The acrosome is a cap that covers the head of the sperm. The acrosome facilitates the acrosomal reaction, which occurs when an egg cell and a sperm cell fuse together, leading to fertilization. Abnormal acrosomes can prevent fertilization and cause male-factor infertility.
What is special about a sperm cell?
Scientists have long thought that exposure to space radiation from solar winds and cosmic rays could damage the DNA of sperm cells and lead to mutations being passed down to offspring. However, a study by researchers at the University of Yamanashi in ...
What is a sperm cell's job?
The function of spermatozoa is to fertilize the egg cell during fertilization, creating a new organism called zygote that will develop from embryo to fetus during the 9 months of pregnancy. Human sperm cells are haploid, which means that they contain 23 chromosomes.
Why is a sperm cell a specialised cell?
What are the 6 types of cells?
- Stem cells. Stem cells are cells that are yet to choose what they are going to become. …
- Bone cells. There are at least three primary types of bone cell:
- Blood cells. There are three major types of blood cell:
- Muscle cells. …
- Sperm cells. …
- Female egg cell. …
- Fat cells. …
- Nerve cells.
Does a cytoplasm have a sperm cell?
Mitotic division of the generative cell generates two sperm cells that remain connected by a common extracellular matrix with potential intercellular connections. In addition, one sperm cell has a cytoplasmic projection in contact with the vegetative cell nucleus.
What happens when sperm is bind to acrosome?
This binding causes a calcium influx into the sperm's cytosol, which stimulates the exocytosis of the acrosome. This has three important consequences: the release of proteolytic enzymes, extension of the acrosomal process, and exposure of membrane proteins. Let's look at each of these in further detail.
What happens when an acrosome is released?
When the acrosome's proteolytic enzymes are released, they begin to degrade the egg's protein-rich protective coat. This creates a path for the sperm to swim through on its way to the egg's plasma membrane.
What happens when the sperm binds to the egg's protective coat?
To review, let's look at this diagram of the acrosomal reaction in the context of a sea urchin egg that's being fertilized: When the sperm binds to the egg's protective coat, the acrosome is exocytosed. The proteolytic enzymes from inside the acrosome digest the proteins in the egg's coat.
What is the pointy projection of the sperm membrane called?
This pointy projection is called the acrosomal process and is the part of the sperm membrane that is going to fuse with the egg's plasma membrane.
What is the acrosome reaction?
The Acrosome Reaction. The acrosome reaction is the exocytosis of the acrosome, or the fusion of the acrosomal membrane with the sperm's plasma membrane. This process releases the acrosomal contents to the outside of the sperm and exposes the inner acrosomal membrane proteins on the sperm's outer plasma membrane.
Why do sperm stay bound to the egg?
Because of the exocytosis of the acrosome, membrane proteins that were on the inner acrosomal membrane are exposed on the outside of the sperm's plasma membrane, surrounding the acrosomal process. Some of these membrane proteins help the sperm stay bound to the egg's protective coat so that it keeps burrowing through.
What proteins bind to the plasma membrane?
Once the sperm has gotten through the protective coat and reached the plasma membrane, other membrane proteins, such as bindin, bind to receptors on the egg's plasma membrane. This binding triggers the fusion of the egg and sperm plasma membranes.
Which organelle provides energy to the sperm cells?
Mitochondria supply energy to the sperm cells and are responsible for carrying out the process of respiration, necessary to provide the tail (flagellum) with the energy supply that it needed to allow the sperm cell to swim towards the egg.
Which part of the sperm cell produces ATP?
Power provided by mitochondria: To be able to move forward towards the ovum, the middle-piece of spermatozoa contains lots of mitochondria that produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the fuel of sperms. Structure and parts of a sperm cell.
How many chromosomes are in a human sperm cell?
Human sperm cells are always haploid, that is, they contain 23 chromosomes. When a spermatozoon reaches and joins an oocyte, which also contains 23 chromosomes, they form a diploid cell of 46 cells.
What is the name of the male reproductive cell that is expelled along with the seminal fluid or semen when
Last Update: 09/24/2018. A spermatozoon, in plural spermatozoa, or sperm cell is the male reproductive cell that is expelled along with the seminal fluid or semen when a man ejaculates. In humans, spermatozoa determine the gender of the baby-to-be, which means that they can carry either the X or the Y chromosome.
Why can't sperm cells divide?
By Zaira Salvador BSc, MSc (embryologist). Sperm cells cannot divide because they are haploid, that is, they contain 23 chromosomes. However, after the fusion with the egg cell, which contains 23 chromosomes as well, they create a diploid cell of 46 chromosomes (totipotent zygote).
What part of the sperm cell is the only part that enters the egg cell?
