Geography of Byzantium
Byzantium
Byzantium was an ancient Greek colony in early antiquity that later became Constantinople, and then Istanbul. The Greek term Byzantium continued to be used as a name of Constantinople during the Byzantine Empire, even though it only referred to the empire's capital. Byzantium was c…
What are the geographic features of the Byzantine Empire?
describe the location of the Byzantine Empire relative to four different locations or geographic features. The location of the Byzantine empire was surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea. The MiddleEast is East of the Byzantine Empire. The Atlantic Ocean is NorthEast of the Byzantine Empire, and controlled the italian and greek peninsula
Why was the Byzantine Empire so powerful?
What are some examples of Byzantine architecture?
- Hagia Sophia – Istanbul, Marmara, Turkey.
- Basilica of Saint’Apollinare Nuovo – Ravenna, Emilia-Romagna, Italy.
- Walls of Constantinople – Istanbul, Marmara, Turkey.
- Basilica of San Vitale – Ravenna, Emilia-Romagna, Italy.
- Basilica Cistern – Istanbul, Marmara, Turkey.
What are the important cities of the Byzantine Empire?
What are the important cities of the Byzantine Empire? In the eastern part of the empire, the most important cities were Alexandria, Antioch, Ephesus, Smyrna, Miletus, Caesarea in Cappadocia, Nisibis (one of the commercia, i.e. points of external commerce control), Nicomedia, Edessa in Mesopotamia, Beirut, Tyre, Laodicea ad Mare, Emesa, Pergamon, Caesarea Maritima, Nicaea …
Why was the Byzantine Empire more Greek than Latin?
the main reason is the aristocracy simply did't know Latin. in the middle-east, Asia minor and Egypt, Greek was enforced in Hellenistic period.
What were the geographic advantages of the Byzantine Empire?
What were the multiple advantages of Constantinople's geographic location? It was a harbor city on the water the geography provided food trade routes, easier transportation and protection from invaders.
What landform was the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire was part of the Eastern Roman Empire. What type of land form was Constantinople built on? Constantinople was built on a peninsula which made it easier to defend than Rome.
What are the geographical features of Constantinople?
Geography. Constantinople is located on the Bosporus River, meaning that it lies on the boundary between Asia and Europe. Surrounded by water, it was easily accessible to other parts of the Roman Empire via the Mediterranean, Black Sea, Danube River, and Dnieper River.
How did the physical geography and climate of the Byzantine Empire?
Describe how the physical geography and climate of the Byzantine Empire affected the way people lived. The physical geography and climate affected the way people lived because the summers were dry and hot in the southern and eastern parts of Europe, and during the winter, the weather was wet and cool.
Where was the Byzantine Empire located?
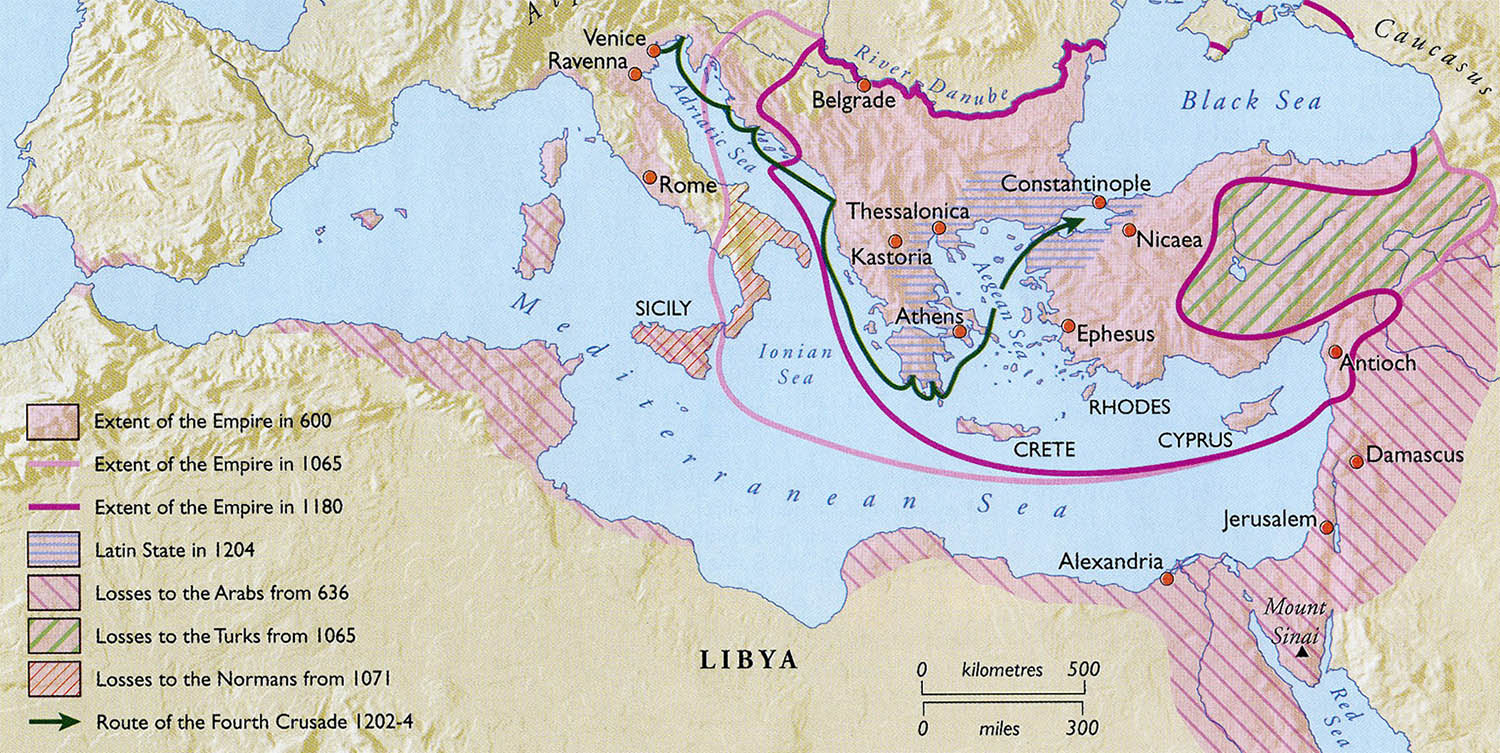
Where was the Byzantine Empire? At its greatest extent, the Byzantine Empire covered much of the land surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, including what is now Italy, Greece, and Turkey along with portions of North Africa and the Middle East.
What is the geographical location of Constantinople?
Constantinople is an ancient city in modern-day Turkey that's now known as Istanbul. First settled in the seventh century B.C., Constantinople developed into a thriving port thanks to its prime geographic location between Europe and Asia and its natural harbor.
How geography and its location affected the development of Constantinople?
The geography of Constantinople affected the development because it was the center where they would go and trade. Constantinople gained its wealth because of trade. They had both the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea which were routes that connected most places.
How did geographical factors influence the success of Constantinople?
How did geographical factors influence the success of Constantinople? It was situated on a strait connecting two major waterways used for trade. How did the fall of Rome impact Western Europe? Trade slowed greatly, and Western Europe became politically divided.
What is one way Constantinople's geography helped the empire?
The eastern half of the Roman Empire proved less vulnerable to external attack, thanks in part to its geographic location. With Constantinople located on a strait, it was extremely difficult to breach the capital's defenses; in addition, the eastern empire had a much smaller common frontier with Europe.
What is the study of geography about?
Geography is the study of places and the relationships between people and their environments. Geographers explore both the physical properties of Earth's surface and the human societies spread across it.
What was the geography of the Middle Ages?
During the Middle Ages, Western Europe was divided into many kingdoms, and Catholic Christianity strongly influenced society. Physical geography shaped Europe's development. The continent of Europe is a huge peninsula, with many smaller peninsulas branching out from it.
What geographic feature connected Byzantine to Russia?
Major rivers ran north to south, linking Russia to the Byzantine world in the south. The city of Kiev was located at the heart of the vital trade network linking Vikings, Slavs, and Constantinople. Kiev would later become the center of the first Russian state. Kiev and other Russian towns were destroyed.
When did the Byzantine Empire exist?
The Byzantine Empire existed from approximately 395 CE—when the Roman Empire was split—to 1453. It became one of the leading civilizations in the w...
How was the Byzantine Empire different from the Roman Empire?
The Byzantine Empire was the eastern half of the Roman Empire, and it survived over a thousand years after the western half dissolved. A series of...
How did the Byzantine Empire get its name?
Modern historians use the term Byzantine Empire to distinguish the state from the western portion of the Roman Empire. The name refers to Byzantium...
Where was the Byzantine Empire?
At its greatest extent, the Byzantine Empire covered much of the land surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, including what is now Italy, Greece, and T...
Did the Byzantine Empire practice Christianity?
Citizens of the Byzantine Empire strongly identified as Christians, just as they identified as Romans. Emperors, seeking to unite their realm under...
What was the Byzantine Empire?
Byzantine Empire. Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων, Basileía Rhōmaíōn. Imperium Romanum. 395–1453 c. Flag (c. 1350) Chi Rho. The empire in 555 under Justinian the Great, at its greatest extent since the fall of the Western Roman Empire (its vassals in pink) The change of territory of the Byzantine Empire (476–1400) Capital.
What dynasty was the Byzantine Empire under?
See also: Byzantine Empire under the Macedonian dynasty. The Byzantine Empire, c. 867. The accession of Basil I to the throne in 867 marks the beginning of the Macedonian dynasty, which ruled for 150 years. This dynasty included some of the ablest emperors in Byzantium's history, and the period is one of revival.
What is the Ottoman Empire?
Ottoman Empire. ^ Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων may be transliterated in Latin as Basileia Rhōmaiōn (literally meaning Monarchy of the Romans, but commonly rendered Empire of the Romans). ^ Roman Empire.
Where is the mosaic of Mary and Jesus?
A mosaic from the Hagia Sophia of Constantinople (modern Istanbul), depicting Mary and Jesus, flanked by John II Komnenos (left) and his wife Irene of Hungary (right), 12th century. Byzantine Empire in orange, c. 1180, at the end of the Komnenian period.
When did Byzantine law come into force?
In 438, the Codex Theodosianus, named after Theodosius II, codified Byzantine law. It went into force not just in the Eastern Roman/Byzantine Empire, but also in the Western Roman Empire. It not only summarised the laws but also gave direction on interpretation.
When did the West and East end?
The west disintegrated in the late 400s while the east ended with the fall of Constantinople in 1453.
Which region was more urbanized than the western Mediterranean?
These territories were home to many different cultural groups, both urban populations, and rural populations. Generally speaking, the eastern Mediterranean provinces were more urbanized than the western, having previously been united under the Macedonian Empire and Hellenised by the influence of Greek culture.
What was the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire at its height (555 CE) controlled almost all of the land of the former Roman Empire, stretching from Egypt to Northern Italy and from the banks of the eastern Black Sea to southern Iberia and had a large influence over the Visigoths and Gauls. This meant that they had many varying climates and geographical theatres ...
What was the Byzantine Empire's influence on the world?
The Byzantine Empire at its height (555 CE) controlled almost all of the land of the former Roman Empire, stretching from Egypt to Northern Italy and from the banks of the eastern Black Sea to southern Iberia and had a large influence over the Visigoths and Gauls. This meant that they had many varying climates and geographical theatres across their Empires. The vastness of their lands and the extreme differences in their features made it extremely hard for the Byzantine emperors to hold control over them for long, and they eventually lost all of their holdings outside of Anatolia and the Balkans.#N#However their capital, Constantinople, was almost impossible to capture, being successfully sieged only twice in history, by the crusaders in 1204 and by the Ottoman Turks in 1453. Constantinople is situated along the European side of the Bosphorus, next to a natural harbor known as the Golden Horn. The city was also built on seven hills, just like its counterpart along the Tiber. However, Constantinople was much harder to siege than Rome, because not only was it only approachable via land in one direction, the city had the largest walls in Europe and in times of siege, a chain was raised from the capital to a tower on the other side of the harbour, preventing enemy ships from landing along the banks of the Golden Horn. The Byzantines could also use their navy to prevent any advancing armies from crossing the strait, if they were coming from Anatolia.
What was the Byzantine art?
Byzantine Art. The Crusades. Fall of Constantinople. Legacy of the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantine Empire was a vast and powerful civilization with origins that can be traced to 330 A.D., when the Roman emperor Constantine I dedicated a “New Rome” on the site of the ancient Greek colony of Byzantium. Though the western half of the Roman Empire ...
What was the Byzantine Empire like at the time of Justinian's death?
At the time of Justinian’s death, the Byzantine Empire reigned supreme as the largest and most powerful state in Europe. Debts incurred through war had left the empire in dire financial straits, however, and his successors were forced to heavily tax Byzantine citizens in order to keep the empire afloat.
How did Byzantine culture influence the Western intellectual tradition?
Byzantine culture would exert a great influence on the Western intellectual tradition, as scholars of the Italian Renaissance sought help from Byzantine scholars in translating Greek pagan and Christian writings. (This process would continue after 1453, when many of these scholars fled from Constantinople to Italy.)
What were the major monuments built by Justinian?
Many great monuments of the empire would be built under Justinian, including the spectacular domed Church of Holy Wisdom, or Hagia Sophia. Justinian also reformed and codified Roman law, establishing a Byzantine legal code that would endure for centuries and help shape the modern concept of the state.
What was the Eastern Roman Empire known as?
Eastern Roman Empire. As a result of these advantages, the Eastern Roman Empire, variously known as the Byzantine Empire or Byzantium, was able to survive for centuries after the fall of Rome. Though Byzantium was ruled by Roman law and Roman political institutions, and its official language was Latin, Greek was also widely spoken, ...
