| Structure | Common Name | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|---|
| HO-CO-OH | Carbonic | |
| HOOC-COOH | Oxalic acid | Ethanedioic |
| HOOC-CH2-COOH | Malonic acid | Propanedioic |
| HOOC-(CH2)2-COOH | Succinic acid | Butanedioic |
What is the systematic IUPAC name for H2CO3?
The systematic IUPAC name is not always the preferred IUPAC name, for example, lactic acid is a common, and also the preferred, name for what systematic rules call 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. This list is ordered by the number of carbon atoms in a carboxylic acid. Despite having an organic-like name, H 2 CO 3 is not considered an organic compound.
What is the IUPAC name for the compound prop-?
Give the IUPAC name for the following compound: The compound is a hydrocarbon with single bonds between the carbon atoms. It is an alkane and will have the suffix -ane. There are three carbon atoms in the longest chain. The prefix for this compound is prop-.
What is IUPAC naming?
What is IUPAC Naming? What is IUPAC naming? In order to give compounds a name, certain rules must be followed. When naming organic compounds, the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature (naming scheme) is used. This is to give consistency to the names.
What is the IUPAC name for an organic compound with 1 3-diene?
Give the IUPAC name for the following compound: The compound is an alkene and will have the suffix -ene. There is a double bond between the first and second carbons and also between the third and fourth carbons. The organic compound therefore contains '1,3-diene'. Remember that the main carbon chain must contain both the double bonds.
What is IUPAC name of HOOC-COOH compound?
ethene dioic acid Was this answer helpful?
What is the IUPAC name of the following dicarboxylic acid HOOC CH2 COOH?
The compound contains two carboxylic acid group along with 4 carbon in parent chain. Thus, its IUPAC name will be as follow: Butanedioic acid.
What is the IUPAC name of ch3 COOH ch3?
ethanoic acidAcetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH (also written as CH3CO2H, C2H4O2, or HC2H3O2)....CHEBI:15366 - acetic acid.ChEBI Nameacetic acidSecondary ChEBI IDsCHEBI:2387, CHEBI:40486, CHEBI:2216911 more rows•Aug 17, 2021
What is the common name of Hooc CH2 4 COOH?
Adipic acidCAS Number:124-04-9Chemical Formula:HOOC(CH2)4COOHMolecular Weight:146.14 g/mol
Is COOH and HOOC the same?
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by a carboxyl (-COOH) functional group. The naming of these compounds is governed by IUPAC nomenclature, which ensures systematic and consistent naming of chemicals....IUPAC nameCommon nameStructural formuladioxobutanedioic aciddioxosuccinic acidHOOC(CO)2COOH21 more rows
What is Hooc in chemistry?
Oxalic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with a chemical formula C2H2O4. It is also known as Ethanedioic acid or Oxiric acid. This organic compound is found in many vegetables and plants. It is the simplest dicarboxylic acid with condensed formula HOOC-COOH and has an acidic strength greater than acetic acid.
What is the IUPAC name of ch3coona?
Sodium acetateSodium acetate / IUPAC ID
How do you write IUPAC name?
In summary, the name of the compound is written out with the substituents in alphabetical order followed by the base name (derived from the number of carbons in the parent chain). Commas are used between numbers and dashes are used between letters and numbers. There are no spaces in the name.
What is the IUPAC name of CH3COOH and CH2?
The IUPAC names for the compounds CH3COOH and CH2 = CH2 are respectively. D. ethanol and ethene.
What happen when HOOC CH2 COOH is heated?
COOH−CH2−COOH. (Malonic acid) on heating produces: Acetic acid. Carbon dioxide.
What is the name of CH2 CH2 COOH?
C. 2-cyano methane carboxylic acid.
What is the name of this compound CH2 4 COOH 4?
Hexanoic acid -5-al-1.
Is oxalic acid a strong acid?
As an organic acid, oxalic acid is a weak acid. Oxalic acid is known to be a soft acid. It’s weaker than (water) H3O+ atom. But it is better than a...
What is the pH of oxalic acid?
The constant acid dissociation of oxalic acid is 5.60 between 10-2 and 5.42 between 10-5. As oxalic acid is a polyprotic acid, there are two values...
What is the world’s strongest acid?
Carborane superacids can be considered the strongest solar acid in the world since fluoroantimonic acid is a combination of hydrofluoric acid and p...
What is the basicity of oxalic acid?
Acid weight equivalent = (acid molecular weight)/Basicity. Oxalic acid basicity is = 2. Oxalic acid (H2C2O4) molecular weight = 90.
What is the Valency of oxalic acid?
The valence factor is the no. of acid and base produced H+ or OH-ion. The acid releases 2 H+ ion, hence the valence factor is 2 in the case of oxal...
Is oxalic acid polar or nonpolar?