Nucleus. It contains all the 23 chromosomes of the sperm cell, that is, half the genetic information that will have the new organism. This is the only part of the sperm cell that enters into the egg cell. For this reason, it is a key part of the spermatozoon, as it is the one that unites with the egg's nucleus to form a 46-chromosome cell called ...
What organelle is located at the end of the sperm cell?
Acrosome. The size of this organelle is 40% to 70% of total sperm head area, and is located at one end of the sperm cell. It contains proteolytic enzymes that help to destroy the outer layer of the egg cell, thereby allowing the sperm to enter into it easily.
What is the acrosome in fertility?
FertilitySmarts Explains Acrosome. The acrosome is important during the earliest stages of fertilization, in a phase known as the acrosomal reaction. During natural conception, sperm travel through a woman’s reproductive system looking for an egg. Once the egg has been located, the sperm attempts fertilization.
What does an acrosome do?
What Does Acrosome Mean? The acrosome is a cap that covers the head of the sperm. The acrosome facilitates the acrosomal reaction, which occurs when an egg cell and a sperm cell fuse together, leading to fertilization. Abnormal acrosomes can prevent fertilization and cause male-factor infertility. Advertisement.
Why are acrosomes not excrete enzymes?
Abnormalities of the acrosome can prevent this process from occurring. Misshapen or dysfunctional acrosomes can impede penetration, as they may not excrete the appropriate enzymes needed to break down the zona pellucida. This can be caused by: Genetic conditions. Health disorders that impact sperm quality.
What is the purpose of acrosome reaction test?
The acrosome reaction test uses a trigger, such as hormones or certain electrolytes to trigger the acrosome reaction sequence in a lab and evaluates the sperm’s performance. The results of this test indicate the quality of the sperm’s acrosome.
Can sperm be tested for acrosome?
While a standard sperm analysis can visually test the sperm for the presence of a typical acrosome, it cannot test the acrosome’s ability to function normally when introduced to an egg.
Is sperm injected in the egg?
If the acrosome reaction is not functioning in vitro fertilization (IVF) with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), in which the sperm is injected in the egg may be necessary, whereas intrauterine injection (IUI) in which the sperm is placed within the cervix, will not be effective.
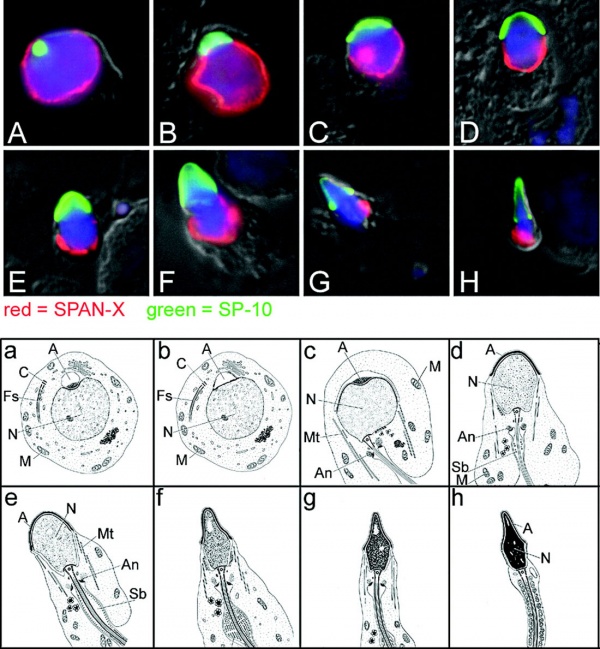
Definition: What Is An acrosome?
Transformation of The Sperm Head
- The acrosome is involved in the transformation (shaping) of the sperm head through the Acrosome–Acroplaxome-manchette complex. Here, the two important structures involved are acroplaxone and manchette. The acroplaxone (consisting of actin and keratin) overlays the acrosome and its complex with manchette contribute to the following: 1. Development of acros…
Gamete Recognition
- In such animal as frogs and sea urchin, proteins referred to as primary ligands have been shown to play an important role in gamete recognition. Although these ligands are usually located on the plasma membrane surface, some have been identified on the acrosome thus involving the organelle in gamete recognition. Once the primary ligands identify specific proteins in the jerry s…
Acrosome Reaction and Exocytosis
- When the spermatozoa (or primary ligands of the sperm) come into contact with the jerry layer that surrounds the female gamete (the egg) acrosome reaction/exocytosis is initiated. Before the sperm can undergo acrosome exocytosis, it goes through a process known as capacitation. Here, the sperm undergoes a number of physiological changes that include: 1. The plasma membran…
Acrosome Secondary Ligands
- Once the sperm cell binds to the zona pellucida surrounding the plasma membrane of the egg, pores are formed allowing acrosome components to be released. This is where secondary ligands (hydrolytic enzymes) come into play. One of the main components of the acrosome is a serine protease known as acrosin. In the acrosome, the protein is stored in an inactive form known as z…