Why was the Eastern half of the Roman Empire less vulnerable to external attack?
The eastern half of the Roman Empire proved less vulnerable to external attack, thanks in part to its geographic location. With Constantinople located on a strait, it was extremely difficult to breach the capital’s defenses; in addition, the eastern empire had a much smaller common frontier with Europe.
What was the threat to the Persian Empire?
During the seventh and eighth centuries, attacks from the Persian Empire and from Slavs, combined with internal political instability and economic regression, threatened the vast empire. A new, even more serious threat arose in the form of Islam, founded by the prophet Muhammad in Mecca in 622.
Why was the Byzantine Empire so strong?
This was important because the empire was located in an area that many enemies tried to invade. When other people did try to attack the empire, the Byzantine soldiers were ready for them. They had a pretty awesome weapon called Greek fire. This was a mixture of chemicals that could burn in water, so if a group was trying to launch an ocean attack they had better watch out!
Who was the leader of the Byzantine Empire?
One of the most significant leaders of the Byzantine empire was Justinian. Normally during this time a person would have to be born into a wealthy and powerful family in order to become a king. However, Justinian was simply a regular soldier. He worked hard and was promoted until eventually he became king. One thing he noticed when he gained control was that the laws of the empire were not written down, and therefore not enforced fairly or consistently. He had all of the laws written down, and this was called the Justinian Code.
What was the eastern half of the Roman Empire?
The fall of Rome in 476 ended the western half of the Roman Empire, and the eastern half continued as the Byzantine Empire, with Constantinople as its capital. The eastern realm differed from the west in many respects: heir to the civilization of the Hellenistic era, it was more commercial and more urban.
What happened after Justinian's death?
After his death the empire weakened. Though its rulers continued to style themselves “Roman” long after Justinian’s death, “Byzantine” more accurately describes the medieval empire. The long controversy over iconoclasm within the eastern church prepared it for the break with the Roman church ( see Schism of 1054).
Who helped the Venetians in the 11th century?
In the late 11th century, Alexius I Comnenus sought help from Venice and the pope; these allies turned the ensuing Crusades into plundering expeditions. In the Fourth Crusade the Venetians took over Constantinople and established a line of Latin emperors.
Overview
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire …
Nomenclature
Modern historians generally regard the term "Byzantine" to have been used as a label of the later years of the Roman Empire from 1557 onwards, 104 years after the empire's collapse, when the German historian Hieronymus Wolf published his work Corpus Historiæ Byzantinæ, a collection of historical sources. According to Anthony Kaldellis, an Athenian Laonikos Chalkokondyles in the mid 15th century who advocated a neo-Hellenic identity of the Romans, was the first to use the term …
History
By the third century AD, the Roman army had conquered many territories covering the Mediterranean region and coastal regions in southwestern Europe and North Africa. These territories were home to many different cultural groups, both urban populations, and rural populations. Generally speaking, the eastern Mediterranean provinces were more urbanized than the western, having previo…
Government and bureaucracy
As stablished by the Hellenistic political systems, the monarch was the sole and absolute ruler, and his power was regarded as having divine origin. From Justinian I on, the emperor was considered nomos empsychos, the "living law", both lawgiver and administrator. The Senate had ceased to have real political and legislative authority but remained as an honorary council with titular mem…
Science and medicine
The Imperial University of Constantinople sometimes known as the University of the Palace Hall of Magnaura (Greek: Πανδιδακτήριον τῆς Μαγναύρας), was an Eastern Roman educational institution that could trace its corporate origins to 425 AD, when the emperor Theodosius II founded the Pandidakterion (Byzantine Greek: Πανδιδακτήριον). The Pandidakterion was refounded in 1046 by Consta…
Culture
The Byzantine Empire was a theocracy, said to be ruled by God working through the Emperor. Jennifer Fretland VanVoorst argues, "The Byzantine Empire became a theocracy in the sense that Christian values and ideals were the foundation of the empire's political ideals and heavily entwined with its political goals." Steven Runciman says in his book on The Byzantine Theocracy (2004):
Economy
The Byzantine economy was among the most advanced in Europe and the Mediterranean for many centuries. Europe, in particular, could not match Byzantine economic strength until late in the Middle Ages. Constantinople operated as a prime hub in a trading network that at various times extended across nearly all of Eurasia and North Africa, in particular as the primary wester…
Legacy
Byzantium has been often identified with absolutism, orthodox spirituality, orientalism and exoticism, while the terms "Byzantine" and "Byzantinism" have been used as bywords for decadence, complex bureaucracy, and repression. Both Eastern and Western European authors have often perceived Byzantium as a body of religious, political, and philosophical ideas contrary to those of the W…