What is the isoelectric point of glycine?
| Name | pK | pI at 25°C |
| Glutamic Acid | 2.19 | 3.08 |
| Glutamine | 2.17 | 5.65 |
| Glycine | 2.34 | 6.06 |
| Histidine | 1.78 | 7.64 |
How to calculate the isoelectric point of glycine?
1. Calculate the Isoelectric point of Glycine? (pK1=2.4; pK2=9.8) Ans: Glycine is a neutral and optically inactive amino acid. According to isoelectric point concept, the given formula will be applied; pK 1 + pK 2 2.4 + 9.8. pI =—————- = —————— = 6.1. 2 2. The isoelectric point of the Glycine is 6.1.
What is the structure of glycine?
Glycine is the simplest (and the only achiral) proteinogenic amino acid, with a hydrogen atom as its side chain. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a hepatoprotective agent, an EC 2.1.2.1 (glycine hydroxymethyltransferase) inhibitor, a NMDA receptor agonist, a micronutrient, a fundamental metabolite and a neurotransmitter.
What are the properties of nonpolar glycine?
(Aliphatic R-group) Physical Properties: Nonpolar Glycineis the smallest of the amino acids. It is ambivalent, meaning that it can be inside or outside of the protein molecule. In aqueous solution at or near neutral pH, glycine will exist predominantly as the zwitterion
What is the fully protonated form of glycine?
The fully protonated form of glycine is + NH3CH2COOH. Step 1 is the loss of H+ from the carboxyl group. Step 2 is the loss of H+ from the less acidic NH+ 3 group. The first equivalence point, at 50 % titration, is at pH = 5.97.
See more
How do you calculate the isoelectric point of glycine?
Isoelectric point (pI) can be calculated using the formula, pI = pKa1 + pKa2/ 2 for molecules with two ionizable groups (e.g. amino acids like glycine). The pKa1 of the carboxylic acid group of glycine is 2.34 and pKa2 of the amino group is 9.60, therefore, pI (glycine) = (2.34+9.60)/2 = 5.94.
Does glycine have isoelectric point?
2:4618:34Isoelectric Point of Amino Acids with MCAT Shortcut - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThen you simply take the average of the two PKA values which is PK 1 plus PK a 2 divided. By 2 toMoreThen you simply take the average of the two PKA values which is PK 1 plus PK a 2 divided. By 2 to find the P I for glycine.
What is the isoelectric point of the amino acid glycine?
(R ) : The isoelectric point of glycine, PI is 6.0.
What are isoelectric points of an amino acid?
The isoelectric point of an amino acid is the point at which the amino acid has no net electrical charge. It is an important characteristic for any amino acid, because every amino acid has at least two acid–base (titratable) groups.
What is isoelectric point?
The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH of a solution at which the net charge of a protein becomes zero. At solution pH that is above the pI, the surface of the protein is predominantly negatively charged, and therefore like-charged molecules will exhibit repulsive forces.
What is glycine pH?
Glycine (0.1 M, pH 2.2)
What type of amino acids have an isoelectric point above 7?
All basic amino acids (three of them) have an isoelectric point above a pH of 7.
How do you find the isoelectric point of a protein?
In order to determine the isoelectric point a given protein, we must follow a general rule that consists of two steps (1) Estimate the pH value at which the protein will have a net charge of zero (2) Determine the pKa value right above and right below the estimated pH and find their average.
How do you calculate the isoelectric point of a polypeptide?
0:279:29Determining the isoelectric point of a polypeptide - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIf you only have two pka's the equation that you use is P I is equal to PKA 1 plus PKA 2 divided byMoreIf you only have two pka's the equation that you use is P I is equal to PKA 1 plus PKA 2 divided by 2 however for polypeptides we often have multiple ionizable groups and more than two pka's.
Why is glycine nonpolar?
Since glycine lacks an R group it is placed into the "nonpolar" category for the lack of better placement. Glycine is also the only achiral amino acid as it has 2 hydrogens bonded to its alpha carbon.
What makes amino acid glycine polar?
The only exception to this being the simplest amino acid glycine with its variable group being another hydrogen atom....Amino acids.Amino acidglycineSingle Letter CodeGThree Letter CodeGlyCharge (+/-/ neutral)neutralPolaritynonpolar19 more columns•Dec 6, 2018
Do all amino acids have same isoelectric point?
Each amino acid has its own pI value based on the properties of the amino acid. At pH values above or below the isoelectric point, the molecule will have a net charge which depends on its pI value as well as the pH of the solution in which the amino acid is found.
Where is glycine found in the CNS?
The strychnine -insensitive glycine-binding site is located on the NMDA receptor complex. The strychnine -sensitive glycine receptor complex is comprised of a chloride channel and is a member of the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily. The putative antispastic activity of supplemental glycine could be mediated by glycine's binding to strychnine -sensitive binding sites in the spinal cord. This would result in increased chloride conductance and consequent enhancement of inhibitory neurotransmission. The ability of glycine to potentiate NMDA receptor-mediated neurotransmission raised the possibility of its use in the management of neuroleptic-resistant negative symptoms in schizophrenia.#N#Animal studies indicate that supplemental glycine protects against endotoxin-induced lethality, hypoxia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation, and D-galactosamine -mediated liver injury. Neutrophils are thought to participate in these pathologic processes via invasion of tissue and releasing such reactive oxygen species as superoxide. In vitro studies have shown that neutrophils contain a glycine-gated chloride channel that can attenuate increases in intracellular calcium and diminsh neutrophil oxidant production. This research is ealy-stage, but suggests that supplementary glycine may turn out to be useful in processes where neutrophil infiltration contributes to toxicity, such as ARDS.
What temperature should glycine be stored?
Glycine irrigation should be stored at a temperature of 40 degrees C or less; freezing should be avoided. Glycine irrigation should not be heated to temperatures > 66 degrees C.
What is the SRP code for glyphine?
For Glycine (USEPA/OPP Pesticide Code: 103401) there are 0 labels match. /SRP: Not registered for current use in the U.S., but approved pesticide uses may change periodically and so federal, state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses./
What are glycinergic agents?
Glycinergic agents include agonists, antagonists, degradation or uptake inhibitors, depleters, precursors, and modulators of receptor function. (See all compounds classified as Glycine Agents .)
How to treat a syringe in the eye?
EYES: First check the victim for contact lenses and remove if present. Flush victim's eyes with water or normal saline solution for 20 to 30 minutes while simultaneously calling a hospital or poison control center. Do not put any ointments, oils, or medication in the victim's eyes without specific instructions from a physician. IMMEDIATELY transport the victim after flushing eyes to a hospital even if no symptoms (such as redness or irritation) develop. SKIN: IMMEDIATELY flood affected skin with water while removing and isolating all contaminated clothing. Gently wash all affected skin areas thoroughly with soap and water. If symptoms such as redness or irritation develop, IMMEDIATELY call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital for treatment. INHALATION: IMMEDIATELY leave the contaminated area; take deep breaths of fresh air. If symptoms (such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or burning in the mouth, throat, or chest) develop, call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital. Provide proper respiratory protection to rescuers entering an unknown atmosphere. Whenever possible, Self-Contained Breath ing Apparatus (SCBA) should be used; if not available, use a level of protection greater than or equal to that advised under Protective Clothing. INGESTION: DO NOT INDUCE VOMITING. If the victim is conscious and not convulsing, give 1 or 2 glasses of water to dilute the chemical and IMMEDIATELY call a hospital or poison control center. Be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital if advised by a physician. If the victim is convulsing or unconscious, do not give anything by mouth, ensure that the victim's airway is open and lay the victim on his/her side with the head lower than the body. DO NOT INDUCE VOMITING. IMMEDIATELY transport the victim to a hospital. (NTP, 1992)
Is glycine a serine?
It is an alpha-amino acid, a serine family amino acid and a proteinogenic amino acid. It is a conjugate base of a glycinium. It is a conjugate acid of a glycinate. It is a tautomer of a glycine zwitterion. Glycine appears as white crystals.
Is glycine a food additive?
Glycine is a food additive permitted for direct addition to food for human consumption, as long as 1) the quantity of the substance added to food does not exceed the amount reasonably required to accomplish its intended physical, nutritive, or other technical effect in food, and 2) any substance intended for use in or on food is of appropriate food grade and is prepared and handled as a food ingredient.
How many PKs does glutamic acid have?
