What is the KF of ethylene glycol?
| Solvent | Boiling point (°C) | K f (°C/mol/kg) |
| Ethylene glycol | 197.3 | –3.11 |
| Formic acid | 101.0 | –2.77 |
| Naphthalene | 217.9 | –6.80 |
| Nitrobenzene | 210.8 | –7.00 |
What is constant kB of ethylene glycol?
Ethylene glycol (C 2 H 6 O 2 ) is a molecular compound that is used in many commercial anti-freezes. A water solution of ethylene glycol is used in vehicle radiators to lower its freezing point and thus prevent the water in the radiator from freezing. Calculate the freezing point of a solution of 400. g of ethylene glycol in 500. g of water.
Why is glycerol heavier than ethylene glycol?
Glycerol (1,2,3-trihydroxypropane) has three -OH groups per molecule while ethylene glycol (1,2-dihydroxyethane) has two -OH groups. The viscosity depends on the amount of hydrogen bonding between molecules, and the more -OH bonds there are, the more hydrogen bonding can occur.
What is the viscosity of ethylene glycol at room temperature?
°F °C Ethylene Ethylene DOWTHERM DOWTHERM 760 mm 0.96 Degree Index Glycol Glycol SR-1 4000 Hg Barr Brix†† 22˚C 32.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 212.0 100.0 0.0 1.3328
What is formula of ethylene glycol?
Ethylene glycol is also known as Monoethylene glycol. It is produced when ethylene oxide chemically reacts with water. The chemical formula of Ethylene glycol is C2H6O2. The chemical structure of Ethylene glycol is as follows: What are the Uses of Ethylene Glycol?
See more
What is the freezing point constant of ethylene glycol?
What is KF equal to?
Is KB the same as KF?
What is KF for ethanol?
How do you calculate KF?
What does a high KF value mean?
What is KF in chemistry solubility?
What does KB and KF depend on?
What is KF in chemistry equilibrium?
What is the KF of water?
What is the kb of ethylene glycol?
| Solvent | Boiling point (°C) | Kb (°C⋅kg/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Ethylene glycol | 197.3 | 2.26 |
| Formic acid | 101.0 | 2.4 |
| Naphthalene | 217.9 | |
| Nitrobenzene | 210.8 | 5.24 |
How do you calculate the freezing point of ethanol?
- ΔTf=iKfm.
- 50mL⋅1.0gmL⋅kg103g≈5.0⋅10−2kg of water, and,
- 50mL⋅0.789gmL⋅mol46.07g≈0.856mol of ethanol.
- ∴Tf=31.9°C ,
- and by extension −31.9°C is the freezing point of that particular solution.
What is ethylene glycol used for?
Ethylene glycol is also commonly used in heating applications that temporarily may not be operated (cold) in surroundings with freezing conditions - such as cars and machines with water cooled engines.
What is the density of a solution at installation temperature?
From the table above we see that the density of the solution at installation temperature can be as high as 1090 kg/m3 - and the medium density at operation temperature can be as low as 1042 kg/m3 .
Does ethylene glycol increase viscosity?
Note! The dynamic viscosity of an ethylene glycol based water solution is increased compared with the dynamic viscosity of clean water. As a consequence the head loss (pressure loss) in the a piping system with ethylene glycol is increased compared to clean water.
Is ethylene glycol a heat transfer?
Note ! The specific heat of ethy lene glycol based water solutions are less than the specific heat of clean water. For a heat transfer system with ethylene glycol the circulated volume must be increased compared to a system only with water.
Can you use ethylene glycol in freezing?
Due to possible slush creation, ethylene glycol and water solutions should not be used in conditions close to freezing points.
Can you use propylene glycol in water?
Ethylene glycol should be avoided if there is a slightest chance of leakage to potable water or food processing systems. Instead solutions based on propylene glycol are commonly used. Specific heat, viscosity and specific weight of a water and ethylene glycol solution vary significantly with the percent of ethylene glycol and the temperature ...
Can you use deionized water for ethylene glycol?
Distilled or deionized water should be used for ethylene glycol solutions. City water may be treated with chlorine which is corrosive. Systems for automatic makeup water should not be used since a leakage would contaminate the environment and dilute the antifreeze protection of the system.
Overview
Toxicity
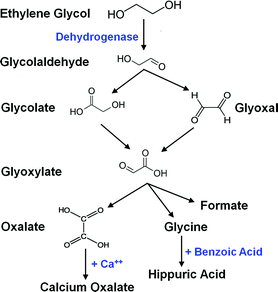
Ethylene glycol has high mammalian toxicity when ingested, roughly on par with methanol, with an oral LDLo = 786 mg/kg for humans. The major danger is due to its sweet taste, which can attract children and animals. Upon ingestion, ethylene glycol is oxidized to glycolic acid, which is, in turn, oxidized to oxalic acid, which is toxic. It and its toxic byproducts first affect the central nervous system, then the heart, and finally the kidneys. Ingestion of sufficient amounts is fatal if untreate…
Production
Ethylene glycol is produced from ethylene (ethene), via the intermediate ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide reacts with water to produce ethylene glycol according to the chemical equation:
C2H4O + H2O → HO−CH2CH2−OH
This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, or can occur at neutral pH under …
Uses
The major use of ethylene glycol is as an antifreeze agent in the coolant in for example, automobiles and air-conditioning systems that either place the chiller or air handlers outside or must cool below the freezing temperature of water. In geothermal heating/cooling systems, ethylene glycol is the fluid that transports heat through the use of a geothermal heat pump. The ethylene glycol either gai…
Chemical reactions
Ethylene glycol is used as a protecting group for carbonyl groups in organic synthesis. Treating a ketone or aldehyde with ethylene glycol in the presence of an acid catalyst (e.g., p-toluenesulfonic acid; BF3·Et2O) gives the corresponding a 1,3-dioxolane, which is resistant to bases and other nucleophiles. The 1,3-dioxolane protecting group can thereafter be removed by further acid hydrolysis. …
Environmental effects
Ethylene glycol is a high-production-volume chemical; it breaks down in air in about 10 days and in water or soil in a few weeks. It enters the environment through the dispersal of ethylene glycol-containing products, especially at airports, where it is used in de-icing agents for runways and airplanes. While prolonged low doses of ethylene glycol show no toxicity, at near lethal doses (≥ 1000 mg/kg per day) ethylene glycol acts as a teratogen. "Based on a rather extensive databas…
External links
• WebBook page for C2H6O2
• ATSDR - Case Studies in Environmental Medicine: Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol Toxicity
• CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
• Antifreeze ratio for Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol