Eubacteria Kingdom Facts
- They live in raw meat, raw milk, human intestine, sewage water, etc.
- Eubacteria derive nutrition from three major sources, viz. ...
- Some eubacteria are harmful and can cause meningitis, cholera, typhus, lyme’s, salmonellosis, tetanus, tuberculosis, etc.
What type of habitat do eubacteria live in?
What type of habitat do eubacteria live in? They are found in the depths of the ocean. They are found in these place also swamps, deep-sea waters, sewage treatment facilities, and even in the stomachs of cows. This type of bacteria is different from the common type of bacteria that we see every day called Eubacteria.
What habitat does the kingdom Eubacteria live in?
What are the main characters of Kingdom Monera?
- The Monerans are unicellular organisms.
- The cell wall is rigid and made up of peptidoglycan.
- Asexual Reproduction through binary fission.
- They contain 70S ribosomes.
- Flagella serves as the locomotory organ.
Why are eubacteria called "true" bacteria?
What is the strongest natural antiviral?
- Oregano. Oregano is a popular herb in the mint family that’s known for its impressive medicinal qualities.
- Sage.
- Basil.
- Fennel.
- Garlic.
- Lemon balm.
- Peppermint.
- Rosemary.
Is eubacteria a domain or Kingdom?
The kingdoms are Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria), Eubacteria (true bacteria), Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. In the three domain system, organisms with cells that contain a nucleus are placed in the domain Eukarya, this contains 4 of the five kingdoms.
Where do bacteria live?
Although bacteria may appear simple, they excel in the diversity and complexity of their metabolic capabilities and they are able to survive in many places. Bacteria are found everywhere on Earth where life is able to exist. They are plentiful in soils, bodies of water, on ice and snow, and are even found deep within Earth's crust. They often take advantage of living in and on other organisms in symbiotic relationships and can be found inhabiting the intestinal tracts and surfaces of animals, including humans. For the most part, the bacteria in and around us bring us more benefit than harm. Sometimes however, bacteria can be pathogenic, or disease causing. This can happen for a number of reasons, such as when the host has a compromised immune system or when a bacterium acquires genes that make it grow more aggressively or secrete toxins into its host environment.
When did bacteria first appear on Earth?
Whether primitive life originated on Earth or elsewhere, current consensus is that bacteria were present on Earth 3.8 billion years ago .
How do bacteria get their energy?
Bacteria show an incredible range of metabolic diversity. Some bacteria can get their energy from light (these are referred to as phototrophic organisms), organic compounds (organotrophic), or inorganic compounds such as hydrogen (H 2 ), sulfur compounds (H 2 S), inorganic nitrogen compounds or ferrous iron compounds (chemolithotrophic). Some bacteria can make all of their organic compounds by fixing carbon (autotrophic), while others need to break down organic compounds to provide a carbon source (heterotrophic). Many bacteria are capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen as a nitrogen source, in addition to organic and inorganic sources of nitrogen. Because of this metabolic diversity, bacteria play an important role in biogeochemical cycles such as the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous cycles.
What are bacteria that use oxygen called?
Bacteria that use oxygen are called aerobes. Those that do not are called anaerobes.
How do bacteria reproduce?
Reproduction in bacteria involves duplicating the genetic material and dividing the cell into two daughter cells, a process known as binary fission. Under very favorable conditions, certain bacterial cells can divide as often as once every twenty minutes. Some bacteria, such as Clostridium and Bacillus species, possess the ability to form a resting state, or "spore," when unfavorable conditions are encountered. These spores are very resistant to heat, drying, radiation, and toxic chemicals. Bacterial spores have reportedly been reawakened from a 250-million-year-old salt crystal that existed before the time of the dinosaurs. Sterilization techniques used in medicine must overcome these resistant properties.
Why are bacteria important to the biogeochemical cycle?
Because of this metabolic diversity, bacteria play an important role in biogeochemical cycles such as the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous cycles. This metabolic diversity also permits them to occupy a wide range of habitats. Bacteria can thrive in extremes of temperature, pH , salt, pressure, or toxic substances.
How big are eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells are approximately one order of magnitude larger, ranging in size from 5 to 20 micrometers in diameter, with an average size of 20 micrometers. The bacteria come in a number of distinct shapes as well. Common shapes include spherical (coccus), cylindrical (rod), and spiral forms (spirilla).
Classification of Bacteria
Taxonomy is the science of classification. Historically, taxonomical classification was based on observable characteristics. The advent of advanced molecular biological techniques allows for the classification of organisms based on quantifiable genealogical relationships.
Cell Membranes
Plasma Membrane : Plasma membranes are essential structures of all cells. These membranes encapsulate the cytoplasm. Plasma membranes are composed of lipids and proteins. Most lipids in the plasma membrane are phospholipids. These amphipathic lipids are composed of a hydrophilic head group and a hydrophobic tail.
Internal Structures
Cytoplasmic Matrix: The watery substance within the plasma membrane is called the cytoplasmic matrix.
External Components
Several external structures exist outside the cell wall. These include fimbriae, sex pili, and flagella.
Morphology
Members of domain Eubacteria vary in size and shape. The most common shapes are cocci and bacillus. Cocci are spherical cells that may exist singularly or in clusters. Some iterations of cocci include pairs of spherical cells, long chains, or clusters. Bacillus refers to rod-shaped bacteria.
Where are Eubacteria Found?
Bacteria are ubiquitous in our world. They form an important part of every food chain and biosphere. Bacteria play a central role in decomposition. They break down larger organic matter into elements necessary for life, including carbon and nitrogen. These elements are then able to re-enter the food chain.
Metabolism
Bacteria display an array of different metabolisms that allow them to thrive in many different environments. Energy and carbon sources are needed for metabolism: energy fuels the construction of biochemical molecules from carbon precursors.
What are the cells of Eubacteria?
Eubacteria can be found as individual cells or in the large colonies shaped like tight coils, grape-like clusters, filaments and thin biofilms. Some Eubacteria are equipped with cilia and flagella which are used for movement. Eubacteria do not have nucleus and cell organelles.
What is eubacteria used for?
Eubacteria are used in the manufacture of cheese, curd, yogurt, soy sauce, vinegar and wine and for pickling. Eubacteria in the human guts play important role in digestion of food and synthesis of vitamin K. They also protect human body from harmful bacteria.
What is the name of the single-celled microorganism that is found in soil?
Eubacteria Facts. Eubacteria Facts. Eubacteria, better known as bacteria (or "true bacteria"), are single-celled microorganisms that belong to a domain Bacteria. With 40 million bacterial cells per gram of soil, Eubacteria are one of the most numerous living things on the planet.
How many species of bacteria are there in the world?
There are 4.000 species of bacteria that can be found all over the world, including the areas with extreme conditions such as volcanoes, areas covered with radioactive waste and deep layers of the Earth's crust. Interesting Eubacteria Facts:
How do bacteriophages exchange DNA?
They exchange DNA material via hair-like projection called pili (in a process called conjugation), absorb DNA from their environment ( in a process called transformation) and alter existing DNA by incorporating bacteriophage into the chromosome (in a process called transduction).
Can Eubacteria cause tetanus?
Some Eubacteria can induce serious diseases such as tuberculosis, meningitis, anthrax, leprosy, cholera and tetanus. Antibiotics disrupt normal functioning of bacterial ribosomes or synthesis of the cell wall and prevent further multiplication of bacteria in the body.
Is eubacteria a heterotroph?
This type of bacteria is harmful for humans and animals due to potent toxin (endotoxin) incorporated in the lypopolysaccharide layer. Eubacteria can be autotrophic (able to produce food on their own) or heterotrophic (they consume organic compounds produced by other organisms).
Why do we eat Eubacteria every day?
You Eat Eubacteria Every Day and Don’t Realize It. Many of the food products that humans eat every day are because of the work of eubacteria. The curds that come from the cheesemaking process are a direct result of eubacteria that are introduced.
What are the different shapes of eubacteria?
There Are Many Different Shapes. Eubacteria can come in many different forms. You will find them to be oval or spherical in many instances, but certain bacteria, like streptococcus, which causes strep throat, can be round as well. If you are thinking about bacteria, then most likely you are thinking about eubacteria.
How fast do eubacteria produce food?
Although some eubacteria thrive in oxygen and others will die from it, eubacteria are naturally resilient. They can even produce their own food, making them autotrophic. They produce very quickly and can reach their fourth generation in just 20 minutes.
Why are bacteria called true bacteria?
Sometimes these bacteria are referred to as “true bacteria” because they can be found virtually everywhere. They are present on many different types of surfaces due to the fact that they are equipped with prokaryotic cells. This means that the cells they have do not have a nucleus. Here are some more interesting facts about these organisms.
Can Eubacteria reproduce asexually?
They can reproduce either asexually or through a process that is known as binary fission. 2. They Can be Found in the Most Extreme Environments. Eubacteria are the only known organisms that are able to stay alive and even thrive in extreme conditions.
Is eubacteria harmful?
They Can Be As Deadly As They Are Useful. Although there are numerous eubacteria that are consumed daily and the human body has many of them living and thriving within it, not all of them are considered beneficial. Some of them can be quite deadly, in fact.
Can bacteria make you sick?
If you are thinking about bacteria, then most likely you are thinking about eubacteria. These living organisms can be found everywhere and are usually helpful, but sometimes they can make you sick. Through antibiotics, healthy living habits, and regular hand washing, it is very possible to keep most of the deadly forms of eubacteria away.
What are the two groups of eubacteria?
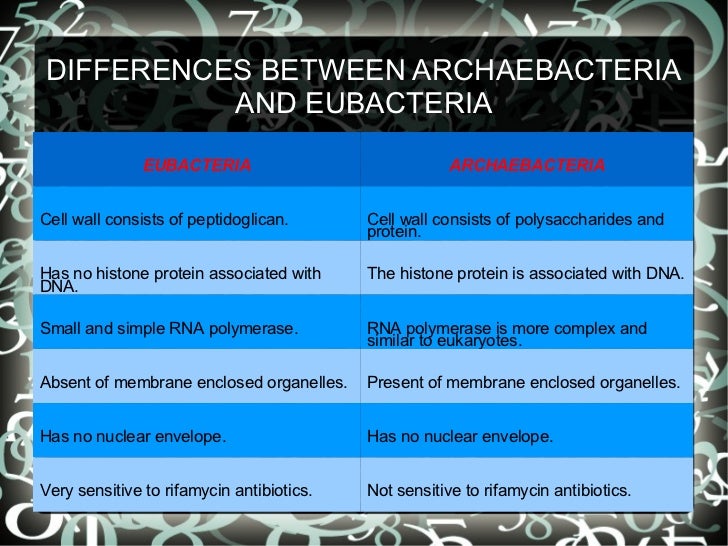
Eubacteria are divided into two groups known as gram positive and gram negative bacteria . Archaebacteria are found in salt brines, ocean depths and hot springs. They have evolved just after the evolution of first life on earth. Three types of archaebacteria are found: methanogens, halophiles and thermoacidophiles.
What are the other shapes of eubacteria?
Vibrio, rods, filaments and spirochetes are the other shapes of eubacteria. Membrane lipids of eubacteria are ester-linked, straight chains of fatty acids, containing L-glycerol phosphates. Eubacteria consists of a single circular chromosome in their cytoplasm.
How are archaebacteria asexually reproduced?
Asexual reproduction of archaebacteria is identified, occurring by binary fission, budding and fragmentation. Individual archaebacterium is 0.1-15 μm in diameter.
What are the three types of archaebacteria?
Three types of archaebacteria are found: methanogens, halophiles and thermophiles.
What is the cell wall of Archaebacteria made of?
The cell wall of archaebacteria is made up of pseudo peptidoglycans. The membrane lipids of archaebacteria are ether-linked, branched aliphatic chains, containing D-glycerol phosphates. According to the structure of cell wall, archaebacteria are more similar to gram positive bacteria.
Where do methanogens live?
Methanogens are found in oxygen-free environments like marshes, lake sediments and digestive tracts of animals, producing methane gas. Halophiles live in water with high concentrations of salts. Thermophiles live in hot water environments in acid sulfur springs. Archaebacteria is shown in figure 1.
What are the different types of reproduction methods in eubacteria?
Other than usual asexual reproduction methods, eubacteria exhibit sexual reproduction methods like conjugation. Individual eubacterium is 0.5-5 μm in diameter. Eubacteria exhibit a variety of shapes and arrangements. Cocci and bacilli are the major shapes.