and solidification of hot magma inside the earth. They appear on the surface only after the denudation processes remove the overlying materials and may be exposed on surface after erosion.
What is extrusive rock bodies?
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff.
Which of the following is an intrusive igneous rock?
Intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below Earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. Examples of intrusive igneous rocks are: diabase, diorite, gabbro, granite, pegmatite, and peridotite.
What are the types of igneous bodies?
Igneous rocks are divided into two groups, intrusive or extrusive, depending upon where the molten rock solidifies. Intrusive Igneous Rocks: Intrusive, or plutonic, igneous rock forms when magma is trapped deep inside the Earth. Great globs of molten rock rise toward the surface.
Is a magma chamber an intrusive igneous body?
In some cases, yes, a magma chamber can be classified as an intrusive igneous body. For a magma chamber to be an intrusive igneous body, the magma in the chamber must cool and crystallize first.
What is the largest pluton?
batholithA batholith is the largest of the pluton types and by definition cover at least 100 square kilometres. A stock is a small discordant pluton, shaped like a batholith but falling below the necessary 100 square km in extent.
What is the body of rock that has been broken off and incorporated into the light-coloured granite?
The fragments of dark rock have been broken off and incorporated into the light-coloured granite. [SE] Some upward-moving magma reaches the surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions, but most cools within the crust. The resulting body of rock is known as a pluton.
What are large irregular shaped plutons called?
Large irregular-shaped plutons are called either stocks or batholiths. The distinction between the two is made on the basis of the area that is exposed at the surface: if the body has an exposed surface area greater than 100 km 2, then it’s a batholith; smaller than 100 km 2 and it’s a stock.
How does magma move?
In most cases, a body of hot magma is less dense than the rock surrounding it, so it has a tendency to move very slowly up toward the surface. It does so in a few different ways, including filling and widening existing cracks, melting the surrounding rock (called country rock[1]), pushing the rock aside (where it is somewhat plastic), and breaking the rock. Where some of the country rock is broken off, it may fall into the magma, a process called stoping. The resulting fragments, illustrated in Figure 3.19, are known as xenoliths (Greek for “strange rocks”).
Does country rock affect magma?
The country rock can also have an effect on the magma within a pluton. The most obvious such effect is the formation of a chilled margin along the edges of the pluton, where it came in contact with country rock that was significantly colder than the magma.
What are intrusive igneous bodies?
Types of Intrusive Igneous Bodies 1 Filling and widening existing cracks 2 Melting the surrounding rock (called country rock) 3 Pushing the rock aside (where the rock is hot enough and under enough pressure to deform without breaking) 4 Breaking the rock.
What is a body of intrusive igneous rock that crystallizes from magma cooling underneath?
A body of intrusive igneous rock which crystallizes from magma cooling underneath the surface of the Earth is called a pluton . If the pluton is large, it may be called a batholith or a stock depending on the area exposed at the surface.
What is a concordant body with a convex top and flat base?
Laccolith: concordant body with roughly flat base and convex top, usually with a feeder pipe below. Lopolith: concordant body with roughly flat top and a shallow convex base, may have a feeder dike or pipe below. Phacolith: a concordant lens-shaped pluton that typically occupies the crest of an anticline or trough of a syncline.
What is intrusive rock?
Intrusive rocks formed at greater depths are called plutonic or abyssal. Some intrusive rocks solidified in fissures as dikes and intrusive sills at shallow depth and are called subvolcanic or hypabyssal. They show structures intermediate between those of extrusive and plutonic rocks.
What are large, irregularly shaped plutons called?
Large, irregularly shaped plutons are called stocks or batholiths, depending on size. Tabular plutons are called dikes if they cut across existing structures, and sills if they do not. Laccoliths are like sills, except they have caused the overlying rocks to bulge upward. Pipes are cylindrical conduits.
What is it called when magma breaks off pieces of rock?
Breaking the rock. When magma forces itself into cracks, breaks off pieces of rock, and then envelops them, this is called stoping . The resulting fragments are called xenoliths. Plutons can have different shapes and different relationships with the surrounding country rock.
How does magma creep?
In most cases, a body of hot magma is less dense than the rock surrounding it, so it has a tendency to creep upward toward the surface. It does so in a few different ways: Filling and widening existing cracks. Melting the surrounding rock (called country rock) Pushing the rock aside (where the rock is hot enough and under enough pressure ...
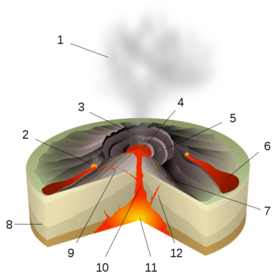
Introduction
Magma is stored below the surface in reservoirs called magma chambers. It creates and follows paths called conduits to the surface. This network is often referred to as the volcano's plumbing system.
Intrusive Igneous Landforms in Parks
The following is a partial list of National Park Service units that include Intrusive Igneous landforms: