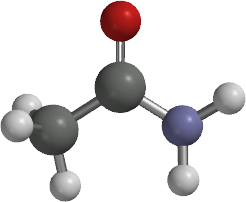
| IUPAC Name | acetamide |
|---|---|
| Alternative Names | acetamide Ethanamide Acetic acid amide Methanecarboxamide Acetimidic acid |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5NO |
| Molar Mass | 59.068 g/mol |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C2H5NO/c1-2(3)4/h1H3,(H2,3,4) |
Precautions
Acetamide (systematic name: ethanamide) is an organic compound with the formula CH 3 CONH 2. It is the simplest amide derived from acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent. The related compound N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA) is more widely used, but it is not prepared from acetamide.
What is the chemical name of acetamide?
In this manner, what is the Iupac name of ch3conh2? Acetamide (or acetic acid amide or ethanamide), CH3CONH2, the amide of acetic acid, is a white crystalline solid in pure form. Secondly, what is acetamide used for?
What is the IUPAC name of acetamide CH3CONH2?
Acetamide was detected at concentrations of 2.4 and 28.6 ug/L in distillate and residue, respectively, in leachate from a landfill for municipal wastes in Japan (1). Acetamide was detected in condensate and process oil-shale retort water at concentrations of 0.6 mg/L and 23.2 mg/L, respectively (2).
What is the concentration of acetamide in water?
It is a tautomer of an acetimidic acid. Acetamide is used primarily as a solvent and a plasticizer. Workers may be exposed in the plastics and chemical industries. It causes mild skin irritation from acute (short-term) exposure.
Is acetamide a tautomer?
See more
What is the structural formula of acetamide?
C2H5NOAcetamide / Formula
Which functional group is present in acetamide?
carboxylic acid amide functional groupAcetamide Formula and Structure The acetamide has a methyl group (-CH3) bound to a carbonyl (CO) and Amine (NH2). Besides, the acetamide primarily comprises of carboxylic acid amide functional group that has a general structure RC (=O) NH2.
What is the meaning of acetamide?
Definition of acetamide : a white crystalline amide C2H5NO of acetic acid used especially as a solvent and in organic synthesis.
What type of particle is acetamide?
Acetamide is a member of the class of acetamides that results from the formal condensation of acetic acid with ammonia. It is a monocarboxylic acid amide, a N-acylammonia and a member of acetamides. It is a tautomer of an acetimidic acid. Acetamide is used primarily as a solvent and a plasticizer.
How do you make acetamide?
Acetamide can be prepared by the rapid distillation of ammonium acetate;2 by heating ammonium acetate in a sealed tube and distilling the product;3 by treating acetic anhydride with ammonia;4 by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium acetate to 240°;5 by the action of cold aqueous ammonia on ethyl acetate;6 ...
Which of the following reactions give acetamide?
Which of the following reactions gives Acetamide? answer: Hydrolysis of CH, CH2CH2CN Heating CH,COOH with NH, followed by further heating Reaction of CH CH CN with LiAIH, followed by H2O Reaction of CH,CN with Na(Hg) and C,H,OH.
What is used of acetamide?
Acetamide is a colorless, crystalline (sand-like) material. It is used in lacquers, explosives, and soldering flux, and as a stabilizer, plasticizer and solvent.
Which is more basic aniline or acetamide?
Statement I : Aniline is less basic than acetamide.
Is acetamide an organic compound?
Acetamide, also known as ethanamid or acetic acid amide, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as carboximidic acids. These are organic acids with the general formula RC(=N)-OH (R=H, organic group).
Is acetamide covalent or ionic?
Properties of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsCovalent compoundElectrical conductivitySolidLiquidGlucoseNon conductorNon conductorAcetamideNon conductorNon conductorNapthaleneNon conductorNon conductor1 more row•Nov 30, 2020
Is acetamide a base?
Answer: Acetamide is a chemical molecule with the formula CH3CONH2. This is the most basic amide among acetic acid derivatives.
How do you convert acetic acid into acetamide?
When we mix acetic acid with ammonia it will turn into sodium acetate. When we heat that sodium acetate it turns into acetamide and water.
1. Why is Acetamide a Weaker Base to That of Ethylamine?
The presence of an electrons lone pair on a base defines its intensity because these electrons are the ones that will “mop up” the H+ ions in a sol...
2. What is Acetamide Used For?
Acetamide is an organic compound, having the chemical formula as CH3CONH2. This compound is the simplest amide of acetic acid derivatives. Also, th...
3. Why is the Acetamide Compound Soluble in the Water?
The primary amide is produced from NH2, which is an amino group replacing the carboxylic hydroxyl group. There is a point in a case, that is, aceta...
What is the chemical formula for acetamide?
These are organic acids with the general formula RC (=N)-OH (R=H, organic group). Acetamide is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa).
What is the amide of acetic acid?
Acetamide (or acetic acid amide or ethanamide), CH3CONH2, the amide of acetic acid, is a white crystalline solid in pure form.
What is acetyl chloride?
Acetyl chloride (CH3COCl) is an acyl chloride derived from acetic acid. It belongs to the class of organic compounds called acyl halides. It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid.
What happens when amides are hydrolysed?
Technically, hydrolysis is a reaction with water. That is exactly what happens when amides are hydrolysed in the presence of dilute acids such as dilute hydrochloric acid. The acid acts as a catalyst for the reaction between the amide and water.
What is an acid anhydride?
As the name indicates, an acid anhydride is a compound that is related to an acid by the loss of water. Acetic anhydride can by prepared by the dehydration of acetic acid at 800°C. Alternatively, the reaction between the acid chloride and a salt of acetic acid (e.g. sodium acetate) yields acetic anhydride and a salt.
What is the name of the compound with the formula CH3NH2?
Methylamine is an organic compound with a formula of CH3NH2. This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine.
Is phenylamine a weak base?
Therefore, phenylamine is a weaker base than ethylamine because its lone pair is less available.
What is acetamide made of?
It can also be made from anhydrous acetic acid, acetonitrile and very well dried hydrogen chloride gas, using an ice bath, alongside more valuable reagent acetyl chloride. Yield is typically low (up to 35%), and the acetamide made this way is generated as a salt with HCl.
What is the name of the compound that is made of acetic acid?
Chemical compound. Acetamide (systematic name: ethanamide) is an organic compound with the formula CH 3 CONH 2. It is the simplest amide derived from acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent.
What compounds were found on the surface of comet 67/P?
On 30 July 2015, scientists reported that upon the first touchdown of the Philae lander on comet 67/P 's surface, measurements by the COSAC and Ptolemy instruments revealed sixteen organic compounds, four of which – acetamide, acetone, methyl isocyanate, and propionaldehyde – were seen for the first time on a comet.
Is acetamide a solvent?
Acetamide is used as a plasticizer and an industrial solvent. Molten acetamide is good solvent with a broad range of applicability. Notably, its dielectric constant is higher than most organic solvents, allowing it to dissolve inorganic compounds with solubilities closely analogous to that of water.
What is Acetamide?
Acetamide is an inorganic compound having the chemical name Acetamide. The chemical formula of Acetamide is C2H5NO. The compound acetamide is also known as Ethanamide, or Acetic acid amide, or also Acetic acid. It originated from acetic acid and it is the simplest amide - an acetamide widely used as a plasticizer.
What is the primary amide?
The primary amide is produced from NH2, which is an amino group replacing the carboxylic hydroxyl group. There is a point in a case, that is, acetamide (acetic acid + amide). The low molecular weight amides that are caused by the formation of hydrogen bonds are soluble in water.`
What is anhydrous acetic acid used for?
On the other side, anhydrous acetic acid is also used to produce acetamide, acetonitrile, and a very well hydrogen chloride gas in dried form, using an ice bath, together with more valuable reagent acetyl chloride. This product is typically low (up to 35%), and the acetamide is generated as a salt with HCl, produced in this way.
Is ammonia soluble in water?
The key findings have been that acetamide and ammonia are water and HCl soluble because they are smaller molecules. The compounds aniline, triethylamine, and N, N-dimethylaniline are not referred to be water - and HCl soluble, but are MTBE-soluble (Methyl Tert-Butyl Ether). MTBE is not soluble in both acetamide and ammonia.
What is acetazolamide?
Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Acetazolamide reduces the formation of hydrogen and bicarbonate ions from carbon dioxide and water by noncompetitive, reversible inhibition of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, thereby reducing the availability of these ions for active transport into secretions.
How is acetazolamide excreted?
Acetazolamide is excreted unchanged by the kidneys via tubular secretion and passive reabsorption. There is no evidence of enterohepatic circulation although small amounts of unchanged drug are eliminated in the bile. Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
Where is acetazolamide absorbed?
Acetazolamide is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Acetazolamide is distributed throughout body tissues; it concentrates principally in erythrocytes, plasma and kidneys and to a lesser extent in liver, muscles, eyes and the central nervous system. Acetazolamide does not accumulate in tissues.
Can acetazolamide cause liver damage?
Idiosyncratic, clinically apparent liver injury from acetazolamide and methazolamide is rare, but several instances have been reported as isolated case reports. Acetazolamide is a sulfonamide and cross reactivity to sulfonamide reactions have been reported. The liver injury typically arises after a few days to weeks of therapy and the pattern of serum enzyme elevations is usually hepatocellular or mixed. Immunoallergic features (rash, fever, eosinophilia) are common, but autoantibody formation is not. Both acetazolamide and methazolamide have been linked to Stevens Johnson Syndrome and a genetic association has been made with HLA-B*5901. Hepatic involvement and jaundice can occur in some cases of Stevens Johnson Syndrome.
Is acetazolamide a dermal absorption?
Oral ingestion is the usual means of exposure. There is no appreciable dermal absorption. There is no significant absorption or local irritation. ANIMAL/PLANT STUDIES: Numerous animal studies have demonstrated that the toxicity of acetazolamide was very low in the species studied (mouse, dog, rat, monkey).
Does acetazolamide help with epilepsy?
The efficacy of acetazolamide in epilepsy is in part due to the production of metabolic acidosis ; however, direct actions of acetazolamide in the CNS also contribute to its anticonvulsant action. Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.).
Does acetazolamide increase oxygen?
The anticonvulsant activity of Acetazolamide may depend on a direct inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the CNS, which decreases carbon dioxide tension in the pulmonary alveoli, thus increasing arterial oxygen tension. The diuretic effect depends on the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase, causing a reduction in the availability of hydrogen ions for active transport in the renal tubule lumen. This leads to alkaline urine and an increase in the excretion of bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, and water.