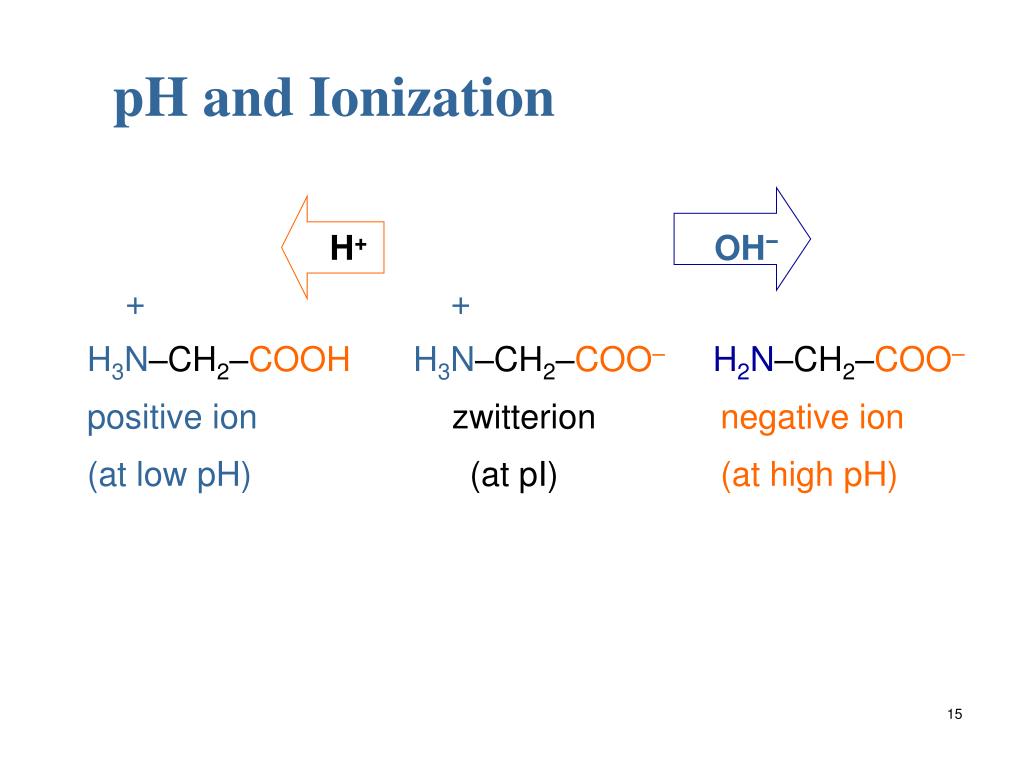
Thus, dicarboxylic acid like glutamic acid can have three pK values (two for carboxyl groups and one for the amino group) and four types of charged molecules as shown below. The name zwitter is derived from the German word which means “hybrid”. Zwitterion (or) dipolar ion is a hybrid molecule containing positive & negatively ionic groups.
What is a doubly charged molecule of amino acids containing a negative and a positively charged group?
This doubly charged molecule of amino acid containing a negative and a positively charged group is electrically neutral and is called Zwitter ion. Index of the Article.
What is the pK of the acid group?
In Strong acid conditions (around pH 1.1) the alpha-COOH group remains undissociated. However when the pH is raised and reaches around pH 3.0, the proton from the carboxyl group is leaving a -COO- group. This is called the pK of the acid group and at this pH, dissociated and undissociated species are found in equal concentrations.
Is an amino acid a neutral or neutral ion?
The amino acids rarely exist in a neutral form with free carboxyl (-COOH) and free amino (-NH2) groups. In strongly acidic pH (low pH), the amino acid is positively charged (Cation). Each amino acid has a characteristic pH at which it carries both positive and negative charges and exists as a Zwitter ion.
Is a molecule a neutral or isoelectric?
Isoelectric pH is defined as the pH which a molecule exists as a Zwitter ion (or) dipolar ion and carries no net charge. Thus, the molecule is electrically neutral, but the charge will cancel each other.
Is Zwitterion a dipolar ion?
Zwitterion (or) dipolar ion is a hybrid molecule containing positive & negatively ionic groups. Basically the proton shifts from carboxyl group to amino group of the self-molecule at normal pH cellular levels. The amino acids rarely exist in a neutral form with free carboxyl (-COOH) and free amino (-NH2) groups.
Why is glycine an inactive amino acid?
Glycine is optically inactive, simplest amino acid because it has no asymmetric carbon atom. Acid-Base titration involves the gradual addition (or) removal of protons. It has three different stages when the Glycine undergoes acid-base titration.
Is glycine a good buffer?
The titration curve of Glycine has two regions of buffering power. At pKa 2.34, glycine is a good buffer near this pH. The other buffering zone is centered on a pH of 9.60. Glycine is not a good buffer at the pH of intracellular fluid (or) blood, about 7.4.