Two carboxylic acid groups are composed of oxalic acid (HOOC-COOH). These groups are polar and are able to form hydrogen bonds with molecules of wa...
What is the natural source of oxalic acid?
The most popular constituent of kidney stones is calcium oxalate. Early researchers isolated Wood-sorrel (Oxalis) oxalic acid. Members of the famil...
How do you neutralize oxalic acid?
Since this is an acid it must be neutralized before any finish can occur. To neutralize the acid two to three times, flood the surface with clean w...
What is the chemical formula for oxalic acid?
Oxalic acid Formula. Oxalic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C2H2O4. Oxalic acid occurs in the cell sap of Oxalis and Rumex species of plants as the potassium and calcium salt. In an aqueous solution, oxalic acid is a weak acid that will only partially ionise. Oxalic acid has two acidic protons.
How to calculate equivalent weight of oxalic acid?
Therefore, the equivalent weight of oxalic acid can be calculated with the help of the following formula: Equivalent weight = (molecular weight)/ (number of equivalent moles) Since 1 mole of oxalic acid can release 2 moles of H + ions and neutralize 2 moles of OH – ions, the number of equivalent moles here is equal to 2.
How many protons does oxalic acid have?
Oxalic acid has two acidic protons. The initial ionisation yields HC2O4-, a weak acid that will ionise as well. Oxalic acid is one of the most powerful of the organic acids and expels carbonic acid and many other acids from their salts.
How is oxalic acid prepared?
Oxalic acid can be easily prepared by oxidation of certain carbohydrates like sucrose by concentrates nitric acid. During oxidation, the carbon atoms are split off in pairs giving oxalic acid.
How much does oxalic acid weigh?
Therefore, the equivalent weight of oxalic acid is 63 grams.
What is the constant dissociation of oxalic acid?
The constant acid dissociation of oxalic acid is 5.60 between 10-2 and 5.42 between 10-5. As oxalic acid is a polyprotic acid, there are two values and it has a chemical formula HOOC-COOH.
What is the molar mass of oxalic acid?
The molar mass of hydrated oxalic acid is 126 grams per mole. Since the chemical formula of this compound can be written as COOH-COOH, it can be understood that oxalic acid is a dibasic acid which has the ability to donate two H + ions.
What is 2H acid?
2H. It is the simplest dicarboxylic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. Its name comes from the fact that early investigators isolated oxalic acid from flowering plants of the genus Oxalis, commonly known as wood-sorrels.
How is oxalic acid made?
Oxalic acid is mainly manufactured by the oxidation of carbohydrates or glucose using nitric acid or air in the presence of vanadium pentoxide. A variety of precursors can be used including glycolic acid and ethylene glycol. A newer method entails oxidative carbonylation of alcohols to give the diesters of oxalic acid: ...
Which acid has the greatest strength?
Oxalic acid has much greater acid strength than acetic acid. It is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate ( C. 2O2−. 4 ), is a chelating agent for metal cations. Typically, oxalic acid occurs as the dihydrate with the formula C. 2H.
Is anhydrous oxalic acid a polymorph?
Anhydrous oxalic acid exists as two polymorphs; in one the hydrogen-bonding results in a chain-like structure whereas the hydrogen bonding pattern in the other form defines a sheet-like structure. Because the anhydrous material is both acidic and hydrophilic (water seeking), it is used in esterifications .
Who discovered that oxalic acid was the first natural product?
By 1784, Scheele had shown that "sugar acid" and oxalic acid from natural sources were identical. In 1824, the German chemist Friedrich Wöhler obtained oxalic acid by reacting cyanogen with ammonia in aqueous solution. This experiment may represent the first synthesis of a natural product.
Does rhubarb have oxalic acid?
Rhubarb leaves contain about 0.5% oxalic acid, and jack-in-the-pulpit ( Arisaema triphyllum) contains calcium oxalate crystals. Similarly, the Virginia creeper, a common decorative vine, produces oxalic acid in its berries as well as oxalate crystals in the sap, in the form of raphides. Bacteria produce oxalates from oxidation of carbohydrates.
Why do we use IUPAC?
This is to give consistency to the names. It also enables every compound to have a unique name, which is not possible with the common names used (for example in industry).
What is the suffix for carbons in the longest chain?
Numbering from left to right (shown in red) the first triple bond is on carbon 1 and the second is on carbon 5. The suffix will therefore be -1,5-diyne. (Numbering from right to left (shown in blue) will give the suffix - 2,6-diyne, and is incorrect).
What is the name of the group of carboxylic acids?
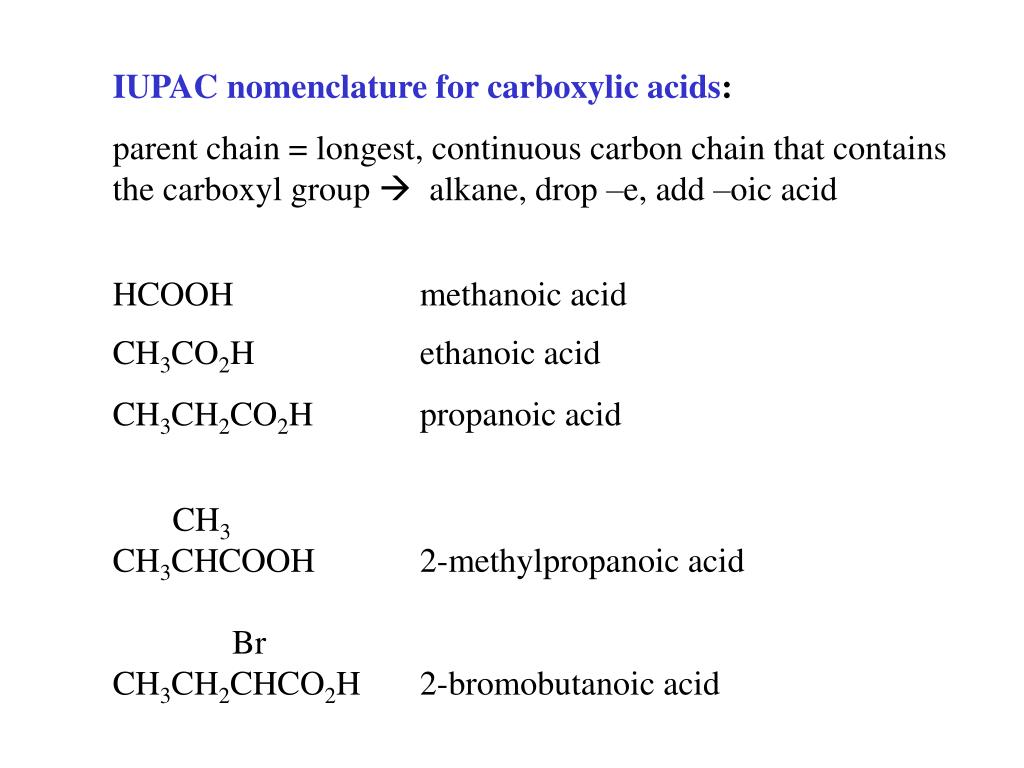
Naming carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids are characterised by having a carboxyl group, which has the formula (-text {COOH}). In a carboxyl group a carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom (a carbonyl group), and is also bonded to a hydroxyl (alcohol) group. The IUPAC suffix for a carboxylic acid is -oic acid.
Carboxylic Acid
Carboxylic acids consist of a carboxyl functional group ( – C O O H) in which a carbon atom is bonded to an oxygen atom by a double bond ( C = O) and a hydroxyl group ( – O H) through a single bond. The carboxyl ( C O O H) group is so-named because of the carbonyl group ( > C = O) and a hydroxyl group.
The Naming of Carboxylic acids
Many carboxylic acids are called by the common names. Chemists assign these names to describe the source from where the compound is obtained. This naming is done by adding – i c to the source name of the compound. Some of these compounds are listed below:
IUPAC System of Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) system assigns a characteristic suffix to this class of compounds. The parent hydrocarbon chain’s -ane suffix is changed to “ oic acid, ” dropping the “ e ” of the parent alkane name. Some basic IUPAC rules for naming alcohols are:
Solved Example on Naming of Carboxlyic Acid
The parent chain consists of seven carbon atoms and is heptane. So, we have heptanoic acid. Halogens and nitrile groups rank very low in the priority list of functional groups. Hence, they are considered substituents and get a prefix.
FAQs on Nomenclature of Carboxylic acid
We hope this article on the nomenclature and structure of carboxylic acids is helpful to you. If you have any questions related to this page, reach us through the comment box below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are carbon compounds with a carboxyl functional group, –COOH. The carboxyl group is made up of a carbonyl group that is joined to a hydroxyl group, hence the name carboxyl.
Sample Questions
Acetophenone can be converted in benzoic acid by oxidation of acetophenone in the presence of acidic or alkaline potassium permanganate.
Why do we use IUPAC?
In order to give compounds a name, certain rules must be followed. When naming organic compounds, the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature (naming scheme) is used. This is to give consistency to the names. It also enables every compound to have a unique name, which is not possible with the common names used ...
What are the names of halogen atoms?
chlorine. chloro. bromine. bromo. iodine. iodo. Table: Naming halogen atoms in organic molecules. Give the halogen atom a number to show its position on the carbon chain. If there is more than one halogen atom the numbers should be listed and a prefix should be used (e.g. 3,4-diiodo- or 1,2,2-trichloro-).